Taxes and Financial Innovation
advertisement

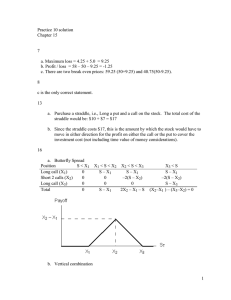
Taxes and Financial Innovation Overview • Basic tax features & security design • Debt versus equity, revisited • Options & put-call parity • Monetizing a gain Basic Features of Income • Timing – Realization (“wait-and-see”) – Accrual • Character – Ordinary or capital – Dividend or interest • Source (Foreign or Domestic) Selective Realization & Tax Planning • Lock-in effect – Time value of deferral • Strategic trading – Hold winners, sell losers Tax Rules as Inputs • Portfolio design (or selection) – Tax arbitrage – Clienteles • Security design – Same issues as portfolio design – Add new securities Position Diagrams Debt vs. Equity • Payoffs depend on the state of the world • Simple 2-period model • Equity has a different structure than debt Equity Payoff Slope = 1 X* X Debt Payoff Slope = 1 X* X Economics • Securities with returns that vary with performance are “equity” – Equity has flexibility • Securities with relatively fixed payoffs are “debt” – Junior versus senior debt? – Junior debt versus preferred stock? Taxation • Debt – No tax on return of principal – No firm level tax; deductions on accrual – Investors taxed on accrual • Equity – No tax on return of principal – Corporate tax – Investors taxed on dividends or capital gains Security Design • Create variable payoff securities that qualify as debt • Convert relatively fixed payoff equity into being taxed as debt Contingent Debt • Contingent debt has variable payoffs – Floating interest rates (no big deal) – Commodity price based payoffs – Stock performance • Index • Another company • Contingent interest or principal? Taxation of Contingent Debt • Control features matter • Contingencies are important • Original issue discount portion • Settling up at the end Disney’s Participation Notes • Minimum interest payment • Revenue contingent payment • “Penalties” for not making movies • Cap on total payoff Disney Notes • Payoff diagram? • Explain features of the contract? • Tax advantage of the contract? – Alternative sources of funds? Monthly Income Preferred Stock • Trust preferred, etc. • Converting “safe” equity into debt for tax purposes • Add an intermediary between the firm and the investors Non-Unique Cash Flows • Position diagrams = options • Derivatives = many copies • Non-tax analysis • Taxation Assumptions for Options • • • • • Common expiration date, T Common exercise price, k No early exercise Stock price, S Position diagrams of future cash flows (ignore sunk costs!) • No transaction costs Buying a Call Payoff Slope = 1 k ST Writing a Call Payoff k ST Slope = -1 Buying a Put Payoff Slope = -1 k ST Selling a Put Payoff k ST Slope = 1 Owning Stock Payoff Slope = 1 k ST Shorting Stock Payoff k ST Slope = -1 Payoff to Lending Payoff Slope = 0 k ST Payoff to Borrowing Payoff k ST Slope = 0 Taxation of Options • • • • • Recall from PS #2 Realization-based taxation Premium affects basis Often capital in character Avoids withholding taxes Put-Call Parity • What is the position diagram for owning a share, buying a put, and writing a call? • Replicates lending • Implications for no arbitrage asset pricing? • Implications for option prices? Share, Put and Short Call Payoff Slope = 0 k ST Put-Call Parity & Taxation • S+P-C=B • Everything on the left is taxed on realization but the bond is taxed on accrual • Same pre-tax cash flows; different taxes OOPS! Routes around Realization • Shorting-against-the-box – – – – Investor shorts a stock already in portfolio Borrows stock from broker Eliminates “risk” Until 1997, not deemed a realization event • “Portfolio” of derivatives -- puts & calls Monetizing a Gain • • • • • • Eli Broad has substantial SunAmerica stock Large capital gain Wants cash & possibly diversification Does not want to pay capital gains tax Solution: Strypes Structured yield product exchangable for common stock Strypes • Buyer pays $56, roughly the SunAmerica share price • Buyer “receives” – Interest payments of 6.75% of $56 for 3 years – Value of SunAmerica if less than $76 OR $76 if share price > $76 – Does not receive the dividends Decompose Strypes • Buyer pays $56 for a portfolio of: – SunAmerica share (no voting rights) – Writes a 3-year call option, strike = $76 – “Swaps” dividend for 6.75% fixed interest • At year 3, buyer must sell security • Decomposition is not unique Strypes: Issuer’s Perspective • Retains voting control • Might get interest deductions (corporate issuer might even get the DRD) • Avoids (defers) tax on capital gain • Retains upside potential • Sheds downside risk