Chemical Bonds / Formulas
advertisement

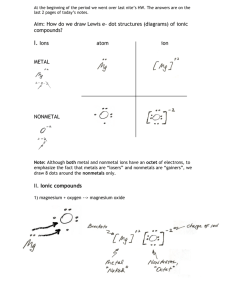
Atoms want 8ve- to be stable “happy” Chemical Bonds / Formulas Atoms bond to become stable or “happy” – octet rule (full valence shell) When they bond they form compounds. Each compound has a special formula Subscripts show how many of each element is in the compound FORMULAS MgCl2 The subscript is the number at the bottom of a formula. There is 1- Mg & 2 – Cl Never use 1 as a subscript! IONIC BOND bond formed between two ions by the transfer of electrons Ions Atom that gains or loses electrons to become stable “happy” Cation: loses e- to form (+) charged ion Anion: gains e- to form (-) charged ion Formation of Ions from Metals Ionic compounds result when metals react with nonmetals Metals lose electrons to form a positive charge Nonmetals gain electrons to form a negative charge Metals: Nonmetals: Na+ N -3 Ca+2 S -2 Al+3 Br - IONIC BONDS Bonds form from the (+) & (-) charges. Form a network of ions. – very strong bonds. Conduct electricity when melted or dissolved in water. Writing Ionic Formulas – binary Representative metals Calcium & oxygen Write the metal ion Ca +2 Write the nonmetal ion O -2 If charges cancel – ratio is 1:1 ( 1 of each) CaO Magnesium & chlorine Write the metal ion Mg +2 Write the nonmetal ion Cl If charges DO NOT cancel – drop & swap MgCl2 Writing Ionic Formulas – binary Transition metals Ion charges change – an element can have more than one ion charge The charge is given as a ROMAN NUMERAL Ex: Iron (II) Fe+2 / Iron (III) Fe+3 Gold (I) Au + / Gold (III) Au+3 You will never have to memorize all the charges each transition metal forms – the charges will be given to you !!!!! Practice Magnesium & iodine Strontium & bromine Barium & nitrogen Aluminum & phosphorus Naming Ionic Formula - binary Representative Metals Name the metal Change the ending of the Transition Metals Name the metal & Include the charge using a Roman Numeral nonmetal to – ide MgCl2 - magnesium chloride AlP - aluminum phosphide Ex: Iron (II) Fe+2 / Iron (III) Fe+3 Gold (I) Au + / Gold (III) Au+3 Change the ending of the Cl – chloride F – flouride I – iodide P – phosphide Br – bromide C - carbide Se - selenide N – nitride S – sulfide O – oxide nonmetal ending to –ide Fe +2 Cl - iron (II) chloride Au + O -2 gold (I) oxide Practice CaBr2 FeCl3 Na3N Ni3N BCl3 ZnO MgO FeS Ternary Ionic Bonds – contain Polyatomic Ions Polyatomic ion : a group of (covalently) bonded nonmetals that form a charge. Act as a single ion in an ionic bond Have special names that DO NOT CHANGE You need to write down the polyatomic ions and their names on a sheet of paper and DO NOT LOSE IT!!! You will use your list on all quizzes and tests! Ammonium NH4+ Carbonate Chromate Acetate C2H3O2Dichromate Hypochlorite ClOOxalate Chlorite ClO2 Sulfate Chlorate ClO3Sulfite Perchlorate ClO4Phosphite Phosphate Cyanide CNPermanganate Hydroxide OHPeroxide Nitrite NO2 Nitrate NO3Bicarbonate/Hydrogen Carbonate HCO3- CO3-2 CrO4-2 Cr2O7-2 C2O4-2 SO4-2 SO3-2 PO3-3 PO4-3 MnO4O2-2 Writing Ionic Formulas - ternary Write the cation – all metals (only polyatomic cation is ammonium: NH4+ ) Write the anion – all nonmetals and polyatomic ions If charges cancel – 1:1 ratio If charges DO NOT cancel – drop & swap You must use parenthesis if more than one polyatomic ion is present Practice cesium nitrate Iron(III) chlorite barium sulfite Zinc(II) nitrite aluminum hydroxide Gold(III) carbonate strontium phosphate Silver(I) phosphite ammonium sulfide Copper(I) acetate Naming ionic formulas - ternary Representative metal Name the cation Use the same name for the polyatomic ion If the anion is a nonmetal – change the ending to -ide Transition metal Name the metal and include a ROMAN NUMERAL for the charge of the metal Use the same name for the polyatomic ion If the anion is a nonmetal – change the ending to -ide Group 1 - Alkali Metals reacts violently with water VERY reactive, one valence eto lose; +1 cation Alkali metals http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m55k gyApYrY&safety_mode=true&persist_sa fety_mode=1 Group 2 - Alkaline Earth Metals 2 valence e-; +2 cation reactive http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m55k gyApYrY&safety_mode=true&persist_sa fety_mode=1 Transition Metals Groups 3-12 Ions charges change – changes properties NOT REPRESENTATIVE! Halogens -Group 17 -1 ions, highly reactive 7 valence e- Noble Gases Group 18 unreactive, 8 valence edo not form ions exist as single atoms, don’t bond - inert COVALENT BOND bond formed by the sharing of electrons Covalent Compounds Covalent compounds result when nonmetals react with nonmetals Both nonmetals share their valence electrons to be happy – Octet Rule Examples: CO2 SCl2 H 2O CH4 Naming Covalent formulas Use prefixes to show the # of atoms of each element in a covalent compound 1 – mono 6 - hexa 2 – di 7 - hepta 3 – tri 8- octa 4 – tetra 9 - nona 5 – penta 10 – deca 1st element – use prefixes only of the # of atoms is greater than 1 2nd element – use prefixes; change ending to – ide Practice CO2 carbon dioxide N 3F 8 trinitrogen octaflouride Se4Br9 tetraselenium nonabromide S 7O heptasulfur monoxide Writing Covalent formulas Use the prefix to identify how many of each nonmetal atoms are in each molecule The prefix becomes the subscript. Carbon Tetrahydride ○ CH4 Disulfur Hexachloride S2Cl6 1) Name the following covalent compounds: a) SiF4 b) N2S3 c) H3Br7 d) S5Br9 e) H2O 2) Write the formulas for the following covalent compounds: a) diboron hexahydride b) nitrogen tribromide c) sulfur hexachloride d) diphosphorus pentoxide