Types of Businesses Sole Proprietorship
advertisement

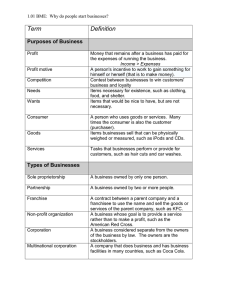
Vocabulary Sole-Proprietorship- A business owned by a single person. Partnership- A business owned by 2 or more people. Corporation- A business that is owned by its stockholders (people who buy company stock). Labor Union- Group of workers that unite to attempt to get better pay and working conditions. Arbitration- Method of conflict resolution where a 3rd party listens to each side and then makes a decision. Lockout- When employees are prevented from attending work. (NFL) review Why is it that Monopolies are considered bad for our economy? How are Monopolies sometimes good for our economy? How are American Anti-Trust Laws an example of a mixed-market economy? What is an oligolopoly? What is a conglomerate? What is the differerence b/w a horizontal and vertical merger? Warm Up Why has the U.S. Gov’t created laws in order to prevent monopolies? Types of Businesses Sole Proprietorship Business owned by a single person Ex: Pizza place, beauty salon Easiest form of business to set up. Anyone can start one. Advantages Owner receives all the profit & makes all decisions. Disadvantages Unlimited Liability The owner is financially responsible for all problems Limited Life Function only when the owner does Difficult to raise financial capital Small Business Administration Partnership & Cooperatives Partnership Business owned by 2 or more people. Ex: Law firms & Doctors offices Cooperatives Involves much more people than a typical partnership Board of Directors elected by owners to oversee company Advantages Easier to raise financial capital due to multiple owners Each owner brings special skills and run different parts of business. Disadvantages Difficult to reach decisions that satisfy everyone Difficult to dissolve partnership if it breaks apart Unlimited Liability Corporation A business recognized by law that has many similar rights to an individual. Ex: Own property Owned by shareholders who buy stock in the company. Shareholders elect a Board of Directors to run company Advantages Easy to raise financial capital Sells stock & bonds Bonds are a means of borrowing money. In addition to cashing in the bond at a later date the person also collects interest Limited liability Owner not responsible for debts Shareholders can only lose what they invest Unlimited life Ownership can be easily transferred. Disadvantages Business owners have little say in how business runs Double taxation Corporation is taxed based on profits Shareholders must pay taxes on any Dividends or Capital Gains Franchises Sole Proprietors or Partnerships purchase the rights to a trademarked corporation McDonalds Advantages Name recognition and support of national corporation Disadvantages Uphold “chain” identity and sell only certain products What are Labor Unions? A group of workers that unite to get better pay and working conditions. Engage in Collective Bargaining What are the Two types of Unions? Craft/Trade Unions Workers who have the same skills. Ex: Plumbers, Teachers, NFL Industrial Unions Workers with different skills who make one product. Ex: Construction, Car Factories Labor Union Legislation Labor Union Relations Act 1935 Gave employees the right to join unions Fair Labor Standards Act 1938 Restricted child labor, granted minimum wage, regulated workplace safety Social Security Act 1935 Provided income to retirees and unemployment benefits Unfavorable Legislation Taft-Hartley Act 1947 Prohibited closed shops Workplaces that could only hire union members Union Criticism Minimum wage Leads to increased unemployment Hurt quality Difficult to fire union members for poor performance Labor Management Conflict Let’s say the union workers and the boss are having problems. The workers want higher wages but the boss refuses to pay. What are the steps are actions they must go through to solve their problem? At each step the problem can be solved but if it isn’t the next step is needed. 1. Collective bargaining Boss and workers try to come up with an agreement. 2. Mediation Bring in a third party to help create an agreement. 3. Arbitration Third party makes an agreement for them. 4. Strike Refuse to work. Lockout Boss refuses to let workers in building until they accept the terms. If the problem led to a strike or lockout most likely workers will lose because the boss can always get someone else to do the work. But sometimes a strike does work and the workers get what they want. Reflection Name at least one advantage and disadvantage for each of the following business types: Sole proprietorship Partnership and cooperatives Corporation Franchise What are two types of labor unions? Name at least one advantage and one disadvantage of labor unions. Activity ***Your business must be school appropriate! Your business may NOT focus on Drugs, Sex, or Alcohol*** Instructions: Using your notes and the textbook (p.480-485) Create a poster or pamphlet that describes your business. You must include the following criteria. Create a name for your business Answer the 3 questions all businesses must answer: What will you produce? How will you produce the product? (How will you make it…assembly line, cottage industry, computers, etc?) For whom will you produce it? (Who will be your target audience?) How will you use the 4 factors of production? Identify the 4 factors, give a brief definition, and how you will use each factor in your business For Labor describe a job for each type of labor: White/Blue Collar, Skilled/Unskilled Type of Business: Sole Proprietorship, Partnership, or Corporation Explain why you chose the business model. Discuss the advantages Explain the challenges you may face ahead. Discuss the disadvantages you will have Include pictures that will make your business come alive Closing? Name 1 positive and 1 negative about Labor Unions.