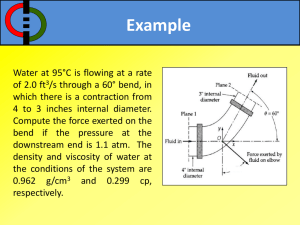
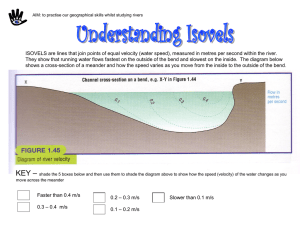
Standards Calkins Reading Workshop (Bends) Calkins Writing
advertisement

Standards Calkins Reading Workshop (Bends) Calkins Writing Workshop (Bends) Other Literacy Components 3rd Grade - August/September Reading Literary Text (RL) RL 3 Know and apply grade level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words RL 4.2 Read grade-level prose and poetry orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, expression, intonation, and phrasing on successive readings RL5 Determine meaning and develop logical interpretations by making predictions, inferring, drawing conclusions, analyzing, synthesizing, providing evidence, and investigating multiple interpretations RL 6 Summarize key details and ideas to support analysis of thematic development RL 10 Apply a range of strategies to determine and deepen the meaning of known, unknown, and multiple-meaning words, phrases, and jargon; acquire and use general academic and domain specific vocabulary RL13 Read independently and comprehend a variety of texts for the purposes of reading for enjoyment and acquitting new learning and building stamina reflect and respond to increasingly complex text over time Reading Informational Text (RI) Writing (W) W3 Write narratives to develop real or imagines experiences or events using effective techniques, well-chosen details, and well-structured event sequences W4 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing and speaking W5 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English, capitalizations, punctuation, and spelling when writing W6 Write independently, legibly, and routinely for a variety of tasks, purposes, and audiences over short and extended time frames Communication (C) C1 Interact with others to explore ideas and concepts, communicate meaning, and develop logical interpretation through collaborative conversations; build upon the ideas of others to clearly express one’s own views while respecting divers perspectives Read Aloud And Testing As A Genre 3rd Grade – August/September Building a Reading Life Crafting True Stories Word Study: Reading Bend I: Making a Reading Life Choosing Just Right Books Building Reading Stamina Tracking Reading Setting Goals for Reading Setting up Reading Partnerships Bend I: Writing Personal Narratives with Independence Visualizing Generating Ideas for Writing Storyteller’s Voice Ongoing Editing Short Vowel Versus Long Vowel Patterns (Ex: CVCe, CVVC (ai, oa, ee, ea, ay, ow, ue), and CV open syllable –y ( like cry, sky, why, try ) Bend II: Becoming a Storyteller on the Page Generating Leads Writing a Quick Draft Author’s Craft Developing Most Important Parts Paraphrasing The Reading Strategies Book by Jennifer Serravallo Stone Fox By John Reynolds Gardiner (mentor text; see p.xv for pacing) Each Kindness by Jacqueline Woodson Freckle Juice by Judy Blume Mt. Lincoln’s Way by Patricia Polacco Thank You Mr Falkner by Patricia Polacco Crickwing by Janell Cannon The Hundred Dresses by Eleanor Estes The Bee Tree by Patricia Polacco Donavan’s Word Jar by Monalisa DeGross The Stories Julian Tells by Ann Cameron The Junkyard Wonders by Patricia Palocco Every Living Thing by Cynthia Rylant Baseball in April and Other Stories by Gary Soto Bend II: Understanding the Story Asking Questions While Reading to Check for Comprehension Visualizing While Reading Thinking About Their Reading Predictions Bend III: Tackling More Challenging Using Strategies to Figure Out Hard Words Figuring Out Difficult Vocabulary Figurative Language Author’s Purpose Assessment Bend III: Writing With New Independence on a Second Piece Revising During Writing Dialogue Bend IV: Fixing Up and Fancying Up Our Best Work: Revision and Editing Revising Endings Using Editing Checklists Final “K” Sound Spelled: -ck, -ke, -k - Reading Engagement 2.8 Set a Timed Goal (p.55) 2.9 Most Desirable/Least Desirable (p.56) 2.10 “Party” Ladder (p.57) 2.12 Ask Questions to Engage with the Text (p.59) 2.14 Track Progress on a Stamina Chart (p.61) 2.18 Reading Log Rate Reflection (p.65) 2.24 Read with a Focus to Focus (p.71) Monitoring for Meaning 2.4 Keep Your Eyes and Mind in the Book (p.51) 2.6 Fixing the Fuzziness (p.53) 2.17 Visualize to Focus (p.64) 2.21 You’ve Got to “Get It” to be Engaged (p.68) Vocabulary 11.7 Picture It (p.306) 11.9 Stick to Your Story (p.308) 11.15 Context + Clues = Clarity Writing Come on, Rain! By Karen Hesse (mentor text; read during IRA time) Mr. Putter & Tabby Write the Book by Cynthia Rylant Smoky Night by Eve Bunting I’m in Charge of Celebrations I Love My Hair! By Natasha Anastasia Tarpley We Had a Picnic This Saturday Past by Diane Greenside Give Unit 1 pre-assessment before starting unit Give Unit 1 post-assessment after finishing the unit **See www.heinemann.com for assessments** Give narrative on demand before starting the unit Give same narrative on demand after completing the unit **See Writing Pathways** 1st running record See Narrative Reading Learning Progression in Reading Pathways book or www.heinemann.com Standards Calkins Reading Workshop (Bends) Calkins Writing Workshop (Bends) Other Literacy Components 3rd Grade - October Reading Literary Text (RL) Reading Informational Text (RI) RI1 Demonstrate understanding of basic features of print RI2 Demonstrate understanding of spoken words, syllables, and sounds RI3 Know and apply grade level phonics and word analysis skills when decoding words RI4 Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension RI5 Determine meaning an develop logical interpretations by making predictions, inferring, drawing conclusions, analyzing, synthesizing, providing evidence, and investigating multiple interpretations RI6 Summarize key details and ideas to support analysis of central ideas RI9 Apply a range of strategies to determine and deepen the meaning of known, unknown, and multiple meaning words, phrases, and jargon; acquire and use general academic and domain specific vocabulary RI12 Read independently and comprehend a variety of texts for the purposes of reading for enjoyment, acquiring new learning, and building stamina; reflect and respond to increasingly complex texts over time Writing (W) W2 Write informative/explanatory texts to examine and convey complex ideas and information clearly and accurately through the effective selection, organization, and analysis of content W4 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing and speaking W5 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English, capitalizations, punctuation, and spelling when writing W6 Write independently, legibly, and routinely for a variety of tasks, purposes, and audiences over short and extended time frames Communication (C) C2 Articulate ideas, claims, and perspectives in a logical sequence using information, findings, and credible evidence from sources C3 Communicate information through strategic use of multiple modalities and multimedia to enrich understanding when presenting ideas and information Reading to Learn: Grasping Main Ideas and Text Structures Bend I: Determining Importance in Expository Texts Previewing Text Summarizing Categorizing Information Main Idea and Details Text Features Bend II: Lifting the Level of Thinking about Expository Texts Reading to Learn New Information Think and Talk Back to the Text Author’s Point of View and Perspective Bend III: Synthesizing and Growing Ideas in Narrative Nonfiction Narrative Nonfiction Text Structures Narrative Nonfiction: how details fit under overarching storylines Reading Biographies Through Two Different Lenses Read Aloud And Testing As A Genre Assessment 3rd Grade - October The Art of Information Writing Word Study: Bend I: Organizing Information Various Ways of Structuring Topics and Subtopics Table of Contents and Chapters R-Influenced Vowel Patterns (ar, are, air, er, ear, eer, ir, ire, ier, or, ore, oar, ur, ure, ur-e) Bend II: Reaching to Write Well Mentor Texts to Shape Writing Transitioning From Chapter to Chapter in Informational Texts Writer’s Style Enhancing Topic Through Researching Creating Introductions Bend III: Moving Towards Publications, Moving Toward Readers Goal Setting Using Text Features Researching to Check Facts Paragraphing Bend IV: Transferring Learning From Long Projects to Short Ones Planning and Drafting Content –Specific Informational Text Self-Assessing/Revising Crafting Speeches, Articles, Brochures The Reading Strategies Book by Jennifer Serravallo - Main Idea and Details 8.1 One Text, Multiple Ideas (or Topics) (p.222) 8.3 Topic/Subtopic/Details (p.224) 8.5 Boxes and Bullets (p.226) 8.6 Survey the Text (p.227) 8.7 Paraphrase Chunks, Then Put It Together (p.228) 8.11 Add Up Facts to Determine Main Idea (p.232) 8.14 Time = Parts (p.235 Narrative NF) 8.15 Why Does the Story Matter (p.236 Narrative NF) Writing About Reading 13.10 Note Taking Helps to Understand Nonfiction (p.364) Talking Back to the Text 12.11 Keep the Line Alive (p. 338) Reading: Articles from the Expository Text Sets on www.heinemann.com Frogs! By Elizabeth Carney Frogs and Toads by Bobbie Kalman Gorillas by Lori McManus The Life Cycle of the Bobbie Kalman & Robin Johnson Make Way for Dyamonde Daniel by Nikki Grimes The Penguin, A Funny Bird by Beatrice Fontanel Penguins by Bobbie Kalman Time For Kids I Wonder Why Camels Have Humps and Other Questions About Reading by Anita Ganeri Cactus Hotel by Brenda Z. Guiberson and Megan Lloyd Writing: Dangerous Animals by Melissa Stewart Deadliest Animals: National Geographic by Melissa Stewart VIP Pass to a Pro Baseball Game Day by Clay Latimer Give Unit 2 pre-assessment before starting unit Give Unit 2 post-assessment after finishing the unit **See www.heinemann.com for assessments** Give informational on demand before starting the unit Give same informational on demand after completing the unit **See Writing Pathways** Informal running records as needed. See Informational Reading Learning Progression in Reading Pathways book or www.heinemann.com See “Retelling/Summary/Synthesis” strand of the Narrative Reading Learning Progression in Reading Pathways book or www.heinemann.com Standards Calkins Reading Workshop (Bends) Calkins Writing Workshop (Bends) 3rd Grade – November/December Reading Literary Text (RL) RL1 Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features of print RL 2 Demonstrate understanding of spoken words, syllables and sounds RL 3 Know and apply grade level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words RL 4 Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension RL5 Determine meaning and develop logical interpretations by making predictions, inferring, drawing conclusions, analyzing, synthesizing, providing evidence, and investigating multiple interpretations RL7 Analyze the relationship among ideas, themes, or topics in multiple media, formats, in visual, auditory and kinesthetic modalities RL 8 Analyze characters, setting, events, and ideas as they develop and interact within a particular context Reading Informational Text RI Writing (W) W1 Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence W4 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing and speaking W5 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English, capitalizations, punctuation, and spelling when writing W6 Write independently, legibly, and routinely for a variety of tasks, purposes, and audiences over short and extended time frames Communication (C) C1 Interact with others to explore ideas and concepts, communicate meaning, and develop logical interpretation through collaborative conversations; build upon the ideas of others to clearly express one’s own views while respecting divers perspectives Unit 3 Character Studies Bend I: Getting to Know a Character as a Friend Characters (dialogue, feelings and actions) Character Traits/Character Analysis Make Inferences About Characters Notice Patterns of a Character to Grow Theories Make Predictions About Characters Based on Theories Bend II: Following a Character’s Journey Book Clubs Begin Story Mountains/Climax How Characters Resolve Problems and Respond to Challenges Pay Attention to How Secondary Characters Play a Role in the Main Character’s Journey What Role Do Illustrations Play in the Story Analyze Author’s Craft 6.16, 7.7 Bend III: Comparing and Contrasting Characters Across Books Comparing and Contrast: Characters Character Problems and Response to Change Character Lessons 6.11, 6.14 Other Literacy Components Read Aloud And Testing As A Genre Assessment 3rd Grade – November/December Baby Literary Essay (see Curricular Calendar) Bend I: Structuring Essays Developing a Sense of Structure and Organization of Essay Writing Boot Camp: Shared Planning and Writing of an Essay Choose and Evaluate details in Support of an Idea, Cite Text Evidence Clearly and Organize their Writing into Paragraphs Bend II: Raising the Level of Baby Essays Move from Whole-Class Guided Practice to Group or Partner Work Work on a New Text to State Thesis Statements Rehearse and Flash Draft an Essay Techniques to Raise the Level of Introductions and Conclusions Create Cohesion Across the Essay Bend III: Crafting Compare or Contrast Essays Write Essays that Compare or Contrast Two Texts More Nuanced Writing – Sorting and Weighing Details, Being More Specific when Citing Evidence, Explaining that Evidence more Fully for Readers Devise Organizational Structures for Comparing or Contrasting Characters, Themes, or Other Ideas Across Two Texts Word Study: Ambiguous Vowel Sounds: (oi, oy, oo, aw, au, wa, al, ou, ow) Silent Beginning Consonants: (kn, wr, gn) The Reading Strategies Book by Jennifer Serravallo Thinking About Characters 6.1 How’s the Character Feeling? (p.166) 6.2 What’s in the Bubble? (p.167) 6.4 Feelings Change (p.169) 6.6 Back Up Ideas About Characters with Evidence (p.171) 6.12 Empathize to Understand (p.177) Reading: Opening Read Aloud: Because of Winn Dixie, Peter’s Chair by Ezra Jack Keats, and Make Way for Dyamond Daniel by Nikki Grimes (G/H/I/J) Henry and Mudge, Frog and Toad (K/L/M) Magic Tree House, Bailey School Kids, Mercy Watson series Amber Brown is not a Crayon by Paula Danziger Houndsley and Catina by James Howe Horace, Morris and Dolores by James Howe Amazing Grace by Mary Hoffman Jamaica series by Juanita Havill For a Better World by Katherine and Randy Bomer Writing Those Shoes by Maribeth Boelts Encyclopedia Brown Cracks the Case by Donald Sobol The Stories Julian Tells by Ann Cameron A Letter to Amy by Ezra Jack Keats Peter’s Chair by Ezra Jack Keats William’s Doll by Charlotte Zolotow Brave Irene by William Steig Chrysanthemum by Kevin Henkes Wilma Unlimited by Kathleen Krull Jamaica’s Find by Juanita Havill Give Unit 3 pre-assessment before starting unit Give Unit 3 post-assessment after finishing the unit **See www.heinemann.com for assessments** Give opinion on demand before starting the unit Give same opinion on demand after completing the unit **See Writing Pathways** Informal running records as needed. See Narrative Reading Learning Progression in Reading Pathways book or www.heinemann.com Standards Calkins Reading Workshop (Bends) Calkins Writing Workshop (Bends) 3rd Grade - January Reading Literary Text (RL) RI1 Demonstrate understanding o f the organization and basic features of print RI2 Demonstrate understanding of spoken words, syllables, and sounds RI3 Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words RI4 Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension RI5 Determine meaning and develop logical interpretations by making predictions, inferring, drawing conclusions, analyzing, synthesizing, providing evidence, and investigating multiple interpretations RI 6 Summarize key details and ideas to support analysis of central ideas RI8 Interpret and analyze the author’s use of words, phrases, text features, conventions, and structures, and how their relationships shape meaning and tone in print and multiple media texts RI9 Apply a range of strategies to determine and deepen the meaning of known, unknown, and multimeaning words, phrases, and jargon; acquire and use general academic and domain-specific vocabulary RI10 Analyze and provide evidence of how the author’s choice of purpose and perspective shapes content, meaning, and style RI12 Read independently and comprehend a variety of texts for the purposes of reading for enjoyment, acquitting new learning, and building stamina; reflect and respond to increasingly complex text over time Reading Informational Text (RI) Writing (W) W3g Use imagery, precise words, and sensory details to develop characters and convey experiences and events Communication (C) C3 Communicate information through strategic use of multiple modalities and multimedia to enrich understanding when presenting ideas and information C4 Critique how a speaker addressed content and uses stylistic and structural craft techniques to inform, engage, and impact audiences C5 Incorporate craft techniques to engage and impact audience and convey messages Research Clubs: Elephants, Penguins, and Frogs, Oh My! Bend I: Researching a Topic Researching to Learn About a Topic Topics and Subtopics Expert Vocabulary Asking Questions, Gathering Information, and Analyzing the Information 9.1, 9.2, 9.5, 9.6, 10.2 Bend II: A Second Cycle of Research Planning Research Voice and Fluency Text Structures (Compare and Contrast) Cause and Effect 9.3, 10.2, 10.3 Bend III: Synthesizing, Comparing, and Contrasting Patterns and Relationships Among Topics Asking Questions and Forming Theories About Topic Think of a Problem, Gather Information, and Plan for a Solution 9.18, 9.19, 11.6 Other Literacy Components Read Aloud And Testing As A Genre Assessment 3rd Grade - January Poetry Word Study: Bend I: Writers Live Writerly Lives, Writing About Things They See and About Which They Care Immersion Into Poetry Getting Inspired Powerful Poems Through Strong Emotion Adding Details Characteristics of Strong Partners Hard and Soft “c” and “g”: (center, circle, cent, cell, giant, gem, germ) Bend II: Poets Care Not Only About Content, but Also About Language and Form Mentor Texts Line Breaks Organization Metaphors and Similes Other Endings: (-tch , ch) Bend III: Poets Revise, Revise, Revise to Perfect Their Craft Storytelling to Enhance Poems Powerful Conclusions Imagery Using Alliteration and Rhyme to Create Sound Bend IV: Poets Build Anthologies and Edit Poems Before Sharing Them With the World Sorting and Categorizing on Order to Create an Anthology Editing Final “e”: (-ce, -ve, -se, -ze) Reading: See Science and Social Studies Materials The Life Cycle of an Emperor Penguin by Bobbie Kalman and Robin Johnson Penguins by Bobbie Kalman The Penguin by Beatrice Fontanel Frogs by National Geographic Hard and Soft “c” and “g” endings” (-ce, -ge, -dge,) Give Unit 4 pre-assessment before starting unit Give Unit 4 post-assessment after finishing the unit **See www.heinemann.com for assessments** Informal running records as needed. Writing: Honey I Love by Eloise Greenfield This Place I know: Poem of Comfort by Georgia Heard Baseball, Snakes, and Summer Squash by Donald Graves Hey World, Here I Am by Jean Little A Writing Kind of Day by Ralph Fletcher See Informational Reading Learning Progression in Reading Pathways book or www.heinemann.com Standards Calkins Reading Workshop (Bends) Calkins Writing Workshop (Bends) 3rd Grade - February Reading Literary Text (RL) RL1 Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features of print RL 2 Demonstrate understanding of spoken words, syllables and sounds RL 3 Know and apply grade level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words RL 4 Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension RL5 Determine meaning and develop logical interpretations by making predictions, inferring, drawing conclusions, analyzing, synthesizing, providing evidence, and investigating multiple interpretations RL7.2 Compare and contrast how an author uses characters to develop theme and plot in different texts within a series RL8 Analyze characters, setting, events, and ideas as they develop and interact within a particular context RL12 Analyze and critique how the author uses structures in print and multi- media texts to shape meaning and impact the reader Reading Informational Text (RI) Writing (W) W1 Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence W4 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing and speaking W5 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English, capitalizations, punctuation, and spelling when writing Communication (C) C1 Interact with others to explore ideas and concepts, communicate meaning, and develop logical interpretation through collaborative conversations; build upon the ideas of others to clearly express one’s own views while respecting divers perspectives C2 Articulate ideas, claims, and perspectives in a logical sequence using information, findings, and credible evidence from sources C4 Critique how a speakers addresses content and uses stylistic and structural crafty techniques to inform, engage, and impact audiences C5 Incorporate craft techniques to engage and impact audience and convey messages Solving the Mystery Before the Detective: Inference, Close Reading, Synthesis, Prediction (see If…Then…Curriculum p. 34) Bend I: Mystery Readers Read for Clues Previewing for Clues Noticing Details Using Character Traits to Solve Mysteries Bend II: Reading Across Mysteries Reading Mysteries by Same Author and Getting to Know the Characters Slowing Down and Reading Carefully (ex: Crime Scenes) Rereading and Taking Notes Using Clues to Make Inferences Thinking Across Books Bend III: Mystery Readers Learn Life Lessons from Books Lessons Learned From Characters Slowing Down When Characters Have a Strong Emotional Reaction Character Motives Other Literacy Components Read Aloud And Testing As A Genre Assessment 3rd Grade - February Changing the World: Persuasive Speeches, Petitions and Editorials Bend I: Launching Work on Persuasive Speeches Drafting a Speech Persuasive Writing About Places, Things, or Ideas Addressing a Specific Audience Editing Setting Goals To Better the Writing Bend II: Raising the Level Persuasive Collect Evidence to Support Opinions Organizing and Categorizing Evidence Providing Examples to Persuade Paragraphing Word Choice Publishing Bend III: From Persuasive Speeches to Petitions, Editorials, and Persuasive Letters Speeches, Letters and Petitions Meeting Deadlines - Making Work Plans Gathering Evidence Revision Introductions and Conclusions Goal Setting for Improving Writing Bend IV: Cause Groups Writing for a Specific Audience Preparing to Persuade Audience by Gathering Information Beforehand Revising While Drafting Editing Word Study: Contractions: (not, is, am, have, had, will, are) Plural Endings: (-s, -es,) Irregular Plural Endings: (-y + -ies and ex. child – children) Three Sounds of Past Tense: (-ed that sounds like “d,” “id”, and “t”) Reading: Cam Jansen Mysteries by David Adler The Boxcar Children series by Gertrude Chandler Warner Jigsaw Jones series by James Preller A to Z Mysteries Nate the Great series Encyclopedia Brown series Nancy Drew series by Carolyn Keene The Hardy Boys series by Franklin W Dixon Trixie Belden series by Julie Campbell Writing: Newspapers Magazines Book Reviews Movie Reviews Travel Guides Running Records As Needed See Narrative Reading Learning Progression in Reading Pathways book or www.heinemann.com Standards Calkins Reading Workshop (Bends) Calkins Writing Workshop (Bends) 3rd Grade - March Reading Literary Text (RL) RL9 Interpret and analyze the author’s use of words, phrases, and conventions, and how their relationships shape meaning and tone in print and multimedia texts RL12 Analyze and critique how the author uses structures in print and multi- media texts to shape meaning and impact the reader Reading Informational Text (RI) Writing (W) Communication (C) C5 Incorporate craft techniques to engage and impact audience and convey messages Little Things are Big: Making Meaning from Poems and Poetic Craft In Literature (see If...Then…Curriculum p. 74) Bend I – Discovering Poetry I n Poems and Prose Poetic devises Elements of poetry How poets play with words Bend II – Reading for Deeper Comprehension Identifying the “idea” of a poem Paying attention to endings of poems Identifying the characters Bend III – Looking at Life and Literature through the Lens of Poetry Looking at things differently Thinking about things differently Making connections between poetry and literature Other Literacy Components Read Aloud And Testing As A Genre Assessment 3rd Grade - March Test Preparation Word Study: Reading and Writing Testing Words: (ex: summarize, compare, contrast, infer, explain, determine, etc) Reading and Writing Testing Words: (ex: summarize, compare, contrast, infer, explain, determine, etc) Reading: Poems by: Ogden Nash, Shel Silverstein, Kenn Nesbitt, Jack Prelutsky, Langston Hughes, Naomi Shihab Nye, Robert Frost, William Wordsworth and Walt Whitman. Writing: Running Records Standards Calkins Reading Workshop (Bends) Calkins Writing Workshop (Bends) 3rd Grade - April Reading Literary Text (RL) RI8 Interpret and analyze the author’s use of words, phrases, text features, conventions, and structures, and how their relationships shape meaning and tone in print and multiple media texts Reading Informational Text (RI) Writing (W) W2 Write informative/explanatory texts to examine and convey complex ideas and information clearly accurately through the effective selection, organization, and analysis content W4 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing and speaking W5 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English, capitalizations, punctuation, and spelling when writing W6 Write independently, legibly, and routinely for a variety of tasks, purposes, and audiences over short and extended time frames Communication (C) C1 Interact with others to explore ideas and concepts, communicate meaning, and develop logical interpretation through collaborative conversations; build upon the ideas of others to clearly express one’s own views while respecting divers perspectives C3 Communicate information through strategic use of multiple modalities and multimedia to enrich understanding when presenting ideas and information Read Aloud And Testing As A Genre Assessment 3rd Grade - April Biography Book Clubs (see If… Then…Curriculum p. 54) Information Writing: Reading, Research, and Writing in the Content Areas Bend I: Biography Readers Use All They Know about Reading Stories Approach to Reading Different Types of Nonfiction Character Analysis Mapping out Story Arcs Reading to Learn New Information Bend I: Writing to Develop Expertise and Grow Ideas Use note taking, annotated time lines for recording and reflecting on ideas Bend II: Biography Readers Use All They Know about Reading Informational Texts Reading for Information Discerning Importance of Facts Organization Bend III: Using Mentor Texts to Help Writers Revise Chapters They’ve Written and to Lift the Level of Upcoming Chapters Trying Out New Techniques Learned From Mentor Texts Elaboration Through the Use of Mentor Texts Citing Sources Bend III: Biography Readers Not Only Follow a Life Story, They Also Grow Ideas Reading a Narrative Without A Traditional Character Forming An Overall Idea about Information Looking for the Bigger Message Other Literacy Components Bend II: Planning a Table of Contents and Writing Chapters Table of Contents Chapters Bend IV: Editing and Publishing to Get Ready to Teach Others Editing and Publishing Word Study: Homophones: (ex: mane, main, sale, sail, waste, waist, etc) ; Homographs (ex: present (noun), present (verb), rebel (noun), rebel (verb), etc.) “I” before “e” except after “c” (weird, deceive, sleigh, shield, ceiling, relieve, etc) Prefixes: (re-, un-, pre-, ex-, mis-) Reading: Ruby Bridges by Robert Coles Who Was Jackie Robinson by Gail Herman Martin Luther King Jr’s speech Books from Categories like: figures in American History, Athletes, Figures in Science and Technology, Artists, Explorers, and Activists Writing: Use Social Science or Science Materials Running Records See Narrative and Informational Reading Learning Progression in Reading Pathways book or www.heinemann.com Standards Calkins Reading Workshop (Bends) Calkins Writing Workshop (Bends) 3rd Grade - May/June Reading Literary Text (RL) RL5 Determine meaning and develop logical interpretations by making predictions, inferring, drawing conclusions, analyzing, synthesizing, providing evidence, and investigating multiple interpretations RL 6 Summarize key details and ideas to support analysis of thematic development RL8 Analyze characters, setting, events, and ideas as they develop and interact within a particular context Reading Informational Text (RI) Writing (W) W3 Write narratives to develop real or imagines experiences or events using effective techniques, well-chosen details, and well-structured event sequences W4 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing and speaking W5 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English, capitalizations, punctuation, and spelling when writing W6 Write independently, legibly, and routinely for a variety of tasks, purposes, and audiences over short and extended time frames Communication (C) C1 Interact with others to explore ideas and concepts, communicate meaning, and develop logical interpretations through collaborative conversations; build upon the ideas of others to clearly express one’s own views while respecting diverse perspectives Social Issues Book Clubs: Applying Analytical Lenses Across Literature and Informational Texts (see If…Then…Curriculum p.94) Bend I: Reading between the Lines to Interpret Issues in Texts Critical Reading to Understand World Issues Understanding Issues Through Character ‘s Actions Understanding Issues Through Important Parts Author’s Word Choice How characters deal with problems Bend II: Analyzing the Way Different Authors Address and Craft Similar Social Issues in Both Literature and Current Events Asking Questions to Analyzing the Hidden Issues Challenging a Text by Examining beliefs Exploring Imbalances in Power in World Problems Bend III: Bringing our Reading Lenses to Our World – And Making Our Thinking More Complex Reflecting on Your Own Thinking Proposing Solutions to Issues Taking on the Role as Activists Other Literacy Components Read Aloud And Testing As A Genre Resources 3rd Grade – May/June Once Upon a Time: Adapting and Writing Fairy Tales Bend I: Writing in the Footsteps of the Classics Study Versions of Fairy Tales When Changes Are Made to Fairy Tales it is Understood Changes Affect Other Elements of the Story Story Telling and Acting Out Stories Rehearsing Story Telling Morals Bend II: Follow the Path: Adapting Fairy Tales with Independence Planning Stories With Alone and With a Partner Refrains Dialogue and Actions Smooth Sentences Bend III: Blazing Trails: Writing Original Fairy Tales Characters, Motivations Troubles, and Resolutions Objects Bring Importance to Characters Writing Descriptive Sentences Adding Element of Magic Revision Editing Word Study Prefixes: (non-, uni-, bi-, tri-, dis-) Suffixes: (-ly, -ful, -less, -ness) Reading: Fly Away Home The Hundred Dresses Time for Kids Scholastic News Highlights New Moon Writing: Little Red Riding Hood Three Little Pigs Cinderella Three Billy Goats Gruff The Emperor’s New Clothes Prince Cinders by Babette Cole Running Records See Narrative Reading Learning Progression in Reading Pathways book or www.heinemann.com