ppt - people
advertisement

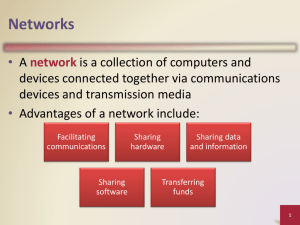
Session 5 Objectives: By the end of this session, the student will be able to: •State the definition of a Local Area Network •List the primary function, activities and application areas of a LAN •Cite the advantages and disadvantages of local are networks •Identify the physical and logical topologies of local area networks •Cite the characteristics of wireless local area networks and their medium access control protocols •Specify the different medium access control techniques LANs 3 LANs Advantages Share resources (H/W: high quality printers, modems, tape backup, plotters, mass storage) (S/W: commercial apps, inhouse apps, data sets) (Comms: email, messaging, web, print jobs, DB records Mix and match of vendor equipment (MAC / PC / Sun...) Disadvantages Depreciation of equipment (lease) Can be expensive- eg. Network server, NOS, cabling, hubs / switches, networkbased apps, security, support and maintenance Interoperability can be an issue as well (my print server and WinXP/Linux and MAC) Transfer rates / low error rates Licensing of S/W can become complex Can be privately owned and maintained: provide services to employees it deems is best Well trained staff required – LAN does not manage and diagnose itself Only as strong as it s weakest link 4 Bus / Tree Topology 5 Bus / Tree Topology 6 Bus / Tree Topology 7 Bus / Tree Topology 8 Star-wired Bus Topology 9 Star-wired Bus Topology 10 Star-wired Ring Topology 11 Star-wired Ring Topology 12 Wireless Topology - BSS 13 Wireless Topology - ESS 14 Wireless Topology – Ad Hoc 15 LAN Topologies 16 CSMA/CD 17 CSMA/CA Wireless - CSMA/CA Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance IFS – Interframe Space, a period of time. 3 types: Short IFS: used by devices that require an immediate response such as an acknowledgement, a clear to send or response to poll Midlength IFS used by access device when it is issuing polls to user devices Long IFS the minimum delay a device can wait while contending for access to network. Allows higher priority devices to transmit first IF Medium Idle •device wait IFS •if medium still idle then transmits IF Medium busy •wait for medium to go idle •Wait IFS •if still idle, calculate a random Back off factor (multiple of IFS) •when back off counter reaches zero transmit packet. 18 Token Ring 19 IEEE 802 20 IEEE 802.3 (CSMA/CD) 21 IEEE 802.5 (Token Ring) 22 Ethernet 23 FDDI (Fibre Distributed Data Interface) 24