The Silk Road - Oakwood City Schools

The Silk Road
- What is it? Why is it important?
The Silk Road
The Silk Road lasted for 1200 years.
From the Roman Empire until Medieval
Europe.
There were three phases where it was traveled more than other times.
Han Dynasty (2 nd Century B.C.E. – 2 nd
Century C.E.)
Tang Dynasty (7 th – 10 th Century C.E.)
Yuan Dynasty (12 th – 14 th Century C.E.)
Marco Polo visits China
The Silk Road
The Silk Road was not actually a road. It was not paved. It was not even a single route.
The Silk Road was a name given to a series of interconnected trade routes that led across
China to Rome. It was a 4000-mile trip. At one end was China. At the other end was
Rome.
After the Silk Road the “East” and
“West” become Interdependent
Each had something the other wanted.
Rome had gold and silver and precious gems.
China had silk and spices and
ivory.
Ideas also traveled along the Silk
Road, ideas that affected everyone.
The spreading of goods and ideas between cultures is known as cultural diffusion.
Exchange of Goods
CARPETS
OUD ITEMS TRADED ALONG THE
SILK ROAD
BACTRIAN
CAMELS
METAL
WORK
GLASS
PORCELAIN
JADE
SILK
SPICES
1. What do you see?
2. How can we compare this to the trade of today?
3. Why was this important to global history?
WHAT WAS LIFE LIKE
TRAVELING ON THE SILK
ROAD?
What do you see?
What is this?
The Silk Road
Over the centuries, the Silk Road developed a civilization of its own.
Where possible, the Silk Road became lined with huge Buddhist temples, Islamic mosques and booming cities where much cultural diffusion.
It became far easier to travel the road. The journey became safer during the high trade eras.
But it was never easy. There were still vast stretches of deserts and mountains to cross, with no city or water in sight.
Turn, talk, and answer:
0 Do you think that cultural diffusion benefits civilizations? Why or why not?
Byzantine
Empire
Ottoman
Empire
The Asian
Empires we will study next.
Mongol
Empire
China
Empire
Mughal
Empire
Dangers of the Silk Road
It was incredibly dangerous to travel along the Silk Road.
You faced desolate white-hot sand dunes in the desert, forbidding mountains, brutal winds, and poisonous snakes.
There was one nice section, called the Gansu Corridor, a relatively fertile strip that ran along the base of one of the mountains.
To reach this strip, you had to cross the desert or the mountains.
And of course, there were always bandits and pirates.
Even the traders did not make the whole trip.
They worked in relays. Each trader would go a certain distance, exchange their goods for other goods, and hopefully return. The next would move along the road, trade, and hopefully return.
There were three main routes, and all were dangerous.
Northern Route – Westward to Black Sea
Central Route – Westward to Persia, Mediterranean Sea, Rome
Southern Route – Westward to Iran, India
: Even though there were many physical obstacles, trade continued.
Taklimakan Desert
Himalayan Mountains
Pamir Mountains
Kunlun Mountain Painting
Taklamakan Desert:
Western China
“ The Desert of Death ”
The Silk Roads avoided the Taklamakan Desert and passed through the oasis towns on its outskirts
Making Silk
0 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v
=f1RTqAWKenM&safe=active
Hear the story of a Silk Road Merchant
MERCHANT - a person whose job is to buy, sell & trade goods. (salesman or businessman)
Prepare to be a Silk Road Trader
Glassware
Spic es
Carpet
Go ld
Silk
Debriefing
What aspects of the activity were the most challenging? Why?
Would you have wanted to be a trader along the Silk Road? Why or why not?
Make a connection from the class to the history… fill in the T-chart in your packet with your seatmates.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Center table (Kashgar) was most crowded
Piece of paper with drawing on it
Farthest east room was
Duoyang
Couldn’t walk further west than Antioch
Crawling on floor
Climbing over desks
Closing eyes
One of the trade goods you got
Most people didn’t make it to all five trading spots
Now let’s discuss as a class
5.
6.
7.
8.
1.
2.
3.
4.
9.
Center table (Kashgar) was most crowded
Pictures on the papers
Farthest east room was
Duhyuang
Couldn’t walk further west than Antioch
Crawling on floor
Climbing over desks
Closing eyes
One of the trade goods you got
Most people didn’t make it to all five trading spots
What did you learn so far about the Silk Road
On the Post It:
1.
Grade yourself on your listening in class.
2.
3.
Did you finish all homework. Yes or No.
Evaluate yourself on your understanding of the homwork.
4.
5.
6.
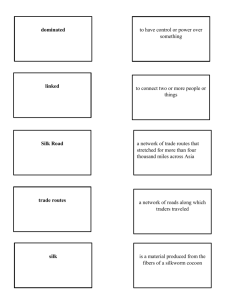
Define Silk Road including where it started and ended.
What are four goods traded?
What other than goods were spread and what is that called?
Cultural Exchange and Silk Road
0 Silk Road created cultural diffusion in which goods, ideas, technology and knowledge spread between cultures
0 China and Rome not only received new products but learned how to make them for themselves
0 By 500 CE the Chinese understood the technology Roman glassmaking.
0 Around the same time, Rome learned how to produce silk
Changes to China
1.
2.
3.
In addition to learning to make glassware, gardening and agriculture changed.
China imported many new foods such as grapes, cucumbers, figs, pomegranates, walnuts, chives, sesame
Near China, draw and label two symbols for two foods or products that China learned about as a result of trade on Silk Road.
1.
2.
3.
Changes to the
West (especially Rome)
In addition to learning to make silk, there were diet, gardening and agricultural changes.
Rome and western people imported oranges, peaches, pears and flowers like roses, mums, peonies and more
Near Rome, draw and label two symbols for two foods or products that Rome learned about as a result of trade on Silk Road.
Buddhism spreads from India along Silk
Road
Buddhism had its beginnings in India.
Because the Silk Road passed through India, and
India was in the middle, many people learned of
Buddhism
Buddhism was introduced in China in 1 st century
Some Chinese Buddhists would travel the Silk Road just to get to India to get sacred texts on the religion.
Buddhism is now a world religion
0 Near India, draw and label a symbol for
Buddhism. Then draw and arrow that shows how
Buddhism spread from India to China.
0 Then answer the two thought questions below the map.
Effects of Trade
What other effects might there be to trade other than just the exchange of goods and the chance to get rich?
Silk Road Today – 2009 Visit
0 http://www.cbsnews.com/video/watch/?id=564764
4n
Now, how would you do on a practice quiz over the Silk
Road?
Look at the target questions on the Unit
Target Guide I’m about to give you.
Answer the Silk Road target questions with your Asian Empires partner.