Chapter
13
Motivating and
Rewarding Employee
Performance
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Principles of Management
© 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
13 - 3
Learning Objectives
1. Diagram and summarize the MARS model.
2. Describe four-drive theory and explain how these drives influence
motivation and behavior.
3. Describe the characteristics of effective goal setting and feedback.
4. Diagram the expectancy theory model and discuss its practical
implications for motivating employees.
5. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of the four reward objectives.
6. Discuss ways to measure employee performance more accurately.
7. Summarize the equity theory model, including how people try to reduce
feelings of inequity.
8. Diagram the job characteristics model of job design.
9. Define empowerment and identify strategies to support empowerment.
13 - 4
Employee Engagement
• Employees emotional and rational motivation
- Their perceived ability to perform the job
- Their clear understanding of the organization’s vision
- Their belief that they have been given the resources to
get the job done
• It encompasses the four main factors that
contribute to employee performance
13 - 5
Motivation: True or False?
• I can motivate people
• Fear is a damn good motivator
• I know what motivates me, so I know what
motivates my employees
• Increased job satisfaction means increased job
performance
Source: Managementhelp.org
13 - 6
MARS Model
Ability
Motivation
(effort)
*Direction
*Intensity
*Persistence
Role
Perceptions
Situational
factors
Employee
behavior and
results
Ability & Role
Perceptions
13 - 7
• Ability – consists of both the natural aptitudes and
learned capabilities required to successfully complete
a task
- Important factor of employee development
• Role perceptions – they understand the specifics,
importance, and preferred behaviors of the tasks. Ways
to improve is through job description and ongoing
coaching
Managing Employee
Motivation
13 - 8
1. Drives and
needs
Motivation
(effort)
*Direction
*Intensity
*Persistence
2. Goals,
expectations,
and feedback
Employee
behavior and
results
3. Extrinsic
and intrinsic
rewards
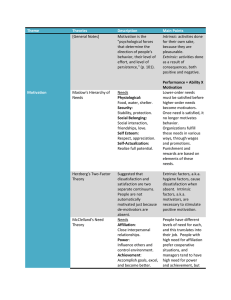
Maslow’s Needs
Hierarchy
Selfactualization
Esteem
Belongingness
Safety
Physiological
13 - 9
Challenging tasks, freedom to try new ideas
Job status, recognition, mastering the job
Human interaction, being accepted as a team
member
Job security, employee benefits, safe
workplace
Work hours, nourishments, air quality,
temperature
Called in Sick?
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
Need a break
Illness in family
Errands
Workers who took a sick day
when not sick
Source: USA Today Snapshots
13 - 10
13 - 11
Question
Money is a powerful
motivator. If an
organization wants to be
motivate employees, all
its managers need to do
is give them more
money. Do you agree?
Explain.
Management Implications
of Maslow’s Theory
13 - 12
1. Employees have different needs at different
times
2. Employees have several interdependent needs,
not just one dominant need
3. At some point, most employees want to achieve
their full potential (self-actualization)
4. Employee needs are influenced by values and
norms
Learned Needs Theory
Need for
Achievement
(nAch)
Need for
Affiliation
(nAff)
Need for Power
(nPow)
13 - 13
Four-Drive Theory Motivation
Drive to
acquire
Drive to
bond
Drive to
learn
Drive to
defend
Social
norms
Personal
values
13 - 14
Past
experience
Mental skill set
resolves competing
drive demands
Goal-directing
choice and effort
13 - 15
Goal Setting
• The process of motivating employees
and clarifying their role perceptions by
establishing performance objectives
• A goal is a desirable future state that an
organization or person attempts to
realize
• Goal setting improves role perceptions
and consequently clarifies the direction
of employee effort
13 - 16
Question
Raj, a new manager at Telcom International, in his first
meeting at the company told his employees that the sales goals
were significantly enhanced for this year and he expects all of
his employees to buckle down and work hard to meet the
goals. Raj’s instructions violates which of the aspects of
effective goal-setting?
a. Precise and measurable
b. Equitable
c. Expectancy-oriented
d. Timely
13 - 17
Expectancy Theory
of Motivation
Outcome valence
E-to-P expectancy
(probability that
effort will result in
a specific level of
performance)
P-to-O expectancy (the outcome’s positive
or negative value to the
(probability that
employee)
performance will
result in specific
outcomes)
Outcome 1
+ or Effort
Performance
Outcome 1
+ or Outcome 1
+ or -
13 - 18
Rewards
• Extrinsic Rewards – anything received from another
person that the recipient values and is contingent on his or
her behavior or results
- Paychecks, performance bonuses, praise, and other
forms of recognition
• Intrinsic Rewards – a positive emotional experience
resulting directly and naturally from the individual’s
behavior or results
- Learning a new task, feeling of accomplishment, etc.
Motivation Through
Extrinsic Rewards
Membership & senioritybased rewards
Nonfinancial rewards
Job status-based rewards
Improving performance
appraisals
Competency-based rewards
Rewards employees
equitably
Performance-based rewards
13 - 19
How to Accurately Evaluate
Employee Performance?
1. Use more objective measures of
performance
2. Use anchored performance appraisal
instruments
3. Use multiple sources of
performance information
4. Use performance appraisal training
13 - 20
Best Practices at Nucor
13 - 21
• Pay for performance – On average two-thirds of a
Nucor steelworker’s pay is based on a production bonus
• Listen to the frontline – According to the Execs, almost
all of the best ideas come from the factory floor
• Push-down authority – minimizing layers of
management
• Protect your culture –compatibility of culture with its
egalitarian philosophy and team spirit is a big focus of
its acquisition research
Source: Business Week, May 1, 2006
Correcting Inequity
Feelings
• Change Inputs
• Change Outcomes
• Change Perceptions
• Leave the Situation
13 - 22
13 - 23
Job Characteristics Model
Core job
characteristics
Skill variety Task
identity Task
significance
Critical psychological
states
Meaningfulness
Outcomes
Work
motivation
Growth
satisfaction
Autonomy
Responsibility
Feedback from job
Knowledge of results
Individual differences
*Knowledge and skill
*Context satisfaction
*Growth need strength
General
Satisfaction
Work
effectiveness
Core Job
Characteristics
13 - 24
• Skill variety – the use of different skills and talents to complete
a variety of work activities
• Task identity – the degree to which a job requires completion
of a whole or identifiable piece of work
• Task significance – the degree to which the job affects the
organization and society
• Autonomy – provide freedom, independence, and discretion in
scheduling work and procedures
• Job feedback – the degree to which employees can tell how
well they are doing
13 - 25
Job enrichment
• A job design practice in which employees
are given more responsibility for
scheduling, coordinating, and planning
their own work
- Combine highly interdependent tasks into
one job
- Establishing client relationships
- Give employees more autonomy over
their work
13 - 26
Loyal vs. Trapped?
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
Loyal
High risk
Workers
Source: CIO, October 1, 2003
T rapped
13 - 27
Empowerment
• A psychological concept represented by four
dimensions:
- Self-determination – they have freedom,
interdependence, and discretion over their work activities
- Meaning – they care about their work and believe that
what they do is important
- Competence – their ability to perform the work well and
have a capability to grow with new challenges
- Impact – Active participants in the organization; that is,
their decisions and actions influence the company’s
success
Inspiring Employees
• Don’t ask for worker input – use it.
• Tell your people you care about them.
• Show employees what they are learning
• Support people when they make a mistake.
• Set clear goals and celebrate accomplishments.
Source: Business Week, May 1, 2006
13 - 28