EOC review ppt
advertisement

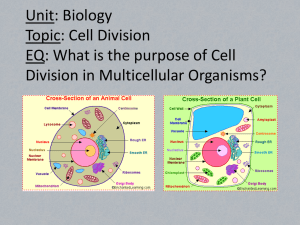
Biology E.O.C. Review Brinkman and Shepherd Men in Science Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1632 - 1723) Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1632 1723) was a Dutch tradesman and scientist, best known for his work on the development and improvement of the microscope. Robert Hooke- Discovered cells. In 1665, the English physicist Robert Hooke looked at a sliver of cork through a microscope lens and noticed some "pores" or "cells" in it. Gregor Mendel Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk who discovered the basic principles of heredity through experiments in his garden. Using Pea Plants. Francesco Redi – Disproving the Theory of Spontaneous Generation The Francesco Redi Experiment Francesco Redi was able to disprove the theory that maggots could be spontaneously generated from meat using a controlled experiment. Louis Pasteur (1822-1895) He debunked the widely accepted myth of spontaneous generation. Watson and Crick discover chemical structure of DNA determined that the structure of DNA was a double-helix polymer, or a spiral of two DNA strands Early Concepts of Evolution: Jean Baptiste Lamarck Lamarck believed that the long necks of giraffes evolved as generations of giraffes reached for ever higher leaves. Charles Darwin- Sailed to the Galapagos on the H.M.S. Beagle Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection. Survival of the Fittest. Wrote the book, “Origin of Species.” Carl Linnaeus- famous for his work in Taxonomy Carl Linnaeus is famous for his work in Taxonomy, the science of identifying, naming and classifying organisms (plants, animals, bacteria, fungi, etc.). Alexander Fleming Biologist, Scientist (1881–1955) Discovery and Development of Penicillin. First Anti-biotic. ECOLOGY REVIEW The study of the environment. Biomass Pyramid- Only 10% of energy goes to next feeding (trophic) level. Producers (Autotrophs) are base of the pyramid. Herbivores- Eats Plants. Omnivores- Eats both Plants and Animals. Carnivores- Eats Meats. DetrivoresDecomposers. Environmental Factors Biotic Factors- Living factors in the environment. Deer Humans Trees Plants Fungi Bacteria Abiotic Factors- Nonliving factors in the environment. Rocks Soil Temperature Water Wind pH Energy Flow in an Ecosystem Food Chain- Direct Feeding Relationship. Food WebInterconnected Food Chain. Biomes Population Growth- Carrying capacity is the maximum # of organisms an environment can hold. Ecological Succession- Primary (starts with no life) and Secondary (life existed, then disappeared and other organisms took over) Cells- The basic building block of all living organisms. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cell Has no Nucleus Has Nucleus No Membrane Bound Organelles Membrane Bound Organelles Has Capsule Bacterial Cell (Prokaryotic Cell) cell does not have Nucleus Kingdom Archaebacteria- Ancient Bacteria Examples Thermophiles, Halophiles Kingdom Eubacteria- New Bacteria Examples Gonorrhea, MRSA, STAPH, E. COLI Viruses- Non-Living Membrane Bound Organelles Cell membrane- Gate Keeper of cell Cytoskeleton- Microtubules and Microfilaments strength of cell Nucleus- Control Center Lysosomes- Garbage Truck of cell Endoplasmic ReticulumManufacturing Department Centrioles- Pulls apart chromosomes Rough Endoplasmic Reticulumproduces proteins Vacuole- Warehouse Chloroplast- Contains Chlorophyll for photosynthesis Golgi- Packaging Department Ribosome- Proteins Mitochondria- Battery or Powerhouse cell (ATP) Cell Transport Across Cell Membrane, Maintaining Homeostasis (constant environment) Diffusion- requires No Energy High to low concentration Osmosis- Diffusion of Water Facilitated- Helping across membrane Active TransportRequires Energy Na+ and K+ pump Cellular Respiration (Aerobic= Oxygen) C6 H12 O6 + O2 --- CO2 + H2O (Reactants) (Products) 1 Glucose molecule yields 36-38 (ATP) Glycolysis KREBS (Breaking Down of Sugars) = 2 ATP cycle = 2 ATP Electron Transport Chain (E.T.C.)= 32-34 ATP Anaerobic Respiration = (NO Oxygen Present) Fermentation- end products sugars form Alcohol or Lactic Acid Photosynthesis CO2 + H2O -- C6 H12 O6 + O2 (Reactants) (Products) Light Dependent- Splitting Water Molecules, Oxygen Released ATP and NADPH must be produced Light In-Dependent CALVIN CYCLE- Take in CO2 to make Glucose (C6 H12 O6) * HAPPENS in the CHLOROPLASTS Interdependence of Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis (Circle of Life) Mitosis- Division of All Body Cells (except Sperm and Egg) 46 chromosomes to 46 chromosomes (EXACT COPIES!!!) Meiosis- Cell Division of SPERM and EGG only! 46 Chromosomes in Humans to 23 Chromosomes Cuts number of chromosomes in HALF! Compare Mitosis VS. Meiosis DNA (Deoxyribosenucleic Acid) Contains Genetic Information DNA Replication- Making a new copy of DNA (MITOSIS) EXACT COPY! PROTEIN SYNTHESIS TRANSCRIPTION WHERE? TRANSLATION- NUCLEUS WHERE? Ribososmes WHAT? mRNA forms WHAT? Forms Proteins CODONS (3 bases CODE for 1 Amino Acid) building blocks of proteins—polypeptides (chains of many Amino Acids!!) Translation of genetic information mRNA tRNA rRNA DNA mutations- Insertion, Deletion, Substitution (for any unknown reasons) Gregor Mendel Law of SegregationSeparate Characteristics Law of Independent Assortment- random separation of chromosome pairs Predicting genetic outcomes using a PUNNETT SQUARE MONOHYBRID- crossing of 1 genetic trait HOMOZYGOUS DOMINANT- 2 of the same traits (GG) HOMOZYGOUS RECESSIVE- 2 of recessive traits (gg) HETEROZYGOUS- 1 of each trait Genetic Allele (Gene Trait) GENOTYPE- The letters of the genes PHENOTYPE- Physical appearance (color) DIHYBRID CROSS- The crossing of 2 genetic traits 9:3:3:1 Incomplete Dominance- Co-Dominance SEX-LINKED: on the X Chromosome only MALE= XY FEMALE= XX Sex-Linked Pedigree Chart BioChemistry and Organic Molecules Atoms- The smallest unit of matter Protons- Positive Charged Particle Neutrons- Particle with NO charge Electron- Particle with Negative Charge Nucleus- Contains Protons and Neutrons Atom Characteristics Atomic Number= # of Protons in Element (Also # of Electrons, they have to be the same) Atomic Mass= # of Protons and Neutrons in Nucleus Element Symbol= The abbreviation of Element Name Types of Bonds- the way atoms attach to form molecules Ionic Bond- Transfer of Electrons Covalent Bond- Sharing of Electrons Polar Covalent- Uneven Sharing of Electrons (WATER MOLECULE) Reactants and Products Reactants Products 4 Organic Compounds of Living Organisms Carbohydrates- Glucose, C6H12O6, Sugar Saccaharide (sugar) Mono, Di, and Poly Made of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen 4 Organic Compounds of Living Organisms Protein- Amino Acids are building blocks or Monomers of Proteins Peptide bonds- Bonding of Proteins 4 Organic Compounds of Living Organisms Lipids Examples (Butter, Wax, Steroids) Long Fats Chain of Carbons Saturated and Unsaturated Hydrophobic: Fears Water 4 Organic Compounds of Living Organisms Nucleic Acids DNA and RNA Nucleotides Phosphate, Sugar, and Nitrogen Base Enzymes- Specialized Proteins to Start a Reaction Ph Scale measures Acids and Bases Acids- Hydronium Ions # of H+ Ions Neutral- Equal # of H+ and OH- Ions Alkalines (BASE)- Hydroxide Ions # of OH- Ions Buffers- Neutralizes Hydroxide and Hydronium Ions Kingdom Plantae Gymnosperms Naked Seeds Examples (Pine trees, Christmas trees, and evergreen trees) Angiosperms Flowering Plants Non Vascular Plants vs. Vascular Plants Non Vascular Plants needs to absorb water Vascular Plants- Has system that allows water and nutrients to flow Will not grow tall (mosses) XYLEM- Transports H20 PHLOEM- Transports Sugars Allows trees to grow tall Reproductive Parts of a Flower