Addendum to Course Outline
advertisement

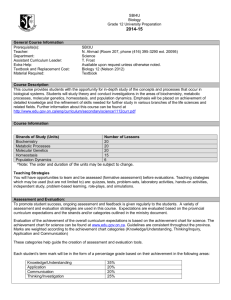
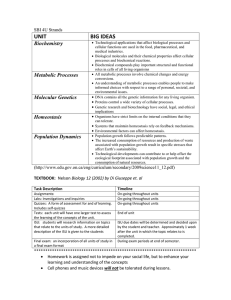
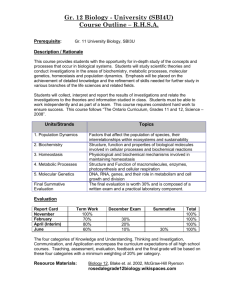
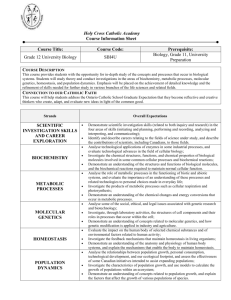
ADDITIONAL COURSE INFORMATION FOR PARENTS – REVISED 2012 YORK REGION DISTRICT SCHOOL BOARD UNIONVILLE HIGH SCHOOL Department: Science Course Code: SBI4U Grade: 12 Credit Value: 1.0 Instructor(s): ______________ Course Title: Grade 12 University Biology Course Type: University Preparation Prerequisite: SBI3U Department Head: Mr. Fung Regional Subject Head: Nathalie Rudner Ministry Guideline: The Ontario Curriculum Grades 11 & 12 Science – Revised 2008 Course Description: This course provides students with the opportunity for in-depth study of the concepts and processes that occur in biological systems. Students will study theory and conduct investigations in the areas of biochemistry, metabolic processes, molecular genetics, homeostasis, and population dynamics. Emphasis will be placed on the achievement of detailed knowledge and the refinement of skills needed for further study in various branches of the life sciences and related fields. Resources: Biology 12.Nelson Cost: approximately $100 (or current market value) Assessment and Evaluation: Knowledge Thinking and Inquiry Communication Application Final Exam 21% 21% 14% 14% 30% Assessment and Evaluation Styles: tests, quizzes, projects, lab reports, presentations, assignments and independent study Teaching Strategies: direct instruction, computer simulation, group work, inquiry activities, independent learning, stations, lecture, laboratory activities Goals of the Secondary Science Program outline the overall skills, knowledge and attitudes students will develop. 1. to relate science to technology, society, and the environment 2. to develop the skills, strategies, and habits of mind required for scientific inquiry 3. to understand the basic concepts of science Curriculum Strands in SBI4U and accompanying "Big Ideas" guide our focus on larger concepts, principles, and processes. There are 5 Major Content Units in this course. The first unit (A – found in the Ministry Document, 2008) is implemented throughout the remaining 5 units. The chronology and number of hours for the units are tentative and may change for the units throughout the duration of the course. B. Biochemistry Technological applications that affect biological processes and cellular functions are used in the food, pharmaceutical, and medical industries. Biological molecules and their chemical properties affect cellular processes and biochemical reactions. Biochemical compounds play important structural and functional roles in cells of all living organisms. C. Metabolic Processes All metabolic processes involve chemical changes and energy conversions. An understanding of metabolic processes enables people to make informed choices with respect to a range of personal, societal, and environmental issues. D. Molecular Genetics DNA contains all the genetic information for any living organism. Proteins control a wide variety of cellular processes. Genetic research and biotechnology have social, legal, and ethical implications. E. Homeostasis Organisms have strict limits on the internal conditions that they can tolerate. Systems that maintain homeostasis rely on feedback mechanisms. Environmental factors can affect homeostasis. F. Population Dynamics Population growth follows predictable patterns. The increased consumption of resources and production of waste associated with population growth result in specific stresses that affect Earth’s sustainability. Technological developments can contribute to or help offset the ecological footprintassociated with population growth and the consumption of natural resources.