Journal entry for oversubscription of shares
advertisement

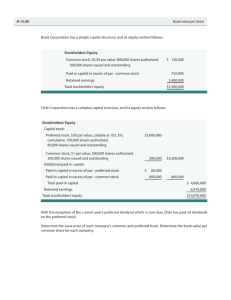
ACCOUNTING FOR STOCK ISSUE Let’s first review the rules of debits and credits by working with the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders’ Equity OR CAPITAL). Assets are increased with debits and decreased with credits. Liabilities are increased with credits and decreased with debits. Stockholders’ Equity consists of several accounts: Common Stock, Retained Earnings, and Revenues all increase Stockholders’ Equity and are increased with credits. Expenses and Dividends are overall decreases to Stockholders’ Equity and are increased with debits. Account Increase Decrease Common Stock Cr Dr Retained Earnings Cr Dr Revenues Cr Dr Expenses Dr Cr Dividends Dr Cr Journal entry for applicants offer for shares issued at par: Debit- Bank Credit- Ordinary share applicant Journal entry for company’s acceptance of applicants offer for shares issued at par: Debit- Ordinary share applicant Credit- Ordinary /preference share capital Journal entry for applicants offer for shares issued at premium: Debit- Bank Credit- Ordinary/preference share applicant Journal entry for company’s acceptance of applicants offer for shares issued at premium: Debit- Ordinary/preference share applicant (nominal value) Credit- Ordinary/preference share capital Debit: Ordinary share applicant (share premium) Credit: share premium Journal entry for oversubscription of shares: Debit- Bank Credit- Ordinary share applicant Debit: Ordinary share applicant (refund) Credit: Bank Debit- Ordinary share applicant (nominal value) share capital Credit- Ordinary/preference Journal entry for issue of shares payable by installments: Application: Debit: Bank Credit: Application and allotment account Debit: Application and allotment account (nominal at installment Credit: Share capital account Refund of application: Debit: Application and allotment (installment rate) application Credit: Bank-refund of Allotment: Debit: Bank (less excess application monies) account Credit: Application and allotment 1st call: Debit: Bank (installment rate) Credit: First call Debit: First call Credit: Share capital account 2nd call: Debit: Bank (installment rate) Credit: Second call Debit: Second call Credit: Share capital account Question solution: Shark School Supply Corporation was organized in 2011. It was authorized to issue 200,000 shares of no-par common stock with a states value of $5 per share, and 40,000 shares of $100 par value, 6% noncumulative preferred stock. On March 1, the company issued 60,000 shares of its common stock for $15 per share and 8,000 shares of its preferred stock for $100 per share. 1. Record the issuance of the stock in T accounts Notes: Issuance of shares with no par value is recorded by: o Debit cash and credit common stock or preferred stock. When par value shares are issued exactly at par: Cash is debited and common stock or preferred stock account is credited. When the issuance of stock is above par, the entry is: o Debit cash account for the total cash received o common stock or preferred stock is credited for the par value * number shares issued o additional paid-in capital account is credited for the excess of cash received (over the par value * number of shares issued) Issuance of shares below par, the entry is: Debit cash for the actual amount received Credit common stock or preferred stock is for the total par value Debit discount on capital for the excess of total par value over cash received o 2. Prepare the stockholders equity section of Shark School Supply Corporations balance sheet as it would appear immediately after the company issued the common and preferred stock Notes: Common stock, Preferred stock, additional paid‐in‐capital, retained earnings, and treasury stock are all reported on the balance sheet in the stockholders' equity section These items are listed and totaled to give total stockholder’s equity in the balance sheet - stockholders equity section. See sample below: