7. economic location updated
advertisement
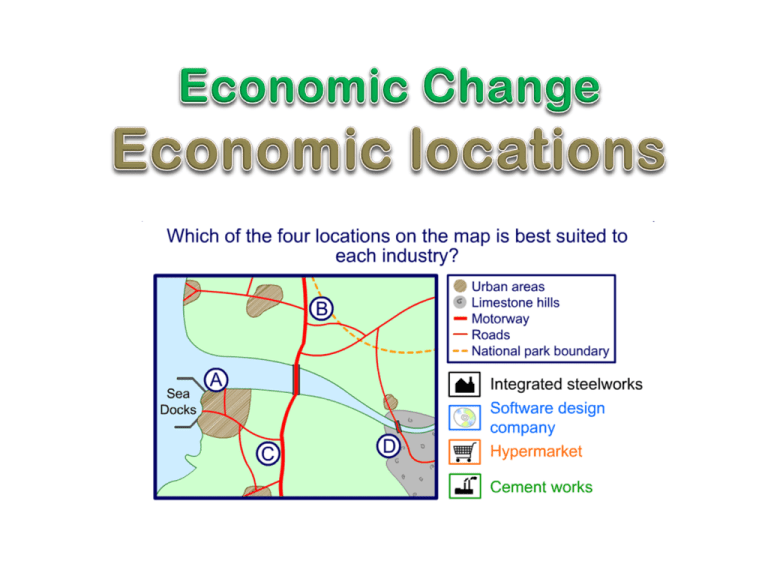
Lesson Objectives • To understand the factors affecting the location of primary, secondary and tertiary activities The location of primary industry Location factors: • Nearly every economic activity is found in a particular place for good reasons: • • • • • • Labour supply Accessibility Raw materials Distance to market Government incentives Power supply 1. Explain why each of these may be important. 2. Would certain factors be more important for different sectors of industry? Why? Use page 161 of Tomorrow’s geography for extra information Location of a primary industry – China Clay, Cornwall • • • • • • • • China clay, also called kaolin, had been mined in Cornwall for 250 years. A man called William Cookworthy had noticed the fine porcelain that had come to Europe from China and decided that he had spotted a gap in the market. He began to search for a material that resembled the kaolin used in China to make the porcelain and in 1745, at Tregonning Hill, he found it - a type of decomposed granite which was like a fine talcum powder in texture. By the mid 19th Century, 65 000 tonnes of china clay were being mined in the St Austell area every year, much of it for export. Seven thousand people were employed. The hamlet of West Polmear, a tiny place of just nine people, grew to a population of three thousand as a result of the jobs in the area. There was an environmental impact, however. Every tonne of china clay mined created five tonnes of waste, which was piled up and nicknamed the Cornish Alps. By 1910, one million tonnes of china clay was mined, 75% for export, so you can see how fast the industry had grown. In 1999, the company mining the deposits was taken over by a French company called Imerys, which has moved most of its production to Brazil where its costs are lower and its profits are higher. Most of the Cornish china clay pits are now idle and the total number of people employed is about a thousand, a fraction of what it had been. (In 1974, it had been estimated at about 6000 workers.) The former workers left unemployed would be classified as a negative social impact. The Eden Project, has transformed a 160 year old pit into a tourist attraction, packed full of exotic plants arranged in biomes to recreate their normal climate. It opened in March 2001 and had received its 10 millionth visitor by 2008. Not only did the pit provide the land and the setting, Imerys provided the sand that was dug into the soil to improve its drainage. Since its opening, the Eden Project has hosted events such as pop concerts, popular with locals and visitors alike, a positive social impact Other leisure attractions making good use of the Cornish china clay landscape are the Clay Trails, a series of bike paths established in 2005. These are also popular with dog walkers and horse riders. These improvements to the landscape would be classified as positive environmental impacts. Primary industry: Factors • Main factor: Physical factor Availability of raw materials Economic factors Market and accessibility Secondary Industry Why did Toyota locate at Burnaston, near Derby? • 1- Accessibility Excellent transport routes. On the junction of two main trunk roads. This allows easy transportation of parts and the finished product throughout the UK 2- Incentives Derbyshire County Council offered to buy a £20 million stake in the company. It also pledged to improve the transport infrastructure. 3- Room for expansion Location on the edge of the city. Greenfield site (an area on the edge of the city, which has never been developed in any way) with ample room for expansion. Large area of land: 280 hectares 4- Suppliers of component parts The area has a tradition in car manufacturing. There are many suppliers of component parts and engineering components 5- Attractive location for managerial workers Attractive village location such as Findern for managerial workers. The Peak District National Park, which is closed by, has many opportunities for leisure activities. C-Location of tertiary industry Less dependent on geographical factors. Given good transport, energy and communications, tertiary companies can locate anywhere. Location of secondary industry Example of a 6 mark question…. Explain the reasons for the location of an activity in the secondary sector. (6) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E5EbrxJkzlQ David Lloyd Gym- What 3 Human factors and 3 physical factors can you work out for the gym locating here? Tertiary Industry Case Study: Great North Leisure parkDavid Lloyd gym 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Location- get a sketch map- annotate it What’s there? Physical factors for its location (inc 2 facts) Human factors for its location (inc 2 facts) Explain the factors that affect the location of tertiary industry. Use an example in your answer. (6) The tertiary sector What is high-tech industry? High-technology industry involves a highly-skilled workforce and its products require a high proportion of research and development. High-technology industry is relatively footloose since access to raw materials is not very important. The ‘raw materials’ that are required are usually lightweight electronic components. Examples of high-tech industry rbaLuo vEnrmiorten cRshaere dna dpvlentmeoe csAces putRnietao Gvtmnoerne ciploeis Labour Environment Research and development Access Reputation Government policies Match these statements to the location factors attracting hi-tech industries Near to, and links with, a top class university Place of high-tech excellence Supply of highly qualified and adaptable labour Availability of good transport networks, raw materials, services and markets Attractive location in which to live and work National and local governments encourage investment and enterprise High-tech industry on the M4 corridor Examination question Explain how the factors affecting the location of industry can change over time. (3) Plenary • http://www.geoggers.net/geoggers/Rural_dei ndustrialisation.html • http://www.cornwallonline.co.uk/attractions/Whealmartyn/Welcome.html






