E307 Syllabus FALL 2..
advertisement

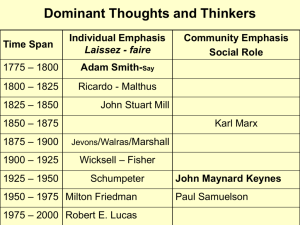
IUPUI— FALL 2013 Syllabus for E307 History of Economic Thought Shahrokh Towfighi e-mail: stowfig@iupui.edu 297-4442(H) Please call between 6:00-9:00 pm. 278-7213 (O) CA 513 MW—9:30-11:45 If you cannot meet me at these hours, please make an appointment. Instructor: Telephone: Office: Hours: Textbooks David Harvey, A Brief History of Neoliberalism, New York: Oxford University Press, 2009 Robert L. Heilbroner, The Worldly Philosophers, 7th ed. New York: Touchstone, 1999 Agnar Sandmo, Economics Evolving, Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2011 Couse Requirements There will be three tests plus the final. The tests will be given after the completion of the specific topics shown below. Course Outline RH: Robert Heilbroner AS: Agnar Sandmo Author RH AS Chapter I II 1. 2. RH AS III 3. RH AS IV 4. RH AS V 5. Topic Introduction The Economic Revolution A Science and Its History Before Adam Smith Mercantilism (pp. 18-20) only The Wonderful World of Adam Smith Adam Smith Wealth of Nations Adam Smith’s Price Theory The Returns to Factors of Production The Invisible Hand The Invisible Hand and the Market Economy Free or Perfect Competition The Public Interest The Market and the State Economic Growth The Gloomy Presentiments of Parson Malthus and David Ricardo The Classical School: Thomas Robert Malthus and David Ricardo Thomas Malthus The Theory of Population Economic Policy: Poverty, Free Trade, and Unemployment David Ricardo The Theory of Rent Long-run Development and the Stationary State The Theory of International Trade The Theory of Taxation The Dreams of Utopian Socialists Consolidation and Innovation: John Stuart Mill Questions of Method Price Theory Labor and Wages RH AS VI 6. RH AS VII 8. Crisis and Unemployment Long-run Development and the Stationary State New Issues: The Progress of Socialism and the Future of the Working Class The Public Sector The Inexorable System of Karl Marx Karl Marx as an Economic Theorist Capitalism and Surplus Value Marx’s Labor Theory of Value Economic Growth The Falling Rate of Profit and the Breakdown of Capitalism TEST 1 9. 10. RH AS VIII 13. RH AS IX 15. RH AS X 14. RH XI David Harvey The Victorian World and the Underworld of Economics The Marginalist Revolution I: William Stanley Jevons and Carl Menger William Stanley Jevons The Mathematical Method Marginal Utility Theory Demand and Prices The Marginalist Revolution II: Léon Walras General Equilibrium Alfred Marshal and Partial Equilibrium Theory Supply and Demand Partial and General Equilibrium Utility, Demand, and Welfare The Concept of Elasticity Externalities Factor Markets and Income Distribution Economy and Society Marshal’s Importance TEST 2 The Savage Society of Thorstein Veblen New Perspectives on Markets and Competition Thorstein Veblen Edward Chamberlin Joan Robinson The Heresies of John Maynard Keynes John Maynard Keynes and Keynesian Revolution The General Theory Keynes and the Classics on Labor and Wages Demand and Employment Keynesian Stabilization Policy Keynes and the Keynesians The Long-run Development of the Market Economy The Contradictions of Joseph Schumpeter The Great Systems Debate The Challenge of Ludwig von Mises Oskar Lange and Abba Lerner Friedrich von Hayek Joseph Schumpeter The End of the Worldly Philosophy? TEST 3 A Brief History of Neoliberalism TEST 4