Biome Project Notes
advertisement

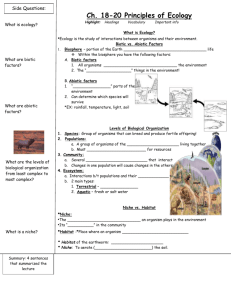
Biome Project Day 1 •Biotic and abotic factors •Climatograms Bio- means life A- means without Biotic factors are those things that have life. Ex. Trees, squirrels, bears, humans Abiotic factors are those things that are without life • Ex. Rocks, soil, water, wind, climate Ecology is the study of the relationships between the biotic and abiotic factors. Climatograms • Are graphs that show two important abiotic climatic factors – temperature and precipitation. –Temperature is plotted as a line graph. –Precipitation is plotted as a bar graph. Day 2 •Food chains/ food webs Food Chain shark fish paramecium algae •The arrows point in the direction of energy flow •Food web: a group of connected food chains Trophic level: the place of an organism on a food chain Tertiary consumer Secondary consumer Primary consumer producer Day 3 •Energy pyramids bass minnows paramecium algae Only 10-20% of the energy moves to the next level on the pyramid. Why is it rare to have animals that eat the tertiary consumer? Day 4 •niches Habitat the place where an organism lives Ex. A tadpole lives in a pond Niche: all strategies and adaptations a species uses in its environment to meet its needs at a given time Niche -how an organism meets its needs for food and shelter -how and where it survives -where it reproduces Niche includes that organisms interactions with biotic and abiotic parts of the habitat. No two organisms can fill the same niche at the same time in the same habitat. So, each organisms niche is unique. An organism in a niche has adaptations that give it an advantage over other organisms that may be competing for the same niche in the same environment. Example: A leopard frog • lives in & along the shore of ponds • is a predator that captures insects with its sticky tongue • reproduces by laying jellylike eggs in the shallow water Day 5 •Symbiosis All those organisms living together in the wild end up forming relationships. (well, not really like that) Lichen is made out of algae and a fungus. The algae gives food to the fungus. The fungus protects the algae. The relationship between the algae and fungus is called mutualism. (Think “mutual”) In mutualism, one helped species is _______ while the other is helped _________. (helped, hurt, not affected) Meet Harvey: He’s my tapeworm. He lives in my intestines and steals my food. The tapeworm and I have a relationship called parasitism. How is a parasite different from a predator? In a parasitism, one helped species is _______ while the other is hurt _________. (helped, hurt, not affected) Certain fish live just beneath sharks to catch food scraps. The shark and fish have a relationship called commensalism. In commensalism, one species is helped _______while the other is Not affected _________. (helped, hurt, not affected) Parasitism, commensalism, and mutualism are all forms of symbiosis. Symbiosis: When organisms from DIF FERENT species LIVE in a relationship