Grade 12 Exercise Science
advertisement

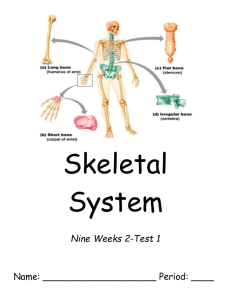
Grade 12 Exercise Science The Skeletal System Terms Anatomy ___________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Physiology ___________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Nervous system ___________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Circulatory system ___________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Human skeleton ___________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ The Human Skeleton The human skeleton is made up of _______ bones Start with over ___ at birth but they fuse together over time Longest is the femur and smallest is the stirrup bone found inside the ear Males and Females have slight differences ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ The Skeletal System Properties of the Skeletal System Extremely hard and durable Bones are composed primarily of calcium Calcium levels vary in people Low levels of calcium mean the bones can become increasingly brittle and breakable Bones are able to repair themselves Casts, splints, pins and other aids are often required for correct healing process Functions of the Skeletal System Structural Support Protection Growth centre for cells Reservoir of minerals Movement About Bone … Composed of 50% water and 50% organic and inorganic material Elements include: phosphorous, zinc, calcium, magnesium, fluorine, iron, chlorine Resists compression and tension Bound by joints (through ligaments) Muscles attach to bone (through tendons) to produce movement 5 Types of Bones Bones are classified according to their shape Long Bones ___________________________________________________ The femur is the best example of a long bone Short Bones ___________________________________________________ Carpal bones are a good example Flat Bones ___________________________________________________ Irregular Bones ___________________________________________________ Sesamoid bones Unusual bones in that they are small, flat bones wrapped within tendons that move over boney surfaces. Example patella Types of Bones Anatomy of a Long Bone Long Bone Anatomy https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q4vXr9IuPVc Cartilage _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ Cancellous bone (spongy bone) ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ Compact bone ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ Long Bone Anatomy https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q4vXr9IuPVc Medullary cavity ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ Periosteum ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ Epiphysis ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ Diaphysis ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ Structure of The Skeleton Axial Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton Structure of The Skeleton Axial Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ Tendons and Ligaments Tendons – __________________________________ Ligament – _________________________________ Types of Fractures Stress fracture – ________________________________ Simple fracture – __________________________________________ Compound fracture – _________________________________________ Comminuted fracture – _______________________________________ Simple fracture Compound fracture Comminuted fracture Epiphyseal Plates and Lines Epiphyseal plates (growth plates) __________________________ Epiphyseal line __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ Epiphyseal lines __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ Epiphyseal plate ©Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 2003. All material is copyright protected. It is illegal to copy any of this material. This material may be used only in a course of study in which Exercise Science: An Introduction to Health and Physical Education (Temertzoglou/Challen) is the required textbook. Habits and Behaviours That Help Maintain and Strengthen our Skeletal System Average person: ??? To prevent Osteoporosis: _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ Bone Formation and Bone Remodeling Bone Formation Compact bone: ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ Cancellous bone: (e.g. skull) ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ Bone Formation and Bone Remodeling Bone Remodeling ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ Most active during early years Declines after mid 30 at at rate of 5-10% every 10 years