Pengelolaan Organisasi Entrepreneurial
advertisement

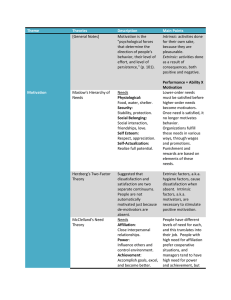
Mata kuliah Dosen Pembuat Tahun : J0754 - Pengelolaan Organisasi Entrepreneurial : D3122 - Rudy Aryanto : 2009 Aplikasi Sistem Penghargaan Chapter 8 Learning Objectives – Explain reward programs found in high-performance organizations – Understand the strengths and weaknesses of nontraditional reward programs Performance Analysis Questions • Antecedent – – – – Do employees know what is expected? Are the standards clear? Have they been communicated? Are they realistic? • Behavior – Can the behavior be performed? – Could employees do it if their lives depended on it? – Does something prevent its occurrence? Performance Analysis Questions • Consequence – Are consequences weighted in favor of performance? – Are improvements being reinforced? – Are improvements noted, even when the employee is below company standards? – Is reinforcement specific? Applied Behavior Modification Manager’s Step-by-Step Procedure Pinpoint specific behavior Measure, count, and formulate baseline point for critical behaviors Perform the ABC analysis • Antecedent • Behavior • Consequence Form action plan, strategies • Positive reinforcement • Negative reinforcement • Extinction • Punishment Feedback to make changes Evaluate critical behavior Compare baseline vs. after-action behaviors ABC Analysis - Absenteeism Problem A ANTECEDENT(S) B BEHAVIOR(S) C CONSEQUENCE(S) Family problems Personal health Illness Jury duty No transportation Company policies Group norm Friends visiting Injured on way to work Hangover No child care facilities Lack of proper tools/clothing Staying home Shopping Oversleeping Getting up late Attending sporting event Working at home Visiting Serving on jury In emergency room At doctor’s office Public reprimand Private reprimand Written record & reprimand Reduction in pay Suspension Firing Social isolation from group Reinforcement Theory • Research results – Strong evidence that OBM makes a positive contribution to organizational behavior – Absenteeism rates, quality of production, and employee safety behaviors improve Reinforcement Theory • Criticisms – Bribery, not a real change in behavior – Reinforcements not linked to beliefs, values, or mental processes – Self-reinforcement ignored – Behavior becomes too dependent on the reinforcer and won’t occur without it – Perceptual differences in utilization of positive reinforcement Reinforcement Theory • When expressing appreciation and reinforcing good behavior – Describe the desired behavior in specific terms, not generalization – Explain why the behavior is good for the organization – Include a personal expression of thanks Behavioral Self-Management (BSM) • Facing response alternatives that have different consequences • Selecting or modifying behavior by managing – Cognitive processes – Causes – Consequences Kafner’s Self-Regulation Model Stage 1 Self-monitoring “A new boss - I wonder whether my performance will be good enough. I hope so.” Stage 2 Self-evaluation “I was considered an excellent performer by Tony (previous boss). He knew my quantity and quality of output were excellent. I need to find out what the new boss considers excellent in terms of quantity and quality.” Stage 3 Self-reinforcement “I really did an outstanding job. The boss smiled when we were talking about my performance. He’s really a lot like Tony (previous boss).” Goal-Setting Theory: Key Concepts • Goal setting – The process of establishing goals • Conscious goals – Goals that a person is trying to achieve and is aware of when directing behavior • Goal specificity – Level of performance required to achieve the goal Goal-Setting Theory: Key Concepts • Goal difficulty – Level of performance required to achieve a goal • Goal intensity – Process of setting a goal or determining how to reach it • Goal commitment – Amount of effort used to achieve a goal Goal Setting: Core Steps Goal-Setting Attributes 1. Specificity 2. Difficulty 3. Intensity 4. Commitment Final Review Anticipated Results 1. Discussion 2. Analysis 3. Development 4. Recycling Improved motivation to • Perform • Plan • Organize • Control Intermediate Review 1. Frequency 2. Exchange of ideas 3. Modifications Feedback Goal Setting Research • Locke and associates found that… – Specific goals lead to higher output than do vague goals – Achieving goals provides workers with a sense of achievement, recognition, and commitment – Having a goal allows workers to compare their performance with that of others Goal Difficulty-Performance Relationship • Need achievement Job performance High Low Easy Moderate Goal difficulty Hard Goal Difficulty-Performance Relationship • Expectancy theory Job performance High Low Easy Moderate Hard Goal Difficulty-Performance Relationship • Goal-setting theory B Job performance High C A = Performance of committed person with ability B = Performance of committed person working at full capacity A C = Performance of person lacking commitment Low Easy Moderate Goal difficulty Hard Participation Factor • Conflicting theories – Latham… when goal difficulty is held constant, there is no difference in goal commitment or performance, whether the goal is assigned or set participatively – Erez… participation in goal setting is crucial to goal commitment • Findings of experiments – Participation had no effect on goal commitment or performance Individual Differences • Participation in goal setting may increase job performance – Social factor of group discussion – Motivational factor of being involved in the goal-setting process – Cognitive factor of information sharing Individual Differences • Social and motivational factors increase – – – – – Performance quantity Learning the task Goal acceptance Group commitment Satisfaction • Conflicting goals – Can lead to decreased performance, regardless of goal commitment, goal importance, or strategies used Criticisms of Goal Setting • Goal setting – – – – Complex and difficult to sustain Works well for simple jobs, but not for complex jobs Encourages game playing. Is used as another check on employees • Goal accomplishment – Can become an obsession Motivation Theory: Key Conclusions • Managers – Can influence employee motivation – Must remember that ability, competence, and opportunity all affect motivation – Must continually monitor employees’ needs, abilities, goals, preferences – Must channel self-motivated behavior into productive results Motivation Theory: Key Conclusions • Managers – – – – Are role models who influence employee motivation Must provide incentives for employees Should establish moderately difficult goals to direct behavior Should provide jobs that offer equity, task challenge, diversity, need satisfaction – Must energize, sustain, and direct motivation Organizational Reward Systems • Main objectives of reward programs – Getting qualified people to join the organization – Keeping employees coming to work – Motivating employees to achieve high levels of performance The Reward Process Intrinsic rewards Ability and skill Performance results: individual Motivation to exert effort Experience Performance evaluation Satisfaction Extrinsic rewards Feedback Lawler’s Conclusions • Reward satisfaction is influenced by… – How much is received and how much the person feels should be received – Comparisons with others • People differ in the… – Rewards they desire – The importance they place on them • Some rewards are satisfying because they lead to other rewards Reward Packages • Any reward package should be… – Sufficient to satisfy basic needs – Considered equitable – Individually oriented Extrinsic and Intrinsic Rewards • Extrinsic Rewards – Salary, wages, fringe benefits – Interpersonal rewards – Recognition and promotions • Intrinsic Rewards – – – – Completion Achievement Personal growth Autonomy Rewards, Turnover, Absenteeism • Managers can… – Influence employee attendance behavior – Punish, establish bonuses, and allow employee participation in developing plans • Absenteeism reduction is determined by… – The perceived value of the rewards – The amount of the rewards – Whether employees see a relationship between attendance and rewards Rewards and Job Performance • Key points – Each person has different needs and perceptions, so outcomes have different values – Managers must consider individual differences when choosing rewards – Valued rewards can result in the exertion of effort and high levels of performance Commitment Attitudes • Commitment to an organization involves... – A sense of identification with the organization’s goals – Involvement in organizational duties – A feeling of loyalty for the organization Organizational Commitment • Use intrinsic rewards to develop organizational commitment – Provide achievement opportunities – Recognize achievement when it occurs – Develop intrinsic reward systems that focus on personal importance or self-esteem Reward Systems & High Performance • New, innovative, but untested reward systems – – – – Cafeteria-style fringe benefits Banking time off Skill-based pay Gainsharing Reward Criticisms • According to Kohn, rewards… – – – – – Injure relationships Are really punishment Have a Skinner bias Ignore reason Discourage risk taking