File
advertisement

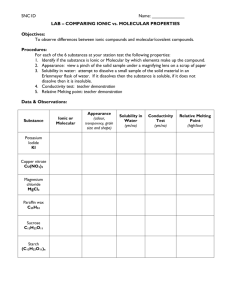
Chem 20 Solutions 3 & 4 Chemical reactions/entities in Solution When substances dissolve, they become individual ions (if ionic) or individual molecules (if molecular). Turn water into wine, milk, beer experiment Follow the instructions on the handout and demo for the class. Hints: The wine is created by phenolphthalein indicator turning red in a base The milk is created by a precipitate. The concentrated hydrochloric acid in the fumehood is very dangerous. Use goggles! A watchglass must be used to cover the fumes. Review the rules for listing entities before answering the following questions. Questions: 1. What is the name of the precipitate that caused the milk? 2. Why did the final glass have a yellow color (what indicator was responsible)? Listing Entities in Solution and predicting reactions 1. First, you must classify the type of compound as ionic, molecular, acid or metal a) Ionic: contains a metal. Exception: NH4 (polyatomic ion) compounds eg. CaCl2, Mg3(PO4)2, NH4NO3 , Ba(OH)2 _____________________________________________________________ b) Molecular: Contains no metals. Remember, H acts like a metal but is not a true metal. eg. C2H5OH, SO2, Cl2, H2O2 _____________________________________________________________ c) Acid: Formulas can be of two types: H____(aq) or _____COOH(aq) eg. HNO3(aq) or CH3COOH(aq) _____________________________________________________________ d) Metal: Monoatomic metal formula eg. Fe, Cu, Mg, Ca p 202 #8 , and p 41 #24 (Classify the type of substance present and give the formula or name) 2. Next, follow the rules for each compound type: a) Ionic: Charged water molecules pull apart ions from soluble ionic compounds (solute): http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EBfGcTAJF4o&feature=related Soluble ionic compounds dissociate into ions. Therefore ions are listed. eg. NaCl… Na+(aq) , Cl-(aq) , H2O(l) Al2(SO4)3 (aq) …. Al3+(aq) SO42- (aq) , H2O(l) Ba(OH)2….. Ba2+(aq), OH-(aq) , H2O(l) Low soluble ionic compounds do not dissociate to any great degree eg. AgCl…. AgCl(s) , H2O(l) _____________________________________________________________ b) Molecular: Soluble molecular compounds are aqueous, but don’t dissociate into ions eg. C6H12O6…. C6H12O6 (aq) , H2O(l) Insoluble molecular compounds remain in the state they were in eg. C8H18 (l)…. C8H18 (l) , H2O(l) _____________________________________________________________ c) Acid: Strong acids ionize 100% eg. HCl(aq)…. H+(aq) , Cl-(aq) , H2O(l) HNO3(aq)….. H+(aq) , NO3 -(aq) , H2O(l) Weak acids remain mainly in molecular form and do not ionize to any great degree eg. CH3COOH(aq) …. CH3COOH(aq) , H2O(l) _____________________________________________________________ d) Metal : Remain as solid metals eg. Fe…. Fe(s) , H2O(l) ----------------------p. 202 Lab ex 5B, 1-3, 8 (list entities and write dissociation/ionization equations for each compound), p 41 #24 (list entities and write dissociation/ionization equations for each compound)