12Chem Calorimetry - OISE-IS-Chemistry-2011-2012
advertisement

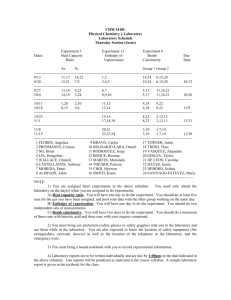
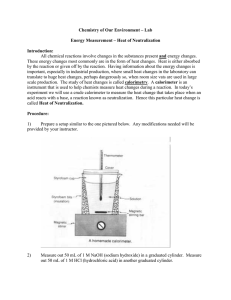
Calorimetric Equations Putting it Together Calorimetry What is Calorimetry? What is a Calorimeter? Three Assumptions of Simple Calorimeters: 1. No heat is transferred between the calorimeter and the outside environment 2. Any heat absorbed or released by the calorimeter materials, such as the container, is negligible 3. A dilute aqueous solution is assumed to have a density and specific heat capacity equal to that of pure water (1.00g/ml and 4.184 J/g°C) Solution Combustion Neutralization Remember what we’ve seen ΔH = nΔHx ΔHsystem = ±|qsurroundings| q = mcΔT n = m/MM n=CxV Doing Calorimetric problems is about using these equations ΔH = nΔHx ΔHsystem = ±|qsurroundings| nΔHx = qsurroundings nΔHx = mcΔT n = mcΔT / ΔHx m/MM = mcΔT / ΔHx Calorimetry of Solution One substance dissolves in another NaBr(s) Na+(aq) + Br-(aq) Heat of Solution Demo http://www.teachersdomain.org/resource/lsps07.sci.phy s.matter.dissolvesalt/ Question 1 In a calorimetry experiment, 7.46 g of potassium chloride is dissolved in 100.0 mL (100.0 g) of water at an initial temperature of 24.1°C. The final temperature of the solution is 20.0°C. What is the molar enthalpy of solution of potassium chloride? Question 2: On your own What mass of lithium chloride must have dissolved if the temperature of 200.0 g of water increased by 6.0°C? The molar enthalpy of solution of lithium chloride is –37 kJ/mol. Calorimetry of Combustion Burn a substance in oxygen to yield CO2 and H2O C3H8(l) + 5O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(l) Question 3 If the molar enthalpy of combustion of propane is -2220KJ/mol, what mass of propane will have to be burned in order to raise the temperature of 1.00L of water from 50.0 to 85°C. Question 4 A calorimeter (C=0.850J/˚C) containing 5.00 x 102 ml of water at 22 oC is warmed to 100oC when 9.00 g of cheddar cheese is burned. Calculate the heat absorbed by the water and the heat of combustion, per gram, of cheese. Calorimetry of Neutralization Acid + Base Salt + Water HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) Use the same strategy for other reactions CuSO4(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) → Cu(OH)2(s) + Na2SO4(aq) Question 5 A chemist wanted to find the heat of neutralization of HCl with NaOH. She added 61.1ml of 0.543M HCl to 42.6ml of 0.779M NaOH. The initial temperature of both solutions was 17.8oC and the highest recorded temperature of the solution after neutralization was 21.6˚C. What is the enthalpy of neutralization of HCl? ASSUME: The density and heat capacity of the solutions is the same as that for pure water Question 6 50.0 mL of 0.300 mol/L CuSO4 solution is mixed with an equal volume of 0.600 mol/L NaOH. The initial temperature of both solutions is 21.4oC. After mixing the solutions in the coffee-cup calorimeter, the highest temperature that is reached is 24.6oC. Determine the enthalpy change of the reaction. CuSO4(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) → Cu(OH)2(s) + Na2SO4(aq)