World Religions

World Religions
Take out a piece of paper and write the date and
“World Religions” on the top
Reflect on the following questions:
What does religion mean to me?
How important is religion in society today?
What do I know about different religions?
What do I wonder about different religions?
Importance of respect and trust
Fertile Cresent
1. Why is the Fertile Crescent significant to the development of ancient civilizations and religions?
What role does this area play in world politics today?
Read beginning of chapter 5
Where are we going?
2. What are the key characteristics of the 8 major religions?
What are the 8 world religions?
What are major similarities and differences between them?
Focus on Islam, Christianity and Judaism
Where are we going?
3. How was Christianity a vital part of medieval society?
Consider economic, political and social roles
What factors enabled the spread of Christianity between
0-1000 CE?
4. Describe the spread and the influence of Islam between the 5 th and 10 th Centuries? (Interactive mapping project).
How did Islam promote tolerance?
What were the differences between Christian and Islam society during the same period?
Where are we going?
5. What factors led to conflict between religions?
Re-conquista
Crusades
Modern Day conflict
How can we overcome these differences for a peaceful co-existence again?
Parts of Chapters 2, 4, and 5 end of Nov.
Reading packages, skits, movies, field trip, poster project, quizzes, tests, interactive maps
Fertile Cresent
1. Why is the Fertile Crescent significant to the development of ancient civilizations and religions?
What role does this area play in world politics today?
Read beginning of chapter 5
Question to guide your thinking…
In what way does geography have a profound influence on the creation, expansion and shaping of the religions? Why might the religions dominate where they do?
Is the area of dominance related to the area of founding?
Refer to these questions often…you may need to synthesis information for the answers!
Question to guide your thinking…
8 Major World Religions
2. What are the key characteristics of the 8 major religions?
What are the 8 world religions?
What are major similarities and differences between them?
Focus on Islam, Christianity and Judaism
Story
This is a story about a wall — the separations it's meant to enforce, and the unintended ones it gives birth to. The security wall being constructed by Israel on the West Bank has divided Palestinian families and communities. It has also isolated the Catholicrun Our Lady of Sorrows nursing home outside of
Jerusalem, leaving its feisty residents to face old age in the throes of one of the world's most bitter conflicts. With beautiful imagery, moments of laughter and use of a quietly eccentric older guide,
This Way Up examines the social, economic and religious barriers that arise from physical ones.
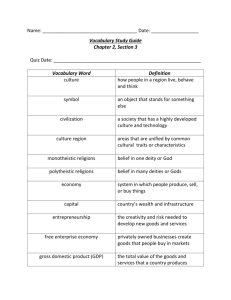
What are the world religions?
Brainstorm 8 World religions
Christianity, Judaism, Islam, Buddhism,
Confucianism, Shintoism, Hinduism, Taoism,
Sikhism
Create a graphic organizer with 8 rows & 4 columns
List the religions in rows
What are the world religions?
What are similarities exist between religions?
Differences?
Which religions allow adherents of different beliefs and why? Which do not?
What factors have allowed certain religions to become widespread and sustainable?
Ways to categorize
Polytheistic or monotheistic?
Exclusive or non-exclusive?
Occidental or oriental?
Ethnic or universal?
Polytheistic vs. montheistic
Refers to how many Gods the religion adheres to
Example: the ancient Greek and Roman religions believed in many Gods (polytheistic)
Buddhism believes in many Gods (polytheistic)
Christian, Jews and Islam religions believe in one
God (monotheistic)
Do you need to believe in a God or many Gods to be considered a religion?
Polytheistic vs. montheistic
Refers to how many Gods the religion adheres to
Example: the ancient Greek and Roman religions believed in many Gods (polytheistic)
Buddhism believes in many Gods (polytheistic)
Christian, Jews and Islam religions believe in one
God (monotheistic)
Do you need to believe in a God or many Gods to be considered a religion?
Exclusive vs. non-exclusive
Are you “allowed” to believe in more than one religion or set of beliefs?
How false does one religion regard the others?
People following non-exclusive traditions may follow several religions with overlapping beliefs
What do you think the connection between conflict and exclusivity may be?
Occidental vs. Oriental
Refers to birthplace of religion
Connection to geography of religion today
Occidental: Western world (pre-exploration)
Oriental: Eastern world
Ethnic vs. Universality
Ethnic religions are closely tied to a group of people, place (nationality or state), and heritage
Religion and ethnicity can become inseparable
Ex. Judaism “chosen people” and Hinduism and the caste system
Ethnic vs. Universalized
A universalizing religion is dependent on how open the religion is to accepting outsiders. Universalizing religions have four characteristics:
adherents believe what they think is proper for all human kind have a means of transmission are not inextricably linked to a nation, ethnicity, or place are dominant somewhere
Ex. Christianity, Islam, Buddhism
Categorize religions
Exclusive, Monotheistic & Occidental:
Christianity
Judaism
Islam
Categorizing Religion
Non-exclusive, polytheistic & Oriental:
Confucianism
Taoism
Taoism
Hinduism
Buddhism
Importance of physical features
Importance of physical features
Importance of physical features
Importance of physical features
Sacred Structures
Religion, Society &
Government
The idea of a truly secular state is a recent idea
Theocracy: religious organization provides the body of government (Israel, Middle Eastern governments)
State Religions: provide rituals / validation. The State provides the religion official recognition and protection (Middle Ages)
Separation of State and Religion: a trait of modern day democracies (Canada, USA, Australia, England)
Transmission of religions
Migration: population growth, trade, transmission of cultures
Conversion: marriage, missionary work
Competition: Exclusivity? Co-existence?
Christianity – Roman Empire, Charlemagne period
Islam/Judaism/Christianity and Crusades
Asian approach to religious co-existence