Parts of Speech PowerPoint
advertisement
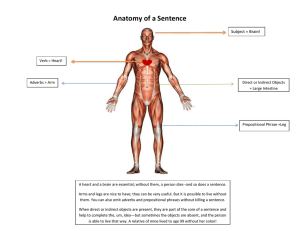
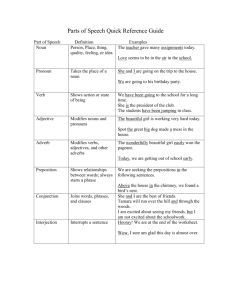
Parts of Speech Grammar Review Noun • Names a person, place, thing or idea • Examples: • • • • • Walt Disney (person) Australia (place) Notebook (thing) friendship (idea) love (idea) Verb • • A verb expresses an action, states something that exists (state of being), or links the subject with a description. Action verb: An action verb tells what the subject is doing. • • Example: Jonah threw the ball. Being verb: State existence • • Examples: Jonah is happy. Jonah seems tired. Also included as helping verbs Adjective • • • • • • • A word that modifies or describes a noun or pronoun. They help give your reader a clearer picture of what you are talking about. Adjectives do three things: Tell what kind Tell how many Tell which one or ones Examples: jubilant child, generous man, thirteen apples… Pronoun • A pronoun is a word used to take the place of a noun or another pronoun. • Examples: • • I, You, We, They, He, She, It Me, Us, Them, Him, Her Adverb • Adverbs are used to modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. • There are four basic types of adverbs: • • • • Adverbs of time, i.e. He cleaned yesterday. Place, i.e. We can stop here for lunch. Manner, i.e. Casey did well on the exam. On the other hand, Ben did badly. Degree, i.e. Harry is quite talented for his age. Preposition • • A word that shows position or direction or introduces a prepositional phrase Examples: • • • • • • Around Up Under Over Between Example of Prepositional Phrase: Over the rainbow Conjunction • A word that connects other words or groups of words • Examples: • • For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, So Because, Since, As... Interjection • A word (set off by commas or an exclamation point) that shows strong emotion • Example: • Stop! Hey, how are you?