Chapter 16 Other RNA Processing Events
advertisement

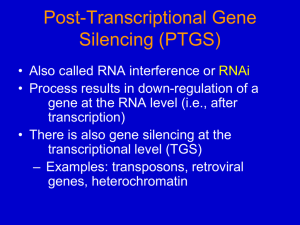
Chapter 16 Other RNA Processing Events Trans-splicing, Editing, RNAi, miRNAs Trans-splicing section 16.3 First seen in a parasitic protozoa Trypanosomes, protozoan that causes African sleeping sickness trans-splicing used to generate changing surface coat proteins that help outwit the immune system trans-splicing Figure 16.12 200 copies of a 35 n leader encodes in a different place in the genome. Editing Focus on this one protozoa = U-insertion protozoa = U-deletion mammals, insects & plants = nucleotide deaminiation 16.4 RNA editing by deamination ADAR = Adenosine deaminase acting on RNA adenosine -> inosine inosine bp with cytidine So codons change ACG codon (threonine) changes to an ICG codon which is read as GCG (alanine) pg 493 4th ed. Results in major changes in properties of the protein Example Glutamate receptor ion channel GluR-B changes glutamine->arginine Reduces Ca2+-permeability. How? Usually codons to be changed are near introns. A guide RNA molecule base pairs to an intron and then points ADAR at the correct codon. So what? Not a trivial change. It is extremely important for the normal development and function of the nervous system. In mammals, it appears to be part of the way that the nervous system generates diversity and complexity (ADAR 3 unique to brain). Cytidine deaminaton CDAR cytidine deaminase acting on RNA C-->U Discovery of post-transcriptinal gene silencing (PTGS) or posttranscriptional control of gene expression • Involved attempts to manipulate pigment synthesis genes in petunia • Genes were enzymes of the flavonoid/anthocyanin pathway: CHS: chalcone synthase DFR: dihydroflavonol reductase When these genes were introduced into petunia using a strong viral promoter, mRNA levels dropped and so did pigment levels in many transgenics. Discovery of PTGS First observed in plants (R. Jorgensen, 1990) Introduction of a transgene homologous to an endogenous gene resulted in both genes being suppressed! Also called Co-suppression involved enhanced degradation of the endogenous and transgene mRNAs DFR construct introduced into petunia CaMV - 35S promoter from Cauliflower Mosaic Virus DFR cDNA – cDNA copy of the DFR mRNA (intronless DFR gene) T Nos - 3’ processing signal from the Nopaline synthase gene Flowers from 3 different transgenic petunia plants carrying copies of the chimeric DFR gene above. The flowers had low DFR mRNA levels in the non-pigmented areas, but gene was still being transcribed. RNAi RNA interferance Discovered in a control experiment pg 501 Weaver 4th edition RNAi RNAi discovered in C. elegans (first animal) while attempting to use antisense RNA in vivo Control “sense” RNAs also produced suppression of target gene! sense (and antisense) RNAs were contaminated with dsRNA. dsRNA was the suppressing agent. Craig Mello Andrew Fire 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology & Medicine 2. The experiment. unc22 gene nonessential myofilament protein. Mutations in unc22 cause a twitching phenotype. dbstded unc-22 RNA phenocopies. Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) induced interference of the Mex-3 mRNA in the nematode C. elegans. Inject antisense RNA (c) or dsRNA (d) for the mex-3 (mRNA) into C. elegans ovaries. mex-3 mRNA was detected in embryos by in situ hybridization with a mex-3 probe. Fig. 16.29 Weaver 4th Ed. negative control positive control no probe mex-3 antisense mex-3 dsRNA Conclusions: (1) dsRNA reduced mex-3 mRNA better than antisense mRNA. (2) the suppressing signal moved from cell to cell. Hammond et al. 2000. Nature 404:293-296. An RNA-directed nuclease is purified from Drosophila cells that seems to specifically degrade mRNAs. S2 cells extract destroys cognate RNAs T7 dsRNA T7 As others have seen, notice the accumulation of a 25 nt RNA which can bp to the target mRNA. Destruction of 25 nt RNA with micrococcal nuclease blocks reaction. Hammond et al. 2000. An RNA-directed nuclease mediates post-trancriptional gene silencing in Drosophila cells. Nature 404:293-296 Figure is not in Weaver 4th but is mentioned on pg 501-502. Short interfering RNAs -siRNAs Drosophila embryo lysate system simplifies step by step analysis. Processes the trigger to the 21-23nt fragments. Both strands of the trigger are cut. - show by radiolabelling one strand and then the other strand (sense, antisense). Processing of trigger is not dependent on mRNA. dsRNA Zamore et al. 2000. Cell 101:25-33 p p p Fig 16.30 4th ed p The dsRNA that is added dictates where the destabilized mRNA is cleaved. The dsRNAs A, B, or C were added to the Drosophila extract together with a Rr-luc mRNA that is 32P-labeled at the 5’ end. The RNA was then analyzed on a polyacrylamide gel and autoradiographed. Results: the products of Rr-luc mRNA degradation triggered by dsRNA B are ~100nt longer than those triggered by dsRNA C (and ~100 nt longer again for dsRNA A-induced degradation). Fig 16.31 High resolution gel analysis of the products of Rr-luc mRNA degradation from the previous slide. Results: the cleavages occur mainly at 21-23 nt intervals; 14 of 16 cleavage sites were at a U.There is an exceptional cleavage only 9 nt away from the adjacent site (induced by dsRNA C); this site had a stretch of 7 Us. Enzyme cleaves at ~23-nt intervals & after U. In 2001 Hammond et al purify the enzyme and name it DICER. Fig. 16.32 dsRNA Weaver 4th edition pg 501-507 DICER - RNase III family member ATP ADP+Pi p p p Dicer leaves 2nt 3’ overhangs & phosphorylated 5’ ends p Argonaute has a PAZ and a PIWI domain. p 21-23 nt siRNP -R2D2 p -Armitrage The 2 domains of Argonaute RISC loading complex p ATP ADP+Pi p Argonaute PIWI PAZ p -Dicer RISC=RNAinduced silencing complex. RISC - one of the proteins is SLICER. In Drosophila SLICER is the product of the Argonaute gene. Dicer mRNA In mice there are 4 Ago genes but only Ago2 appears to be SLICER. RISC Target recognition p p Target cleavage mRNA p PIWI domain forms a shape like an RNase H. p Dicer participates in selecting the guide RNA that is passed on to Argonaute. Roles of R2D2 and Armitrage are not clear. Argo2 is Sliceris shown by building highly specfic siRNA complexes in vitro using bacterially expressed Argo2. Bizarre figure see next one for explanation. Argo2 is Sliceris shown by building highly specfic siRNA complexes in vitro using bacterially expressed Argo2. RNA transcript made siRNA1 could bp about 140n from 5’ end of transcript siRNA2 could bp about 180n 3’ end of transcript Argo2 that has been produced in bacteria lane1 lane 1 transcript + siRNA2 + Argonaute + MgCl2 lane2 lane 2 transcript + siRNA1 + Argonaute + MgCl2 Argo2 is Sliceris shown by building highly specfic siRNA complexes in vitro using bacterially expressed Argo2. Ago2 knock out in mice embryonic lethal with severe defects important for RNAi & miRNA Function of RNAi Antiviral - Double stranded RNA is an intermediate in the replication of some RNAi viruses. Suppress transposon activity Great research tool because it provides a way to experimentally eliminate a gene product Might be a useful therapy for cancer, etc. How to evoke RNAi • Inject double stranded RNA • Express or inject antisense RNA inside a cell • Express a gene which has an inverted repeat. • Two promoters which point at one other. • Expression of 2 different genes whose mRNAs can base-pair over a short region. But wait there’s (too much )more Amplification of siRNA Role of RNAi machinery in the formation of heterochromatin miRNAs - inhibition of translation miRNAs - stimulation of translation But wait there’s (too much )more Amplification of siRNA Tiny amounts of a trigger can have a very large and long lasting effect. Occurs in Plants, Drosophila and C. elegans. Role of RNAi machinery in the formation of heterochromatin miRNAs - inhibition of translation miRNAs - stimulation of translation dsRNA Amplification (pg508 4th ed) mRNA ATP Dicer ADP+Pi p p p Dicer leaves 2nt 3’ overhangs & phosphorylated 5’ ends p p p -Armitrage ATP ADP+Pi mRNA RISC Target recognition p p Target cleavage mRNA p Dicer p RISC loading complex p p Argonaute ATP ADP+Pi 21-23 nt siRNP -R2D2 RdRp p (RNA directed RNA polymerase) p p -Dicer RISC=RNAinduced silencing complex. NTPs PPi p p p p p p Potential for exon spreading Reference: Nishikura 2001 Cell 107:415-418. But wait there’s (too much )more Amplification of siRNA Role of RNAi machinery in the formation of heterochromatin miRNAs - degradation of mRNA or inhibition of translation miRNAs - stimulation of translation Role of RNAi machinery in the formation of heterochromatin Heterochromatin - condensed chromatin, silenced chromatin Centromeres - include much heterochromatin Centromeres - One does not observe transcription from material adjacent to the centromeres. In yeast, mutations in Dicer, Argonaute and RdRp cause such transcripts to appear. meH3lys4 - associated with active genes meH3lys9 - associated with inactive genes. Normally centromeres would have low meH3lys4 and high meH3lys9. Mutants have the opposite. RdRP found associated with centromere (but called RDRC there). Swi6 is required to form heterochromatin. It is attracted to meH3lys9 outer edge of a centromere Histone methyl transferase bound by RITS. Supposed to indicate that the RDRC copies (amplifies) the siRNA RITS - RNA-induced initiator of transcriptional gene silencing contains Ago1 + siRNA RDRC - RNA-directed RNA polymerase complex contains RdRp But wait there’s (too much )more Amplification of siRNA Role of RNAi machinery in the formation of heterochromatin miRNAs - degradation of mRNA or inhibition of translation miRNAs - stimulation of translation Comparison of Mechanisms of MiRNA Biogenesis and Action Better complementarity of MiRNAs and targets in plants. 40 Fig. 16.45 Source of miRNA’s Why RNA silencing? • Original view is that RNAi evolved to protect the genome from viruses, and perhaps transposons or mobile DNAs. • Some viruses have proteins that suppress silencing: 45 References • Baulcombe, D. (2004) RNA silencing in plants. Nature 431: 356-363. • Millar, A.A. and P.M. Waterhouse (2005) Plant and animal microRNAs: similarities and differences. Functional & Integrative Genomics 5: 129-135.