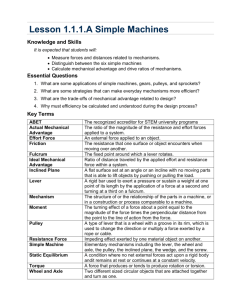
Simple Machines
EQ: How do simple machines make work easier?
Machines make doing work easier.
But they do not decrease the work that you do.
Instead, they change the way you do work.
In general you trade more force for less distance or less force for more distance
Changes the input force to greater output force (changes force)
Allows you to exert your input force over a short distance (changes distance)
Changes the direction of your exerted force (changes direction of the force)
INPUT FORCE
Force you exert on a machine
Your push or pull
The input force moves a machine a distance
Using a shovel to lift dirt
Input force: Your pull on the handle of the shovel
OUTPUT FORCE
Force the machine exerts on an object
The machine’s push or pull
The work the machine does by moving an object over a distance
The shovel “blade” moving the dirt
Where is the input force?
Where is the output force?
In some machines, the output force is greater than the input force.
Less force, more distance
Examples:
Ramps
Stairs
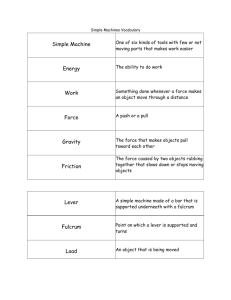
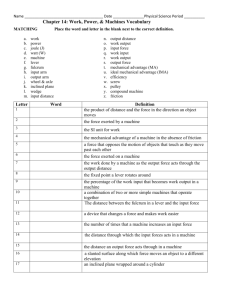
Simple Machines:
Inclined plane
In some machines, the output force is less than the input force.
More force, less distance
Examples:
Riding a bike in high gear
Simple Machines:
Wheel and axle
Some machines change neither force nor distance.
Output force equals input force
Same force, same distance, direction changes
Examples:
Weight machine
Knives
Simple Machines:
Pulley
Wedges
Screws
A machine’s mechanical advantage is a number that tells how a machine’s output force compares to the input force.
Mechanical advantage tells us how a machine changes force.
Mechanical Advantage =
Output force/Input force
Increasing Force
When the output force is greater than the input force.
Increasing Distance Changing Direction
When distance is increased, the output force is less than the input force.
The input force will always equal the output force
Can opener:
Walking up a ramp
Input force = 10 N
Input force= 20 N
Output force = 30 N
Output force = 10 N
30N/10 N = 3 N
MA = 3N 10N/20N = 0.5 N
MA= 0.5 N
You tripled your force!
Output force is less than input force, but it’s over a longer distance
Machines make work easier.
However, most machines are affected by the frictional forces
In every machine, some work is wasted overcoming friction.
The less friction there is the more efficient the machine will be.
Many people think of machines as complicated devices such as elevators, cars or computers.
• Complex machines
But some machines are as simple as a hammer, a shovel or a ramp.
• Simple Machines
A simple machine does work with only one movement.
There are six simple machines:
Pulleys
Levers
Wedges
Screws
Wheel and Axles
Inclined Planes
Please Leave When
She Walks In
An inclined plane is a sloped surface
Ramps, stairs, hills
Less force is needed to move an object from one height to another using an inclined plane than is needed to lift the object.
More distance is required
As the IP becomes longer, less force is needed to move the object
An inclined plane that moves is called a wedge.
It can have two or more sloping sides
They change the direction of the force being exerted to do work
Examples: knives, axes, doorstops, teeth
A screw is an inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder or post.
Screws change the direction of the force being applied.
Examples: screws, bottle tops, bolts, jar lids
A lever is a plank that pivots or rotates about a point
Changes force
The point at which a lever pivots is called the fulcrum
There are 3 classes of levers that are determined by the placement of the fulcrum, effort (input force) and resistance (output force)
Changes force
A first class lever looks like a see-saw with the fulcrum in the middle and the effort and resistance,
(load) on either side.
Examples: see-saw, scissors, pliers
A second class lever has the fulcrum at one end, followed by the load and effort in that order.
2ELF
Examples: wheelbarrow,
A third class lever has its fulcrum at one end, followed by the effort and load.
3FEL
Examples: baseball bat, golf club, fishing pole
A wheel and axle is several levers joined together to form a circular pattern .
Changes distance
To be considered a wheel and axle, the wheel must turn the axle .
If the wheel spins on an axle and does not turn it, it is simply a fulcrum in a lever.
Examples : spigot for a hose, ferris wheel, doorknob
A pulley is a grooved wheel with a rope or chain wrapped around it.
Pulleys change the direction of the force needed to move an object.
Pulleys can be fixed
( flagpole, window blind )
Or they can be moveable
(construction crane)
Dr. Machinellator, an evil dictator plans to take over the world. His nefarious goals include eliminating all but one simple machine from the Earth. As an expert in simple machines, you know that simple machines make work easier by changing the force, distance or direction of work being done. You even have a simple machine in mind that you consider the most important.
Using your evidence from your machines notes and your debate, recommend which simple machine should survive
The Machinellation.
Be sure to explain and give evidence as to how this machine makes work easier (changing force, distance, direction), why the work it does is essential to human survival, and what would happen if your recommended machine was to disappear!