PowerPoint slides used in chapter 14 lecture.
advertisement

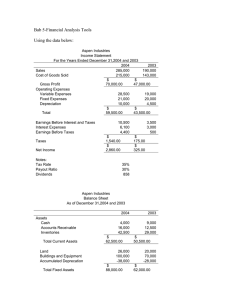
Using Financial Information and Accounting Chapter 14 I. Purpose of Accounting A. Who uses financial reports and accouning information? 1. Financial reports give information about a company’s past, present and future performance to: a. Managers - use reports to make decisions about firm’s operations b. Employees - to see the financial wealth of the org., to see how individual efforts helped c. Investors and customers -use reports to make investment and purchasing decisions d. Suppliers, creditors, and government agencies - use reports to determine their relationship with the org. II. Types of Accountants A. Public Accountants - independent accountant who serves organizations & individuals on a fee basis; offers a wide range of services 1. auditing 2. Tax returns 3. Financial statement preparation 4. consulting B. Private Accountants C. Fund and not-for-profit accountants (charities, hospital, gov’t, schools) III. Basic Accounting Procedures A. The Accounting Equation Assets = Liabilities + Owners’ Equity – – – – – – – assets liabilities owners’ equity revenues expenses net income double-entry bookkeeping (debits, credits) B. The Accounting Cycle 1. Analyze business transaction documents 2. Record business transactions in journal 3. Post entries to ledgers 4. Prepare trial balance 5. Prepare financial statements & management reports 6. Analyze reports IV. The Balance Sheet • Summarizes a firm’s financial position at a specific point in time (on a specific date) A. Assets (resources) current, fixed, intangible, depreciation B. Liabilities (obligations) current, long-term C. Equity(Assets minus obligations) retained earnings V. The Income Statement • Summarizes the firm’s revenues & expenses and shows total profit or loss over a period of time A. Revenues gross sales, net sales B. Expenses cost of goods sold, operating expenses C. Net profit or loss VI. The Statement of Cash Flows • Summarizes the money flowing into and out of a firm for a period of time A. Sources of cash flow: 1. operating activities 2. investment activities 3. financing activities VII. Analyzing Financial Statements A. Ratio analysis: calculating & interpreting financial ratios taken from financial reports to assess a firm. 1. liquidity ratios - measures firm’s ability to pay its short-term debt a. current ratio b. acid-test (quick) ratio c. net working capital Ratio Analysis (Cont’d) 2. Activity Ratios - indicates how efficiently the firm uses its assets to generate revenue a. accounts receivable turnover b. inventory turnover 3. Profitability ratios - measures operating success a. net profit margin b. return on equity c. earnings per share 4. Debt ratios - measures a firm’s ability to pay its long-term debt a. debt to equity ratio VIII. Trends in Accounting • Accountants expand their role – more involvement in operations, advise clients on systems, software, and acctg. regulations • Valuing knowledge assets – R&D, brands, trademarks, employee talent • Tightening the GAAP – reducing loopholes, cleaning up records