Role of HR
advertisement

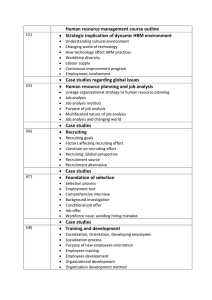
Strategic Human Resource Management Strategy Abell’s (1993) ‘ mastering the present and pre-empting the future. Strategy It is forward looking. It is about deciding where you want to go and how you mean to get there. Strategy formulation The process of deciding on a strategic direction by defining a company’s mission and goals, its external opportunities and threats, and its internal strengths and weaknesses Formulation of Strategy It is a process for developing a sense of direction and ensuring strategic fit. Whittington model 1. Define the mission 2. Set objectives 3. SWOT 4. Analyze existing strategies 5. Define the light of the analysis Formulation of Strategy 6. Define the key strategic issues 7. Determine corporate and functional strategies 8. Prepare integrated strategic plans for implementing strategies. 9. Implement the strategies 10. Monitor implementation and revise. Concept of SHRM Strategic HRM is an approach that defines how the organization’s goals will be achieved through people by means of HR strategies and integrated HR policies and practices. Strategic HRM focuses on actions that differentiate the firm from its competitors. Fitting HR characteristics to competitive strategies • Innovation Strategy • Quality Strategy • Cost Leadership Strategy Challenges related to technology • • • • • Telecommuting Employee Surveillance and Monitoring e-HR Ethical Behavior Intrapreneurship at intel- New Business Initiative (NBI) • Workforce Demographic changes and diversity Challenges in SHRM- demographics changes on job satisfaction A shifting Industrial Base Age Gender Immigration Company size Communication Work/life balance Relationship with supervisor Career development and opportunities Job security Benefits and Compensation 5- P Model • • • • • HR Philosophy HR Policies HR Programs HR Practices HR Processes Traditional HR Vs strategic HR Responsibility for HR Staff specialistsLine managers Focus Employee relations - internal /external customers Role of HR Transactional, change follower, and respondent Transformational, change leader, and initiator Initiatives Slow, reactive, fragmented Fast , proactive, integrated Traditional HR Vs strategic HR Time horizon short term short, medium, long Control Bureaucratic-roles, policies, procedures Organic- flexible Job design Tight division of labor, independence, specialization Broad, flexible, cross-training, teams Key investments Capital , Products People, Knowledge Accountability Cost center Investment center Barriers to strategic HR • Short term mentality/ focus on current performance • Inability of HR to think strategically • Lack of appreciation of what HR can contribute • Failure to understand general manager’s role as an HR manager • Difficulty in quantifying many HR outcomes • Perception of human assets as higher-risk investments • Incentives for change that might arise Best- HR Practices General Electric (GE) Leadership Programme Succession Planning Learning and Development 360 degree performance appraisal Regular employee satisfaction surveys Flattened organization structure Best- HR Practices WIPRO 1. Recruitment 2. Succession Planning 3. Rigorous Leadership Training Programme 4. Open and Transparent 5. Family like work atmosphere INFOSYS 1. Competency based HR Practices 2. Promoting based on competencies 3. Continuous appraisal Process 4. Developing Training programmes Best- HR Practices South West Airlines - ‘LUV’ & ‘FUN’ - Value creating -Value capturing -Value sharing - Rigorous Training Programme -Treat employees well Best- HR Practices • IBM Developing Leaders Classroom and internet courses Work-life balance Variable pay program based on Individual performance. Changing Technology- Strategy • Hero Honda Employment engagement Developing leadership skills through broad vision Family like work atmosphere Uniformity in Dress codes Best- HR Practices • Caterpillar Welfare and Fringe benefits Incentive (Profit sharing) Flexible hours Food Coupon Pass On –the- job and Off-the –job Training Best- HR Practices • TCS -Competency Mapping exercises - Balanced Scorecard - Benchmarking of remuneration Strategies with that of the industry - Performance Linked Variable Compensation Others Diversity in the work place (Intel) HPWS (high performance work systems) HR Value chain-employee, organizational, financial& accounting and market based Intelligence Vs Conscientiousness Sarasota Memorial Hospital “Pillars of exellence” Service, people, quality, finance and growth Cross functional teams Leadership development Service recovery Reward and recognition Inpatient, outpatient satisfaction Customer satisfaction increased from 43% to 97% First Tennessee National Corporation HR -Maximize Financial performance -Demonstrate to shareholders the value added benefits of HR programs and policies -Strategic Partnership-HR and finance HR Strategies • • • • • • • HR Strategies Purpose Types Main areas in Which HR Strategies are developed Criteria for an effective HR Strategy Development of HR Strategy Implementation of HR Strategy HR roles at Mercantile Bank • • • • Strategic partner Change agent Administrative expert Employee Champion -1990’s strategically redesigned its HR functions -record keeping and compliance -streamlining work processes, eliminating unnecessary activities -reevaluating technology, outsourcing non strategic functions. -39 M& A’s Barriers to strategic HR • Short term mentality/focus on current performance • Inability of HR to think strategically • Lack of appreciation of what HR can contribute • Failure to understand general manager’s role as an HR manager • Difficulty in quantifying many HR outcomes • Perception of human assets as higher-risk investments • Incentives for change that might arise Strategic reorganization of the HR at GE • Decentralization • 3T’s- technology ,talent and transformation. Design of work systems Job Enlargement IBM -Product quality -Reduction in idle time Eli Lilly Pharma -Salary increases -Promotions -Career development opportunities Design of work systems • Job enrichment • Job rotation U.S. and Japanese Culture 1. Conflict and conformity 2. Power and hierarchy 3. Time orientation 4. Cultural and demographic homogeneity Employment Law • EEOC pay’s $1 million to the victims of sexual harassment case. • Equal Pay Act • Racial Discrimination at Coca-cola Staffing • Kroger Co -1,400 supermarkets , 200,000 employees -45 min • Turnover Cost differs based on sectors • Recruiting- Temporary versus Permanent employees - Internal versus External Recruiting Recruiting Internal -Advantages Have performance data available Motivational Less training/socialization time Faster Less Expensive -Disadvantages Possible Politics “Loser” effects Inbreeding Promotions chain Recruiting External Advantages Fresh ideas and viewpoints Expand Knowledge base Disadvantages Unknown entities Detrimental to internal applicants Training and socialization Time consuming Can be expensive Recruiting When and how extensively to recruit Stages of Recruiting Process which takes 15 weeks. Accept Job Offer 10 Receive job offer 15 Attend Second Interview 30 Invited to Second Interview 40 Invited to first interview 60 Applicants 120 Recruiting Methods word of mouth internet J & J (employee referral) Staffing at St.Peter’s Health Care - nurses biding for shifts at a rate/hr Outsourced Recruitment at Kellogg College Recruiting via Internships at Microsoft Call – Center Staffing at Capital One-VISA credit cards , consumer Master Card –extensive assessments in selection. Training and Development • Benefits of Training and Development • Planning and Strategizing Training • Integrating Training with Performance systems and compensation • *Marketing Products • *e-Training • *Boot camp (exposed and committed to culture) T &D T & D framework Plan Do Check Act Targeting and the four P’s of Training level analysis Place on-the-job off- the –job Equipment required T &D • Product purpose, content , constraint, Presentation option • Promotion Strategic Planning Involvement Company newsletter Personal communication Word-of-mouth • Price (budget) Employees materials Equipment Travel Employee Separation Layoffs at Kodak Range of services Allowance of two weeks’ pay for each year of employment retained medical, dental, and life insurance for four months; outplacement counseling; and a retraining allowance of up to $5000 for schooling.