Case Study Day 2 - the Biology Scholars Program Wiki
advertisement

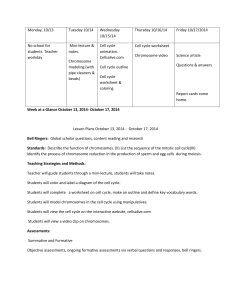
Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Students will be able to… Describe the molecular mechanism dictating the biosynthesis and transport of proteins via the endomembrane system. Understand protein sorting via the endomembrane system & clathrin-mediated exocytosis Connect vesicle transport to the cell cytoskeleton by describing the molecular mechanism of A-B toxins Identify molecular targets that when non-functional would disrupt exocytosis and describe the resulting phenotype(s). Predict experimental results when given novel experimental conditions that modulate protein sorting or clathrin-mediated exocytosis. Bloom’s Taxonomy Level Learning Activities Formative Assessment Low stakes online quizzes prior to class (LO Bloom’s) Outside of Class: Reading relevant textbook passages Knowledge Understand In Class: Mini-lecture Outside of Class: pre-case study reading and video Analyze In Class: Case Study Day 1, think-pair-share, group discussion Outside of Class: Answer HO Q’s Clicker questions, think-pair-share, Strip Sequence Evaluate LO Exam question Reading summary Group Qs report Pre-activity Thought Qs Analyze In Class: Case Study Day 2, Jigsaw Summative Assessment HO Bloom’s Exam question Group Thought Qs Report Exit Poll LO = Lower Order HO = Higher Order Qs = Questions Assessment Clicker Questions Think- Pair-Share Strip Sequence Group Report for Qs Mini-lecture: Review Concepts and check for student understanding Case Study Day 1: Think-PairShare, Group Discussion In Class Activities Sa/Su Outside of Class Activities Assessment Read correspondi ng textbook section Electronic Reading Quiz M T Case Background reading & Video 1-page summary W Group Report for Jigsaw Qs, Exit Poll Case Study Day 2: Jigsaw HO Qs R Review Case and work on correspondi ng HO thinking questions Pre-activity Higher Order Qs F Institute Reflection “Every challenge you encounter in life is a fork in the road. You have the choice to choose which way to go - backward, forward, breakdown or breakthrough.” - Ifeanyi Enoch Onuoha, Overcoming the Challenges of Life Sa/Su –Read Corresponding Textbook Passages • Students will be assigned the intracellular transport (protein trafficking) chapter from Essential Cell Biology (Alberts et al.) course textbook to help students navigate the content and assess learning gains. To assess student reading a 10 question multiple choice quiz available through the course management system (due at 11:59 p.m. Sunday evening) will be assigned. Mini-lecture: Review Concepts and check for student understanding • Instructor may use just-in-time teaching technique to address any misconceptions regarding the out of class electronic quiz. The mini-lecture will start off with a clicker-question reviewing protein sorting. Students will be encouraged to discuss the questions via think-pair-share if a large fraction of the class responds incorrectly. At this point questions are encouraged and fielded by the instructor. The instructor will have a mini-lecture prepared to review content if there are limited student questions. Additional clicker questions and think-pair-share activities will be integrated throughout the mini-lecture with student invited to pose questions related to the content. The session will finish up with a strip sequence activity to test protein sorting and clathrin-mediated exocytosis. Summative assessment will include examination questions that test lower order Bloom’s taxonomy concepts. Mini-lecture Formative Assessment • Example Clicker Question Which of the following is/are made on free ribosomes? 1) proteins that are to remain in the cytosol 2) peripheral proteins of the inner cell membrane surface 3) peripheral proteins of the outer cell membrane surface 4) proteins to be transported to the nucleus A. B. C. D. E. 1 2 3 4 1, 2 and 4 Mini-lecture Formative Assessment • Example Think-Pair-Share – How does clathrin physically interact with components of membranes in order to induce clathrin coated pit formation? Mini-lecture Formative Assessment • Example Strip Sequence for Protein Sorting – Free ribosome begins initial translation of mRNA – SRP binds to exposed ER signal sequence and ribosome – SRP-ribosome complex binds to SRP receptor in ER membrane – Translocation channel inserts the polypeptide chain into the membrane – Translocation channel binds the signal sequence and transfers polypeptide across lipid bilayer – Signal peptide is cleaved from the polypeptide – Pore of the translocation channel closes Case Background reading & Video • Students will be assigned a popular press article describing use of botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) for comedic applications in addition to second article that highlights medical uses for BoNT. Students will also be given a link to view a video interview of a recipient of Botox cosmetic treatment. Student will be assigned to write a summary/reflection paper to review the content of the articles as well as their initial thoughts of the use of botulinum toxin for medical and cosmetic applications. Case Study Day 1: Think-Pair-Share, Group Discussion • The instructor will have two willing students act out the case study, which involves a conversation between a Botox patient experiencing nontargeted muscle paralysis (drooping eyelid) and a physician. The doctor will help explain the cellular biology behind the patients drooping eyelid condition (molecular mechanism of Botox) to the patient. Students will then answer a series of questions (formative assessment) using think-pairshare, followed by breaking out to discuss the questions in small groups. Questions will include describing and illustrating the molecular mechanism of BoNT muscle paralysis. Students wrap of the period by turning in a group summary of their responses to the provided questions. Summative assessment will be in the form of exam questions. Case Study – Day 1 Assessment • Example Formative Question – Having bud off of the trans-Golgi network, how are vesicles, specifically synaptic vesicles containing acetylcholine, transported to the axon terminus? Case Study – Day 1 Assessment • Example Summative Question – Describe the location and dynamics of acetylcholine biosynthesis and it’s eventual packaging within a neuronal synaptic vesicle. Compare and contrast this process to that of a acetylcholine receptor. Review Case and work on corresponding HO thinking questions • Students will be assigned to read “Part 2” of the case study and answer a list of higher order thinking questions related to the case study to be completed before the next class session. Case Study Day 2: Jigsaw HO Qs • The instructor will divide the class into small groups and assign one of homework questions per student group for students to discuss and come to a consensus on a solution. The instructor will be floating around the room helping groups during this process. The students will then participate in a Jigsaw activity, by forming new groups composed of 1 student from each original group. Each student within their new group will explain (peer teaching) their original groups collective solution to each homework problem. Students will wrap up the class session with an exit poll (formative assessment) to help student practice metacognition and reflect on the completed case study. Case Study – Day 2 Assessment • Example Formative Question – You isolate a new species of Clostridium, which produces a novel neurotoxin resulting in flaccid paralysis of exposed mammals. Identify potential molecular targets that this neurotoxin may target. Case Study – Day 2 Assessment • Example Summative Question – Imagine a mouse that has a temperature sensitive allele of dynamin, such that at room temperature dynamin protein is functional, but at elevated temperatures dynamin protein is non-functional. Predict how a mouse would respond to an injection of BoNT after being shifted to an elevated restrictive temperature. What would be a good control for this experiment? Case Study – Day 2 Assessment • Example Exit Poll (formative assessment) – What general principles of vesicle transport did you learn from our discussion of the molecular mechanism of Botox? – Why did we learn about the molecular mechanisms of Botox? – How does what you learned about Botox relate to cell biology concepts that we covered previous classes? – What questions to you have about this topic?
![[] Updated Alignment Grid - Kleinschmit](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009704160_1-d901a4e568906d5703122d0396644221-300x300.png)