MSE 351
advertisement
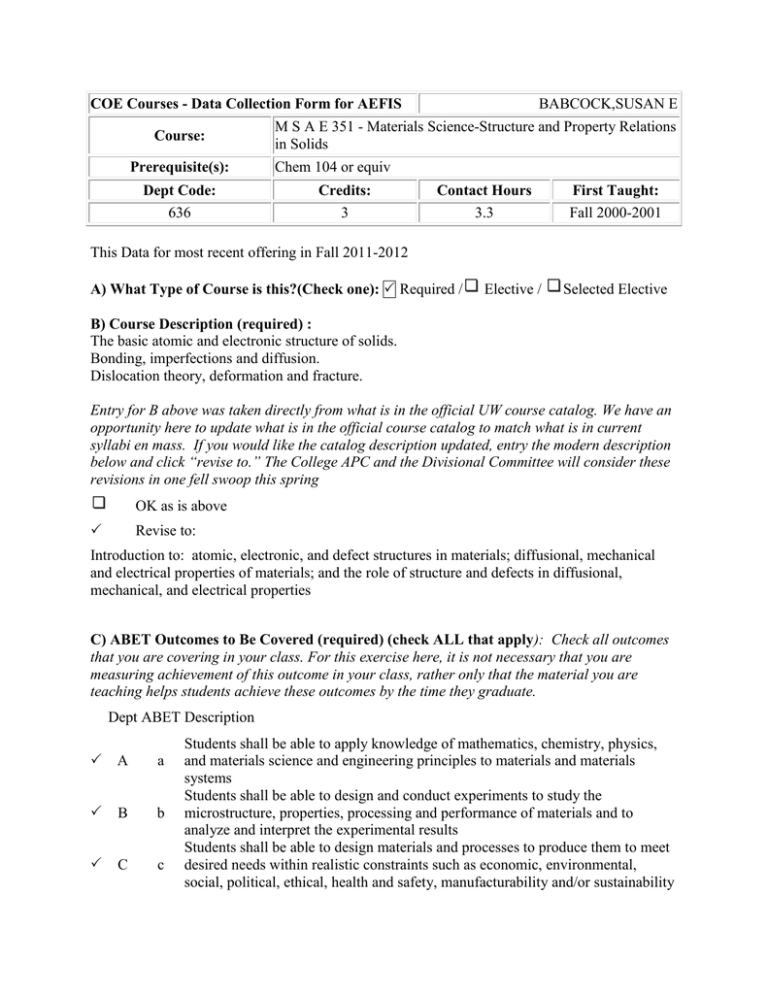
BABCOCK,SUSAN E COE Courses - Data Collection Form for AEFIS Course: Prerequisite(s): Dept Code: 636 M S A E 351 - Materials Science-Structure and Property Relations in Solids Chem 104 or equiv Credits: 3 Contact Hours 3.3 First Taught: Fall 2000-2001 This Data for most recent offering in Fall 2011-2012 A) What Type of Course is this?(Check one): Required / Elective / Selected Elective B) Course Description (required) : The basic atomic and electronic structure of solids. Bonding, imperfections and diffusion. Dislocation theory, deformation and fracture. Entry for B above was taken directly from what is in the official UW course catalog. We have an opportunity here to update what is in the official course catalog to match what is in current syllabi en mass. If you would like the catalog description updated, entry the modern description below and click “revise to.” The College APC and the Divisional Committee will consider these revisions in one fell swoop this spring OK as is above Revise to: Introduction to: atomic, electronic, and defect structures in materials; diffusional, mechanical and electrical properties of materials; and the role of structure and defects in diffusional, mechanical, and electrical properties C) ABET Outcomes to Be Covered (required) (check ALL that apply): Check all outcomes that you are covering in your class. For this exercise here, it is not necessary that you are measuring achievement of this outcome in your class, rather only that the material you are teaching helps students achieve these outcomes by the time they graduate. Dept ABET Description A a B b C c Students shall be able to apply knowledge of mathematics, chemistry, physics, and materials science and engineering principles to materials and materials systems Students shall be able to design and conduct experiments to study the microstructure, properties, processing and performance of materials and to analyze and interpret the experimental results Students shall be able to design materials and processes to produce them to meet desired needs within realistic constraints such as economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety, manufacturability and/or sustainability D d E e F f G g H h I i J j K k Students shall be able to work in multi-disciplinary teams and provide leadership on materials related problems that arise in multi-disciplinary work Students shall be able to identify materials-related problems and formulate plans to solve such problems Students shall have an understanding of the professional and ethical responsibility Students shall be able to communicate materials concepts effectively through written reports, oral presentations, and discussion Students shall have the broad education necessary to understand the impact of materials science and engineering solutions in a global, economic, environmental, and societal context Students shall have the materials science and engineering foundation needed to succeed in materials science and engineering graduate programs, to pursue other forms of continuing education in materials science and engineering, and to engage in life-long learning of materials science and engineering Students shall have an awareness of contemporary and cultural issues Students shall be able to use the techniques, skills, and modern materials science and engineering tools necessary to practice materials science and engineering as a professional D) Default Specific Course Outcomes (required): These are things in addition to A-K above that would appear in your syllabus on opening day as the things you want the students to learn, for example, for MSE 360: hands-on skills in quantitative metallography. You might list three or four and they might look like technical in nature and should be consistent with the course description. Fluency in the materials disciplinary vocabulary used to describe crystal structure, microstructure, structure of amorphous materials, phase diagrams, and mechanical, electrical, and diffusional properties Fluency and breadth in foundational tools of materials science and engineering as a base for subsequent courses ( I took this off a slide from the first day of class) E) Textbook (required): Give title, author last name(s), edition Callister, W.D. and D.G. Rethwisch, Jr., Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering: An Integrated Approach, New York, Wiley and Sons, 2008 F) Supplemental Material (optional): for example lecture slides available on eCOW2 course home page; lectures available on UW media site for MSE 351; or Captured lectures available to stucents on CoE Mediasite Lecture slides available to students on eCOW2 Course Homepage G) Brief Topics to be covered in Addition to B) and any Additional Information (required): for example, field trip to local manufacturing plant is required. Crystallography and Crystal Structure Phase Diagrams Point Defects Diffusional Mechanisms and Properties Mechanical Properties Dislocation Characteristics and Motion Electrical Structure-Property Relationships