Introduction to University Debate
advertisement

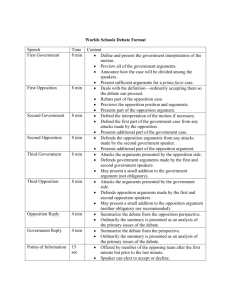
Introduction to University Debate Dylan Williams – Fall 2015 University of Alberta Debate Society 1 Introduction Topics to cover 1. Basics of Debate 2. British Parliamentary Style Speakers and Roles Examples of a debate round Points of Information Judging 3. Learning and Improving in Debate 2 What is Debate? A respectful exchange of ideas between reasonable people Sometimes outside your comfort zone Part content, part style 3 Basic Rules of Debate Respect others, and yourself. Listen and be polite Think and argue in terms of principles and analysis 4 Debate Styles British Parliamentary (Fall) Canadian Parliamentary (Winter) Australs (Summer) 5 British Parliamentary Style – At a Glance Teams Announced -> Motion Announced -> 15 Minutes Preparation -> Debate! Common, balanced, competitive style Topics that reasonable people can disagree about, and are accessible “This House Would do x,” “This House Believes x” “This House Supports” 6 Closing Government Leader of the Opposition 5 Minute Speech Deputy Prime Minister 5 Minute Speech Deputy Leader of the Opposition 5 Minute Speech Member of Government 5 Minute Speech Member of Opposition 5 Minute Speech Government Whip 5 Minute Speech Opposition Whip 5 Minute Speech Closing Opposition Prime Minister 5 Minute Speech Opening Opposition Opening Government British Parliamentary Style – Speakers 7 Speakers The Prime Minister Model and groundwork for the round Constructive Arguments 8 Speakers Leader of the Opposition Clash with PM Opposition Stance Constructive Arguments 9 Speakers Deputy Prime Minister, and Deputy Leader of the Opposition Clash with last speaker Rebuild Constructive Arguments 10 Speakers Member of Government Clash with Opening Opposition Extend on the debate with new argument 11 Speakers Member of Opposition Clash with MG’s extension Extend on the debate with new argument 12 Speakers Government Whip and Opposition Whip Clash with other side’s extension Biased summary of the round – No new material! Emphasize back half material 13 British Parliamentary Style – Example This House Would Intervene Against ISIS Opening Government “ISIS is harming people in the Middle East and we have a duty to protect them” Closing Government “ISIS is a threat to security in the West, and will terrorize us if we don’t stop them” Opening Opposition “ISIS will only get stronger if the West gets involved and causes more violence” Closing Opposition “The West shouldn’t break international law by waging war in countries where it hasn’t been 14 invited” British Parliamentary Style – Example This House Would Publically Fund Elections Opening Government “This gives every party a fair chance to make their views heard” Closing Government “Now, parties focus on actually appealing to individual voters instead of fundraising for cash” Opening Opposition “Public money shouldn’t go towards political parties that people don’t all support” Closing Opposition “Now parties depend on the state instead of supporters, and people have one less way to get involved”15 Points of Information Definition A short question, attack or response given during someone else’s speech Rules Give two, take two Protected How to Give Short Time and snappy How to Take Whenever works for you 16 Points of Clarification Definition A short clarification on a part of the government case or model that you don’t understand Rules Like a POI, but only during PM speech Can be in protected time (but say “clarification”) 17 Judging Criteria Pursuasiveness Whose Engagement Who arguments were most important, convincing played ball with other teams effectively Role Fullfillment Did everyone do what they needed to do in the round? 18 Learning and Improving Debate is about practice and improvement Keep a notebook/folder/binder Seek out and consider feedback Keep an eye on issues that may come up 19