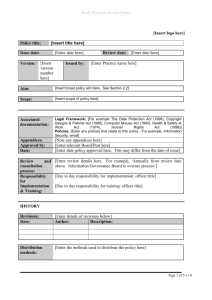
Business Unit
Security & Authentication - An
industry perspective
CCA
Strictly Private
and Confidential
October 2014
Endangering the present
Cyber security threats today have become increasingly sophisticated and complex. As organisations
embrace new technologies without fully comprehending the implications these have on the entire
enterprise, they are rendering themselves susceptible to an array of cyber-security threats.
An efficient and executable strategy, which encompasses the key levers of people, processes and
technology is needed to confront the changing threat landscape, as a few risk issues are as allencompassing as cyber-security.
Cyber security attacks in the news
Stuxnet worm infects critical infrastructure
facilities in Gujarat and Haryana, ONGC offshore oil rig also affected
Instances of state–sponsored espionage
against major European bank uncovered by
Symantec
US Department of Justice (DOJ) sentences
five Chinese military hackers for cyber
economic espionage against American
companies in the nuclear power, metals and
solar energy sectors
The Heartbleed defect, impacts over twothirds of web servers in the world, including
those of popular e-mail and
social
networking sites
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
October 2014
2
Are budgets keeping up with the rising costs?
With the increase in the average cost per security incident from $194 to $414 (113%) and a 20%
increase in the average losses as a consequence of security breaches, an increase in the information
security budget would be anticipated.
However, the average information security budgets actually declined by almost 17%. It seems
counter-intuitive that, even though threats have become more frequent and damaging,
organisations have not increased their security spending.
What drives information security expenditure?
Theft of customer or employee information
Hacktivism (e.g. WikiLeaks)
$4.8
million
Internal policy compliance
Regulatory compliance
2013
Merger or acquisition activity
$4
million
Company reputation
Outsourcing
2014
Business continuity or disaster recovery
Change and business transformation
20%
25%
30%
35%
40%
45%
50%
Drop in total average information
security budgets in India
Key drivers for information security spending in India
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
October 2014
3
The constantly evolving cyber-threat landscape is
driving the increase in security incidents
The marked increase in the number of detected incidents, in our view, is likely driven by the
changing cyber-threat landscape. As the digital channel in financial services continues to evolve,
cybersecurity has become a business risk, rather than simply a technical risk.
Lines between the threats are blurring
Motivators
Impact
Threat vectors
Nation-states
• Global competition
• National security
• Fraud
• Targeted, long-term cyber
campaigns with strategic focus
• Insider
• Third-party service providers
• Loss of intellectual property
• Disruption to critical
infrastructure
• Monetary loss
• Regulatory
Cyber criminals
• Illicit profit
• Fraud
• Identify theft
• Individual identity theft
• Data breaches and intellectual
property theft
• Insider
• Third-party service providers
•
•
•
•
•
• Opportunistic vulnerabilities
• Insider
• Third-party service providers
• Destabilize, disrupt and
destroy cyber assets of
financial institutions
• Regulatory
• Targeted organizations that
stand in the way of their cause
• Insider
• Third-party service providers
•
•
•
•
•
Cyber terrorists/
individual
hackers
Hacktivists
•
•
•
•
Ideological
Political
Disenfranchised
Malicious havoc
• Political cause rather than
personal gain
• Ideological
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
Loss of identity
Monetary loss
Intellectual property loss
Privacy
Regulatory
Disruption of operations
Destabilization
Embarrassment
Public relations
Regulatory
October 2014
4
Insiders are the most likely perpetrators
Insider threat
Current and former employees have been cited by respondents as the most common causes of
incidents. This, however, does not imply that most users exhibit malicious behaviour, a lack of
awareness of common dos and don’ts may lead to instances in which users compromise data
through the loss of mobile devices or through targeted phishing attacks.
Loss of data through associations with customers and vendors also contribute to a reasonable chunk
of incidents caused by insiders. The lack of effective mechanisms to manage risks to data stemming
from 3rd parties, is largely responsible.
50%
2014
40%
2013
30%
Estimated likely sources of
incidents (insiders)
20%
10%
0%
Current employees Former employees
Current service
providers or
consultants or
contractors
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
Former service
providers or
consultants or
contractors
Suppliers or
business partners
Customers
October 2014
4
External sources garner most attention
Outsiders
Cyber incidents that garner the most attention are compromises caused by nation states and
organised crime and are among the least frequent. However, the fact that there has been a two-fold
increase in information security incidents caused by foreign nation-states is alarming.
As nation-states can carry out sophisticated attacks without detection, we believe that the volume of
compromises is, in all probability, are under-reported. Indian organisations also reported twice as
many attacks from competitors when compared with the global average.
45%
2014
40%
2013
35%
30%
25%
20%
15%
10%
5%
0%
Terrorists
Organized crime
Activists or
activist
organizations or
hacktivists
Foreign nationstates
Foreign entities
and
organizations
Competitors
Information
brokers
Hackers
Foreign entities
and
organizations
Foreign nationstates
Estimated likely sources of incidents
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
October 2014
5
How do attacks impact organisations?
Employee and Customer records continue to be the top targets of cyber attacks
The breach of employee (45%) and customer records (42%) remained the most cited impacts of
cyber attacks. Compromise of customer records may interrupt smooth running of business, leave
the organization exposed to legal action, result in loss of customers and may also damage the
reputation of the organization.
40%
2014
2013
35%
30%
25%
20%
15%
10%
5%
0%
Financial losses
Theft of “soft” IP
Theft of “hard” IP Brand or reputation Loss of shareholder Loss of customers
compromised
value
Loss of business
partners or
suppliers
Financial Fraud
Legal exposure or Business or process
lawsuit
interruption
Impact of cyber attacks on business
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
October 2014
6
The ‘human parameter’
Employee training and awareness is a fundamental component of every programme, as the weakest
link in the security chain is often the human resource. However, compared to last year’s 61%, fewer
respondents (56%) require their employees to complete training on privacy policy and practices.
A cross-organizational team (including leaders from finance,
legal, risk, human resources, IT, and/or security) that regularly
meets to coordinate and communicate information security
issues
Employee security awareness training program
Impose disciplinary measures for privacy program violations
Require our employees to complete training on privacy policy
and practices
Require our employees to certify in writing that they comply
with our privacy policies
50.3%
53.6%
54.7%
56.2%
64.4%
How respondents are addressing the ‘human parameter’
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
October 2014
7
Data privacy safeguards
Many organisations have implemented the following data privacy safeguards, however, to prepare
themselves better to the changing threat landscape, all organisations should consider implementing
these data privacy safeguards.
Data privacy safeguards currently in place
People
Require our employees to complete training on privacy policy and practices
56.2%
Impose disciplinary measures for privacy program violations
54.7%
Conduct personnel background checks
58.1%
Processes
Have an information security strategy that is aligned to the specific needs of the business
60.9%
Conduct compliance audits of third parties that handle personal data of customers and employees to ensure they have the
capacity to protect such information
52.9%
Inventory of all third parties that handle personal data of employees and customers
50.2%
Technology
Privileged user access
62.6%
Malware or virus-protection software
67.9%
Security information and event management (SIEM) technologies
61.2%
Security-event-correlation tools
56.2%
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
October 2014
8
Dynamic security practices – Need of the hour
Even with the increase in the average cost per incident and the overall financial losses as a
consequence of security incidents, organisations are still reluctant in adopting technologies and
processes that can help safeguard the organisation against these incidents.
52.1%
46.4%
48.2%
45.6%
45.0%
41.2%
Employee security
awareness training
program
Identity-management Risk assessments (on
tools
third-party vendors)
User-activity
monitoring tools
43.2%
Behavioral profiling Governance, risk, and Data loss prevention
and monitoring
compliance (GRC) tools
(DLP) tools
44.7%
Intrusion-detection
tools
Respondents who answered security safeguards are not currently in place
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
October 2014
9
Are organisations taking identity management
seriously?
Current and former employees continue to be cited as the main causes of security breaches, with
over 65% of incidents being attributed to the group. In the light of these findings, the need for
identity and access management solutions now is greater than ever.
35%
A large number of organisations have identified access controls and identity
management as one of the top security challenges
Over 25% of organisations describe Biometrics for authentication as a top priority
in the next 12 months
50%
Of organisations have identity management solutions already in place
50%
Of organisations have solutions for automated provisioning & de-provisioning of
user accounts already in place
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
October 2014
10
Are organisations moving towards newer
authentication methods?
Newer techniques such as risk based authentication and behavioural profiling are quickly gaining
popularity. Behavioural profiling is used to accurately predict and profile the characteristics of
users that may cause breaches.
Over 47% of organisations have employed behavioural profiling tools to strengthen their
information security programme
41%
Of organisations plan to adopt tokenisation as an
emerging technology for data protection
53%
Of organisations already use multi-factor
authentication to strengthen information security
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
October 2014
11
How prevalent is the use of smart cards and tokens for
authentication?
Security tokens are physical devices that are provided to users to introduce an additional level of
security in authentication.
There are three factors to authentication :
-
Something the user knows
-
Something the user has
-
Something the user is/ does
Traditional methods use the first factor for authentication, smart cards and tokens are used to
introduce the second factor (something the user has) to enhance security.
49%
Of organisations use disposable passwords or smart cards or
tokens for authentication
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
October 2014
12
Are organisations adopting user activity monitoring
tools?
To ensure strong control over the activity of users, organisations are moving towards user activity
monitoring tools.
The use of these tools is more prevalent in the commercial & consumer banking, insurance,
aerospace & defence, pharmaceutical and consumer packaged goods sector.
72.0%
70.0%
68.0%
66.0%
64.0%
62.0%
60.0%
58.0%
Aerospace &
Defense
Consumer
Packaged Goods
Commercial
banking
Consumer banking
Insurance
Pharmaceutical
Adoption of user activity monitoring (sector wise)
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
October 2014
13
Organisations are increasingly adopting risk based
authentication
Risk based authentication solutions enhance traditional authentication methods by assigning a
risk value to the user trying to gain access. Such solutions use additional parameters such as
behaviour profiling, geo-locations etc. to evaluate the user’s risk profile
Transportation & Logistics
Electronics
Software
Telecommunications
Automotive
Pharmaceutical
Utilities
Oil & Gas
Consulting / Professional Services
Agriculture
Aerospace & Defense
0.0%
10.0%
20.0%
30.0%
40.0%
50.0%
60.0%
70.0%
Adoption of risk based authentication (sector wise)
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
October 2014
14
How is authentication on mobile devices being
managed?
One area that organisations are increasingly focusing on is enterprise mobility, which enables
employees, partners and customers to access and work on the organisation’s technology
platforms through any secure enabler (laptops, tablets or smartphones).
How are organisations ensuring security mobile devices?
50%
48%
46%
44%
42%
40%
38%
36%
34%
32%
30%
Mobile security strategy
Mobile devicemanagement software
Strong authentication Protection of corporate
on devices
e-mail and calendaring
on employee- and userowned devices
Initiatives organisations have taken to address mobile security risks
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
October 2014
15
Challenges to security
Challenges from within
Even with the growing impact that cyber security incidents can have on the entire enterprise, boards
of organizations in the country remain oblivious and continue to treat cyber security as an IT
problem.
The lack of leadership to set a clear direction for the overall information security strategy along with
insufficient capital and operating expenditures represent the biggest obstacles in improving the
overall strategic effectiveness of information security.
Poorly integrated or overly complex information and IT systems
Absence or shortage of in-house technical expertise
Insufficient operating expenditures
Insufficient capital expenditures
Obstacles in improving
overall strategic
effectiveness
Lack of an actionable vision or understanding of how future
business needs impact information security
Lack of an effective information security strategy
Leadership: CISO, CSO, or equivalent
Leadership: CIO or equivalent
Leadership: CEO, President, Board, or equivalent
0%
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
5%
10%
15%
20%
25%
30%
35%
40%
October 2014
16
Challenges to security
Increased dependence on 3rd parties
Given today’s interconnected business ecosystem, where the amount of data generated and shared
with business partners and suppliers is exponentially greater, due diligence of third parties has
become a concern. It is worrisome that the focus on third-party security weakened in the past year
in some very key areas; even as the number of incidents attributed to ‘insiders’ increased.
Require third parties (including outsourcing vendors) to comply with
our privacy policies
48.9%
Have established security baselines/standards for external
partners/customers/suppliers/vendors
Maintain inventory of all third parties that handle personal data of
employees and customers
53.8%
50.2%
Conduct compliance audits of third parties that handle personal data
of customers and employees to ensure they have the capacity to
protect such information
52.9%
How respondents are safeguarding relationships with 3rd parties
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
October 2014
17
Security initiatives
Emerging technologies
The applications of SMAC (social, mobile, analytics and cloud) technologies have been debated for
long, but it is about time that Indian companies started leveraging them.
Social
Media
The ambiguity in calculating the return on social media investments, coupled with the
difficulty in understanding the applications of social media in business and leveraging
them to generate a profit stream has led to a slow adoption
Mobile
Organisations are now widely adopting enterprise mobility, while taking initiatives to
address risks from its adoption as well, over 65% respondents already have a mobile
security strategy in place
56%
54%
50%
48%
54%
Respondents that audit
or monitor employee
postings to external
blogs or social
networking sites
41%
41%
Mobile deviceBan of user-owned
Protection of corporate e- Strong authentication on
management (MDM) or devices in the workplace mail and calendaring on
devices
mobile-access
or network access
employee- and usermanagement (MAM)
owned devices
software
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
Device encryption
Internal app store for
employee mobile devices
Mobile security initiatives taken by organisations
October 2014
18
Security initiatives
Analytics
As organisations adopt social media and mobile platforms and the digital footprint of its
customers increases, the shear amount of data that is available for organisations to
analyse and use increases exponentially. More and more organisations are using big data
analytics for data driven insights
Over 69% respondents employ big data analytics to model for and identify information security
threats. Almost one-third respondents use big data analytics as a cloud service.
8%
60%
3%
57%
50%
20%
47%
40%
30%
19%
20%
20%
22%
10%
Currently in place
Currently outsourced
0%
Detected more
incidents
No change in detected
incidents
Detected fewer
incidents
Impact of big data analytics on information security
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
Not in place but is a priority over the next 12 months
No plans to adopt
Do not know
How organizations employ big data analytics
October 2014
19
Security initiatives
Cloud
Migrating to cloud based services marks a fundamental shift in the way business is done,
with a variety of deployment & service models available, organisations need to develop a
sound strategy to manage cloud services
Almost 68% respondents already use cloud services in some form (SaaS or PaaS or Iaas), although
the use of cloud services for file storage and sharing remains the most popular.
80%
Global
India
70%
60%
50%
40%
30%
20%
File storage and
sharing
Database hosting
Application hosting
E-mail hosting
Application
development/testing
Website hosting
E-commerce
Disaster
recovery/business
continuity
Big Data analytics
Security services
How are organisations using cloud services?
India vs Global average
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
October 2014
20
Cyber risk management
Organisations in India have been focused on perimeter security. It is only now that there are visible
signs of organisations moving from the asset and technology centered paradigm for information
security to comprehensive cyber-risk management. The first step for all organisations will be to
align security spending with the organisation’s strategic assets
Safeguards that are a top priority for respondents in the next 12 months
Procedures dedicated to protecting intellectual property (IP)
19.2%
Program to identify sensitive assets
23.0%
Centralized security information-management processes
22.6%
Classification of business value of data
16.3%
Risk assessments (on internal systems)
19.2%
Risk assessments (on third-party vendors)
26.8%
Active monitoring/analysis of information security intelligence (e.g., vulnerability reports, log files)
20.5%
Governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) tools
26.0%
Enterprise content-management tools
22.9%
Protection/detection management solution for advanced persistent threats (APTs)
28.3%
Security information and event management (SIEM) technologies
24.2%
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
October 2014
21
Demographics
Around 30% of our respondents had annual gross revenues of over 1 billion USD, and another 30%
(approx.) had revenues between 100 million USD and 1 billion USD. Almost a third of our
respondents were small enterprises with annual gross revenues of less than 100 million USD,
making it an inclusive survey with a distributed respondent base.
5.3%
7%
3.1%
29.5%
32.6%
3%
Large (> 1 billion USD)
7%
37%
Medium (100 million
USD to 1 billion USD)
CIPS
Small (< 100 million
USD)
FS
TICE
Govt
Non-Profits,
government, educational
Others
Unknown
29.5%
Respondents by annual gross revenues
Security & Authentication - An industry perspective • CCA
PwC
47%
Respondents by industry sector
October 2014
22
Thank you.
This publication has been prepared for general guidance on matters of interest only, and does
not constitute professional advice. You should not act upon the information contained in this
publication without obtaining specific professional advice. No representation or warranty
(express or implied) is given as to the accuracy or completeness of the information contained
in this publication, and, to the extent permitted by law, PricewaterhouseCoopers Private
Limited, its members, employees and agents do not accept or assume any liability,
responsibility or duty of care for any consequences of you or anyone else acting, or refraining
to act, in reliance on the information contained in this publication or for any decision based on
it.
© 2014 PricewaterhouseCoopers Private Limited. All rights reserved. In this document, “PwC”
refers to PricewaterhouseCoopers Private Limited which is a member firm of
PricewaterhouseCoopers International Limited, each member firm of which is a separate legal
entity.