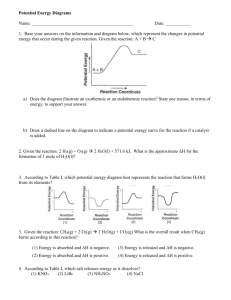
Acids, Bases, Law of Conservation of Mass
advertisement
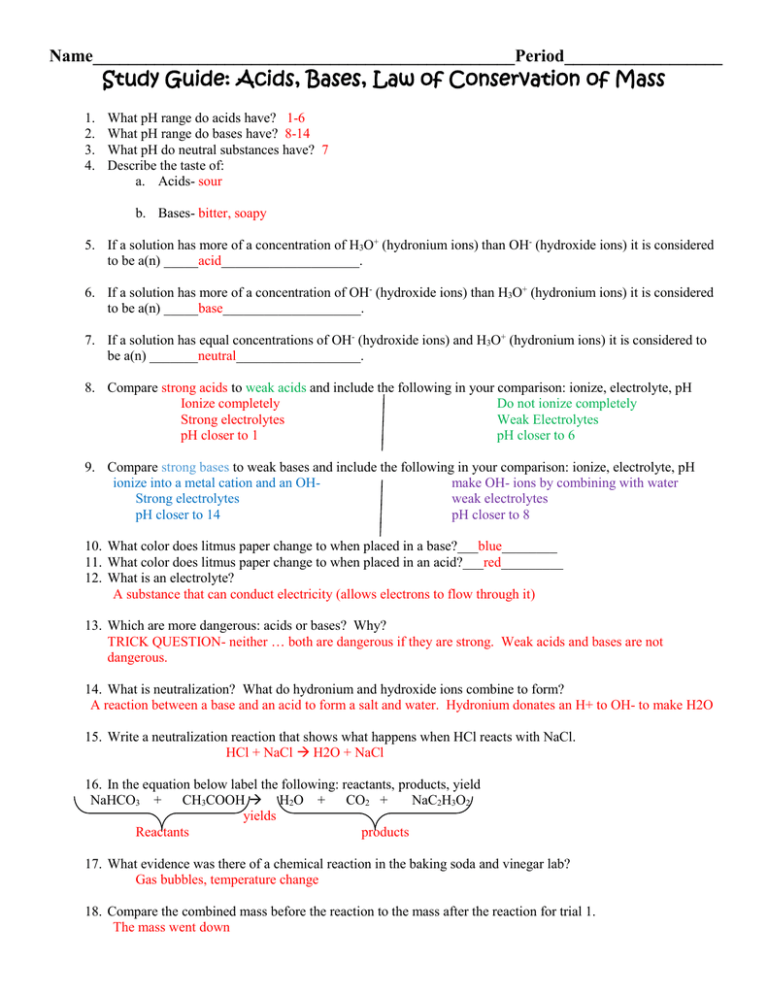
Name________________________________________________Period__________________ Study Guide: Acids, Bases, Law of Conservation of Mass 1. 2. 3. 4. What pH range do acids have? 1-6 What pH range do bases have? 8-14 What pH do neutral substances have? 7 Describe the taste of: a. Acids- sour b. Bases- bitter, soapy 5. If a solution has more of a concentration of H3O+ (hydronium ions) than OH- (hydroxide ions) it is considered to be a(n) _____acid____________________. 6. If a solution has more of a concentration of OH- (hydroxide ions) than H3O+ (hydronium ions) it is considered to be a(n) _____base____________________. 7. If a solution has equal concentrations of OH- (hydroxide ions) and H3O+ (hydronium ions) it is considered to be a(n) _______neutral__________________. 8. Compare strong acids to weak acids and include the following in your comparison: ionize, electrolyte, pH Ionize completely Do not ionize completely Strong electrolytes Weak Electrolytes pH closer to 1 pH closer to 6 9. Compare strong bases to weak bases and include the following in your comparison: ionize, electrolyte, pH ionize into a metal cation and an OHmake OH- ions by combining with water Strong electrolytes weak electrolytes pH closer to 14 pH closer to 8 10. What color does litmus paper change to when placed in a base?___blue________ 11. What color does litmus paper change to when placed in an acid?___red_________ 12. What is an electrolyte? A substance that can conduct electricity (allows electrons to flow through it) 13. Which are more dangerous: acids or bases? Why? TRICK QUESTION- neither … both are dangerous if they are strong. Weak acids and bases are not dangerous. 14. What is neutralization? What do hydronium and hydroxide ions combine to form? A reaction between a base and an acid to form a salt and water. Hydronium donates an H+ to OH- to make H2O 15. Write a neutralization reaction that shows what happens when HCl reacts with NaCl. HCl + NaCl H2O + NaCl 16. In the equation below label the following: reactants, products, yield NaHCO3 + CH3COOH H2O + CO2 + NaC2H3O2 yields Reactants products 17. What evidence was there of a chemical reaction in the baking soda and vinegar lab? Gas bubbles, temperature change 18. Compare the combined mass before the reaction to the mass after the reaction for trial 1. The mass went down 19. How can you account for this change in mass? Matter DID NOT disappear… we just let some of the gas escape by leaving the reaction open to the air. 20. Explain the law of conservation of mass. Does trial 1 disprove this law? Explain. Matter is neither created or destroyed, only changed… ie- atoms can’t appear or disappear, every atom in the products has to be shown in the reactants and vice versa. Trial one does NOT disprove this…we just didn’t capture all of the atoms produced. 21. Compare the changes in mass you calculated for the 1st and 2nd trials. What value would you expect to obtain for change in mass if both trial validated (supported) the law of conservation of mass? In trial 2, the mass stayed the same because we kept the system closed and collected all of the atoms. 22. Baking soda is a base and vinegar is an acid. What type of chemical reaction occurred when these were combined? neutralization 23. Looking at the chemical equation in #18, why isn’t it possible for the element zinc, Zn, to appear on the product side? Because it was not shown in the reactants. 24. During an endothermic reaction, the products have a(n) (greater/equal/less) amount of energy compared to the reactants. 25. Which statement is true? a. Bond breaking releases energy and bond making requires energy. b. Bond breaking requires energy and bond making releases energy. c. Bond breaking can either require or release energy, but bond making does not involve a change in energy. 26. During an exothermic reaction, energy is written as a ( reactant/ product) 27. A reaction in which the bond forming energy is greater than the bond breaking energy is a. exothermic b. electrical c. endothermic (bond forming releases energy!!!) 28. What happens in a chemical reaction? a. Atoms are destroyed. b. Atoms are created. c. Molecules are created. d. Atoms are rearranged. 29. In an exothermic reaction, energy is transferred from a. the reactants to the surroundings. c. one reactant to another. b. the surroundings to the reactants. d. the container to the chemicals. 30. In an endothermic reaction, energy is transferred from a. the reactants to the surroundings. c. one reactant to another. b. the surroundings to the reactants. d. the container to the chemicals. 31. In a balanced chemical equation, the mass of the reactants is equal to the a. atoms in a molecule c. volume of the reactants b. atomic numbers of the elements d. mass of the products 32. A chemical equation is balanced by changing or adding a. chemical symbols. c. coefficients. b. subscripts. d. reactants. Balance the following equations! ___CH4 + _2_O2 ___CO2 + _2_H2O _2_ NaHCO3 ___H2O + ___CO2 + ___Na2CO3 _2_Mg + ___O2 _2_MgO _2__NaCl + ___H2SO4 ___Na2SO4 + _2__HCl _2__H2O _2__H2 + ___O2 ___C3H8 + __5_O2 _3__CO2 + _4__H2O ___KOH + ___HCl ___KCl + ___H2O __2_PaI5 __2_Pa + __5_I2 ___Pb(NO3)2 + _2__KI _2__KNO3 + ___PbI2