The Ancient Greeks
advertisement

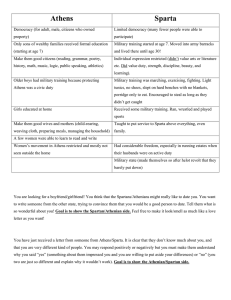
The Ancient Greeks The Early Greeks Geography o They made a living from the sea as well as from land. o They raised sheep rather than cattle and grew olive trees rather than wheat because they were mountainous. o They lived in isolated villages. o They didn’t like to travel on land because they found traveling through the mountains difficult. The Minoans and the Mycenaeans o The Minoans were not Greeks, but their civilization was the first to arise in the region that later became Greece. They made a living from trade. o The Mycenaeans were originally from central Asia. o Heinrich Schliemann (German) discovered one of the walled palaces in Mycenae and named the people of this civilization the Mycenaeans. Dark Age o Trade slowed and poverty took hold. o Before long, Greeks had forgotten the importance of reading and writing. Greek city-states o A Greek city-state was called a polis. o Agora was the open area below the acropolis that was a marketplace. (a market and a place to meet and debate issues) o Greek citizens were free native-born men who owned land. Sparta and Athens Types of governments: o Monarchy = one ruler who usually inherited power and passed on leadership to his son. o Democracy= where all citizens share in running the government. o Tyrant = person who takes power by force and rules with total authority. o Oligarchy= allows for a few people to make decisions. o Direct Democracy= allows all people to decide government matters. o Around 600 B.C., a tyrant came to power in Greece. Sparta o The government was used to control its citizens. o A boy’s life in Sparta: At 7 - lived in barracks and treated harshly to make them tough At 20 – entered regular army At 30 – returned home but stayed in army until age 60 o Spartan women: were trained in running, wrestling, and javelin throwing. Freer than other Greek women Owned property and could go anywhere they wanted Athens o A boy’s life in Athens: Went to school At age 18, finished school and became a citizen o Athenian women: Girls stayed home and were taught by their mothers. Women stayed at home and taught their children. o How did one become a member of Athens’ Council of 500? He was chosen by a random drawing. Persia attacks the Greeks Persia is located in southwestern part of present day Iran. Cyrus the Great was the leader who united the Persians into the largest empire in the world and focused on government and education. The religion of Persia was called zoroastrianaism. They believed in one god. In 499 B.C., the Spartan army and the Athenian army worked together to defeat the Persians. This demonstrates that these rivals will join together to defeat a common enemy. The Battle of Marathon, the Battle of Salamis, and the Battle of Thermopylae have this in common. – They were all won by using clever strategy. The Age of Pericles The Age of Pericles was known as a period of creativity and learning. Beginning in 478 B.C., the Delian League served as the treasury and commander of the fleet. Pericles was a dominate figure in Athenian politics. In 431 B.C., Sparta and other city-states joined forces against Athens to fight in the Peloponnesian War. What made it easier for the Greeks to destroy the Persians at Salamis? Their ships moved more quickly. Review: Relationship between people and their surroundings – Human/Environment Interaction People who study and write about the human past are historians. Nomads followed animals for their food source. Skilled workers in Mesopotamia were called artisans. Moses led the Israelites out of Egypt and into the Sinai Desert. Belief that there is only one god; became the basis for Islam and Christianity. monotheism