The Integumentary System
advertisement

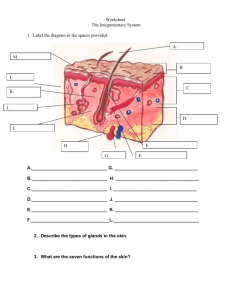
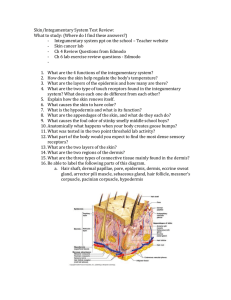
The Integumentary System What is the Integumentary System? It protects the body from injury and pathogens It regulates body temperature It eliminates waste through perspiration It contains nerve endings for cold, heat, pain, pressure, and vitamins It stores fat and vitamins What is it? THE SKIN! (The largest organ in your body) Don’t forget this system also includes your hair and nails! Integumentary System Integument means ‘covering’ Integumentary system covers body (skin) Review Homeostasis Definition: The tendency toward a relatively stable equilibrium Homeostasis and the Integumentary System Normal body temperature Change in temperature Normal body temperature How does the integumentary system respond to changes? Increase in body temp. (hotter) Vessels in skin will dilate (get bigger) Sweat Decrease in body temp. (colder) Vessels in skin will constrict (get smaller) Structure Epidermis Most superficial layer of skin made up of many layers of tightly packed cells Form an impermeable layer Acts as a barrier against bacteria and viruses Dermis Deep layer of skin Most complex layer Location of sweat glands, hair follicles, nerve fibers, and many blood vessels* Hypodermis Largely made of adipose tissue (fat) This layer also contains blood vessels and nerves Homeostatic Imbalances of Skin Athletes foot – caused by a fungus, involves toes and soles of feet Boils – caused by bacteria entering hair follicles or sebaceous glands Eczema – red itchy areas of surface of skin Homeostatic Imbalances of Skin Skin cancer Pressure sores – caused by poor circulation resulting from pressure that destroys skin and creates ulcer Homeostatic Imbalances of Skin Shingles – skin eruption due to viral infection Gangrene – necrosis of tissue cells due to blockage of blood supply to an area, or blockage from disease or direct injury Dermatitis – inflammation of skin (type of eczema) Homeostatic Imbalances of Skin Tears – due to fragile skin Warts – viral infection of skin Burns – first, second, or third degree, depending on amount of skin tissue destroyed Bruising – due to fragile skin and/or effects of medications Observations of the Integumentary System to Report Breaks Rash Complaint of itching Black and blue areas Redness Ulcers, sores, or drainage