Chapter 6 Section 1: Price as signals
advertisement

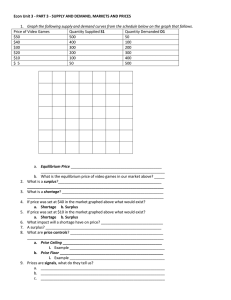
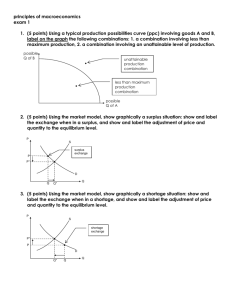
Chapter 6 Section 1: Price as signals Main Idea: Competitive markets and prices are important to capitalism Vocabulary Price Rationing Ration rebate coupon Notes What do high prices signal? What do low prices signal? What advantages to prices have? How does rationing work? What problems do nonprice allocation systems face? Chapter 6 Section 2: The price system at work Main Idea: Changes in demand and supply cause changes in price. Vocabulary Economic model Market equilibrium Surplus Shortage Equilibrium price Notes What do supply and demand curve models help economists examine? How are prices established in a competitive market? What creates a surplus? What creates a shortage? What is the relationship between the elasticity of supply and demand curves and price? What is the theory of competitive pricing? Chapter 6 Section 3: Social Goals vs. Market Efficiency Main Idea: To achieve goals, government sometimes sets prices vocabulary Price ceiling Minimum wage Price floor Target price Nonrecourse loan Deficiency payment Notes Why does the government fix prices? If the price ceiling is below the equilibrium price, will a shortage or surplus occur? When were agricultural price supports introduced? What did a nonrecourse loan allow farmers to do? How did deficiency payments help farmers?