Enzyme Lab2014CP-1
advertisement

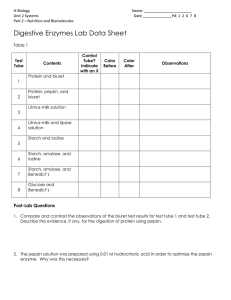
Name: Date: Score:_________/30 points Enzyme Lab - CP Introduction: In chapter 2 section 4, you learned about chemical reactions and how an enzyme speeds up those chemical reactions that keep living things alive. An enzyme only binds to and reacts with a specific substrate. Remember the reactants bind to the enzyme at the active site. Reactant bonds are broken and reconfigured to make the product. Enzymes are designed to speed up the reaction rates of these chemical reactions that would otherwise be too slow to sustain life. Check your understanding: What is the purpose of an enzyme? (1 point) In this lab you will be working with a starch solution. You will use a chemical indicator called iodine. Iodine is used to test for starch. Iodine looks like a brownish red in its normal state. When you drip iodine on starch it turns to a black/blue color. This indicated that starch is present. You will also be using your saliva. There is an enzyme in your mouth called amylase. Amylase is an enzyme that breaks starch down into sugar (glucose) in your mouth before you swallow your food. Amylase is there to help speed up the process of digestion. Check your understanding: If you drip iodine on a substance and it turns blue/black, what does this mean is present? (1 point) Check your understanding: What is the polymer in this scenario? What is the monomer? What is the enzyme? (3 points) In this lab you will be looking at three things. 1. How exactly does amylase work? 2. How does pH affect the enzyme amylase. 3. How does temperature affect the enzyme amylase. *** You will be working with iodine which will stain your skin and clothes, and acids and bases, safety equipment is necessary and you must be very careful with all of these toxic liquids*** Problem: How does a change in pH and temperature affect how the enzyme amylase breaks starch down into sugar? Hypothesis: (Write as an if/then statement that proposes an answer to the above question) (1 point) Procedure Part One: How exactly does amylase work? 1. Choose someone from the group (who is not sick) to spit in the disposable plastic cup provided to you. This person should be the only person to handle the saliva. You will use the plastic pipet with the saliva. Do not use any of the glass droppers. 2. Place 5 drops of the starch solution in the test tube labeled number one. 3. Place 5 drops of starch solution and 10 drops of saliva (containing amylase) into test tube 2. 4. Place your thumb over the top of the tubes and gently mix the contents. 5. After 5 minutes place 3 drops of iodine in each tube, gently swirl. 6. Record results in the data table for part one. (5 points) Data Table Part One: How exactly does amylase work? Test Tube Drops of Starch Drops of Saliva (amylase) Initial Test tube color before iodine Final Test End Tube Color Result after adding (Starch or iodine Sugar in tube) 1 2 Procedure Part Two: Effect of pH change on amylase activity (TEACHER DEMO) 1. Place 10 drops of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in the test tube marked pH1. 2. Place 10 drops of distilled water in the test tube marked pH 7. 3. Place 10 drops of sodium hydroxide (NaOH base) in the test tube marked pH 12. 4. Place 10 drops of saliva in each test tube. (Must quickly get to steps 4-6) 5. Place 5 drops of starch solution in test tubes marked pH 1, pH 7, and pH 12. 6. Stir gently by giving test tubes a gentle swirl. 7. Wait 5 minutes 8. Place 3 drops of iodine in each tube, gently swirl. 9. Record results in the data table for part two. (1 points) Data Table Part Two: Effect of pH – YOU FILL IN END RESULT COLUMN pH Drops of starch Drops of Saliva (amylase) Initial Test tube color before iodine 1 5 10 Cloudy 7 5 10 Cloudy 12 5 10 Cloudy Final Test Tube Color after adding iodine Black Reddish Brown Black End Result (Starch or Sugar in tube) Procedure Part Three: Effect of temperature change on enzyme activity (TEACHER DEMO) 1. Place 5 drops of starch solution in each test tube marked cold, warm, and hot. 2. Place 10 drops of saliva in each tube. (Must get the tubes to the teacher quickly after adding saliva) 3. Gently swirl the contents by placing your thumb over the contents and swirling. 4. Ask your teacher to put a color-coded mark on your tubes before placing them in the proper baths. 5. Place the cold test tube in the ice bath your teacher has prepared in the front of the room. 6. Place the warm test tube in the warm water bath your teacher has prepared in the front of the room. 7. Place the hot test tube in the boiling water bath your teacher has in the front of the room. 8. Let tubes sit for 5 minutes. 9. Ask your teacher to remove the tubes for you after 5 minutes, be sure to come up with your test tube rack. 10. Once back at your lab station, place 3 drops of iodine in each tube, and gently swirl. 11. Record your findings in the data table. (1 point) Data Table Part Three: Effect of Temperature – YOU FILL IN END RESULT COLUMN Temperature Drops of Drops of Initial Test Final Test End starch Saliva tube color Tube Color Result (amylase) before after adding (Starch or iodine iodine Sugar in tube) Cold (8 C) 5 10 Cloudy Black Warm (37 C) 5 10 Cloudy Hot (77 C) 5 10 Cloudy Reddish Brown Black Analysis Questions: 1. What was the function of amylase in this lab? (1 point) 2. What was the substrate for amylase in this lab? What was it being broken down into? (2 points) 3. Was starch a reactant or a product in this reaction? (1 point) 4. Was sugar (glucose) a reactant or a product in this reaction? (1 point) 5. What is the function of enzymes like amylase in living things? (1 point) 6. How did pH change affect enzyme activity? Use data to support your answer (2 points). 7. Why do changes in pH affect enzyme activity? (1 point) 8. The typical pH of the human mouth is usually between 6.5 – 7.5. Does this make sense with your results? Explain. (1 point) 9. How did temperature change affect enzyme activity? Use data to support your answer (2 points). 10. Why do changes in temperature affect enzyme activity? (1 point) 11. The typical temperature of the human mouth is 98.6°F (37°C). Does this make sense with your results? Explain. (1 point) Conclusion: ON LOOSELEAF: Restate your hypothesis. Do you accept or reject your hypothesis? Use data to support your answer. (3 points)