lecture 10 Flowers
advertisement

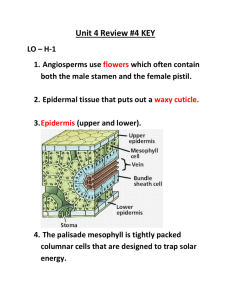
FLOWERS Basic structure of the angiosperm flower The fertilization process Pollen and stigma self-incompatibility The efficiency of animal pollination Some basic types of flower Reproduction and diversity of angiosperms FLOWER • “Bloom” or “Blossom” • It is the part of the plant from which the fruit or seed is developed. FUNCTION OF FLOWERS • Effect Reproduction • Brightening decorations • Worshipping gods • Herbal tea, medicines • Tokens for love and esteem FLOWER ANATOMY REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS • PISTIL – female reproductive organ of the flower which includes the: – Stigma – Style – Ovary • STAMEN – male reproductive organ – Anther – Filament CLASSIFICATION OF FLOWERS Accdg. to PARTS: • COMPLETE FLOWER – A flower having all four floral parts: sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels. • INCOMPLETE FLOWER – A flower lacking either sepals, petals, stamens, or pistils CLASSIFICATION OF FLOWERS Accdg. to SYMMETRY: • REGULAR FLOWER – a radially symmetric flower. Examples: WATER LILY DAISY CLASSIFICATION OF FLOWERS • IRREGULAR FLOWER – a flower in which one or more members of a whorl differ in form from other members – Example: Pea flower CLASSIFICATION OF FLOWERS Accdg. to SEXES: • PERFECT – flower showing both carpels and stamens • IMPERFECT – flower with only one reproductive organ, either female or male CLASSIFICATION OF FLOWERS Accdg. to COMPOSITION: • SIMPLE – a flower head made up of few flowers – Example: Gumamela • COMPOUND - a flower head made up of many small flowers appearing as a single bloom. INFLORESCENCES • It is the mode of development and arrangement of flowers on an axis. TYPES OF INFLORESCENCE EXAMPLES RACEME UNIPAROUS CYME UMBEL EXAMPLES CAPITULUM SPIKE BIPAROUS CYME EXAMPLES CORYMB SPADIX POLLINATION • The transfer of pollen from the anthers of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or of another flower. TYPES OF POLLINATION • Cross-pollination - occurs when pollen is delivered to a flower from a different plant • Self-pollination - occurs when pollen from one flower pollinates the same flower or other flowers of the same individual AGENTS OF POLLINATION • • • • • Wind Water Insects Mammals Birds Basic structure of the angiosperm flower Collective nouns that can cause confusion! Calyx The outer whorl of a flower made up of sepals that are usually green, and protect the flower in bud. Carpel Bears the stigma, and frequently an elongated style, and encloses the ovules (sometimes gynaecium). The megasporophyll of the flower Corolla Ovary Pistil The collective term for the petals of a flower Perianth The floral envelope, it includes the calyx and corolla. Stamen The anther and its supporting filament. The microsporophyll of the flower The total of the carpels in a flower is the ovary Each separate carpel when there are lots of them in the ovary Ways in which Angiosperms are different from Gymnosperms Angio-Gymno 4 Ovules protected within an enclosed structure Evolution of the pistil … about meiosis, mitosis and cytokinesis? Life cycle of angiosperms Fig. 17.12 The fertilization process in Angiosperms (Equivalent to Fig 31.10) Development of gametophytes Ways in which Angiosperms are different from Gymnosperms Angio-Gymno 5. Double fertilization to produce diploid zygote and triploid endosperm nucleus What goes on in the endosperm? The triploid nucleus divides and the endosperm cell becomes a supercell with many nuclei and a milky consistency. Cyotkinesis forms membranes and walls between the nuclei and makes the endosperm more solid. The developing embryo uses the nutrients stored in the endosperm, as does the moncot seedling after germination. In most dicots, food reserves are moved to the cotyledons and the endosperm is not present in a mature seed. Somatic cell division involves two successive steps: mitosis and cytokinesis. In mitosis, the nuclear DNA duplicates and chromosomes segregates equally between the two daughter nuclei; cytokinesis divides these two nuclei and cytoplasm, including related cytoplasmic organelles, into two individual cells. Ways in which Angiosperms are different from Gymnosperms Angio-Gymno 5. Generally angiosperms have hermaphrodite flowers and cross pollinate (70%) … how many alleles there are at a locus? Pollen and stigma incompatibility There can be dozens of alleles of the S-gene. If a pollen grain has an allele that matches an allele of the stigma upon which it lands, then the pollen tube fails to grow. What happens when pollen from plants with three different allele pairs is crossed with an S1S2 plant? This system prevents self-fertilization AND fertilization from close relatives. Pollen Grain Size and Surface Morphology in a Perennial Rye Grass Hybrid Rye grass incompatibility Pollen grain on stigma Attempts to hybridize between particular varieties resulted in production of a web-like substance and incompatibility Stacey Lacoste The efficiency of animal pollination Nucleus of tube cell Generative cell Pollen is up to 30% protein Animal pollination is targeted and so is more efficient than wind pollination. Animal pollinated flowers generally produce much less pollen than wind pollinated flowers. Pollen is important for animals – and many animal pollinated plants do produce excess pollen. Lilium pollen http://www.uri.edu/artsci/bio/plant_anatomy/images/153.gif Some basic types of flower Separate petals Magnolia grandiflora http://www.csdl.tamu.edu/FLORA/gallery4.htm Flowers with a tubular corolla Gentiana algida Rocky Mountain National Park CO http://www.csdl.tamu.edu/FLORA/gallery4.htm A head with many florets http://www.csdl.tamu.edu/FLORA/gallery4.htm Monocotyledons Flower parts in threes Narcissus spp. http://www.csdl.tamu.edu/FLORA/gallery4.htm Monoecious, wind pollinated Oaks, have separate male and female flowers. The female flower (upper left) consists only of carpels and a calyx (collection of sepals). The male flowers are in elongated clusters, called catkins, and consist only of anthers and a calyx. Both sexes are found on the same tree, and thus oaks are monoecious (meaning same house). Some trees, e.g., poplars and willows are dioecious (meaning two houses), and there are male and female trees. Other monoecious genera include birch, walnut, ash, hickory, and most maples. http://forest.wisc.edu/forestry415/INDEXFRAMES.HTM Reproduction and diversity of angiosperms Animal pollination is efficient and associated with the development of the hermaphrodite reproductive axis The diversity of flowers represent mechanisms promoting efficient pollination Prevention of self-fertilization maintains genetic variation by promoting cross pollination Sophistication of the reproductive process enables a large number of ways reproductive isolation can occur and so maintains genetic diversity