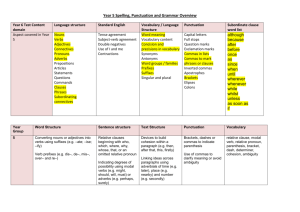
Room 13 - Cayley Primary School
advertisement

MAP OF NATIONAL CURRICULUM GRAMMAR AND SPELLING REQUIREMENTS AS APPLIED TO SFA WINGS TREASURE HUNTS AND WRITING MODULES SFA-UK UNINOT [Company address] 0 INDEX Page Introduction Guidance for usage Wings 2, Phase 1 Treasure Hunts Wings 2, Phase 1 Writing Modules Wings 2, Phase 2 Treasure Hunts Wings 2, Phase 2 Writing Modules Wings 2, Phase 3 Treasure Hunts Wings 2, Phase 3 Writing Modules Wings 3, Phase 1 Treasure Hunts Wings 3, Phase 1 Writing Modules Wings 3, Phase 2 Treasure Hunts Wings 3, Phase 2 Writing Modules Wings 3, Phase 3 Treasure Hunts Wings 3, Phase 3 Writing Modules Wings 4, Phase 1 Treasure Hunts Wings 4, Phase 1 Writing Modules Wings 4, Phase 2 Treasure Hunts Wings 4, Phase 2 Writing Modules Wings 4, Phase 3 Treasure Hunts Wings 4, Phase 3 Writing Modules Wings 5, Phase 1 Treasure Hunts Wings 5, Phase 1 Writing Modules Wings 5, Phase 2 Treasure Hunts Wings 5, Phase 2 Writing Modules Wings 5, Phase 3 Treasure Hunts Wings 5, Phase 3 Writing Modules 3 5 7 9 10 12 13 15 16 18 19 22 23 26 27 30 31 34 35 38 39 41 42 46 47 51 1 2 Introduction This document is intended to give confidence that all elements of the National Curriculum (2014) Grammar and Spelling objectives can be comfortably aligned to the SFA Treasure Hunt materials. This map gives guidance on where the various objectives can be introduced/re-visited in order to ensure a complete curriculum coverage by the end of Year Six. It also gives guidance on how (at which points in the writing lesson) the skills can be most appropriately modelled and practised. The grammar and spelling objectives have been taken from the appendices of the National Curriculum and matched with a level-appropriate Treasure Hunt or Writing Module focus that gives the best opportunity to practise the desired skill. Each objective is revisited many times so that even if one Treasure Hunt is missed, there should be no resulting gaps in knowledge (also it is easy to check back on children’s expected prior knowledge by mapping against the books they are known to have covered). Effective teaching of grammar (and in particular, sentence-level skills), punctuation and spelling is based on the SFA Co-operative Learning Cycle of Instruction: teacher models how to e.g. construct a complex sentence, and guides practice as a whole group before allowing the children to practise the same skill in partnerships and then independently. This is teaching for the purpose of application to the children’s own writing – in this way the children get to see a clear link between what they are learning and the benefits of learning it (i.e. to make the meaning of their writing clearer and more comprehensible). Appropriate Expectations for Grammar Concepts As concepts are re-visited on a regular basis after first introduction, it is not essential that children fully master one aspect of grammar the first time they are exposed to it. There are plenty of opportunities for revision both over the course of the Wings levels that approximate the half-key stage descriptors in the National Curriculum and also in the levels above that. Once teachers are confident that children have fully mastered the skill described for a particular Treasure Hunt cycle, it is not necessary to keep revisiting; instead, they should introduce a skill at a higher-level (or return to an identified gap in the children’s knowledge). Below is a map that shows how the age-related expectations equate to SFA Treasure Hunt levels: Wings 2, Phase 1 Year 2 Wings 3, Phase 1 Years 3 and 4 (plus revision of Year 2) Wings 4, Phase 1 Years 3 and 4 Wings 5, Phase 1 Years 5 and 6 (plus revision of Years 3 and 4) Wings 2, Phase 2 Years 3 and 4 (plus revision of Year 2) Wings 3, Phase 2 Years 3 and 4 Wings 4, Phase 2 Years 5 and 6 (plus revision of Years 3 and 4) Wings 5, Phase 2 Years 5 and 6 Wings 2, Phase 3 Years 3 and 4 (plus revision of Year 2) Wings 3, Phase 3 Years 3 and 4 Wings 4, Phase 3 Years 5 and 6 (plus revision of Years 3 and 4) Wings 5, Phase 3 Respond to gaps in children’s knowledge/areas that require further practice 3 Explanation of Terms A ‘Wings 2.1’ Treasure Hunt is currently aligned to National Curriculum level 2 and is designed to be taught in the first phase (term) of delivering materials at this level. When all Wings 2.1 materials have been delivered, then the teacher moves onto delivering material in Wings 2.2 and then 2.3. When the class is assessed at being ready to move onto Level 3 material, the teacher should begin with Wings 3.1 Treasure Hunts and so on (regardless of when in the calendar year this occurs). This is because the expectations of prior learning (particularly at sentence level) build on each other throughout the three phases. Extended Writing Opportunities in Other Areas of the Curriculum It should be remembered that children write in almost all other areas of the curriculum (not just during literacy). When these opportunities arise, in whatever subject area, children should be reminded of the sentence-level, grammar and punctuation skills they have been practising in SFA (and opportunities taken for the teacher to model these in the same way too). Children should also be reminded that they already know how to structure writing for various purposes (e.g. a nonchronological report). If the children in a class group come from a wide range of SFA groups then the teacher should pitch wherever they feel is most appropriate for the needs of a significant proportion of the class. Paying attention on a regular basis to children’s use of exciting and adventurous vocabulary, ability to compose compound and complex sentences and use of cohesive devices is almost guaranteed to raise the standard of children’s writing in a relatively short period of time. Opportunities should be taken during writing in other curriculum areas to develop layout skills such as use of tables, bullet points etc. This is because these are not explicitly practised in SFA writing (as they do not directly feed into enhancing the overall quality of what is written). 4 Guidance for Usage Grammar Teaching During Shared Writing/Drafting and Re-drafting It is essential that teachers use their Shared Writing (Active Instruction) time as a focused teaching opportunity for modelling aspects of grammar such as constructing more extended (compound and complex) sentences, use of punctuation to structure these and cohesive devices such as paragraphing and devices (e.g. connecting adverbs) to link ideas. Teachers should use Think-Alouds to model their thinking process as they write for and with the children. Children should then be encouraged to replicate the same structures when creating their own first drafts (and testing these out on their partners for feedback). Care should be taken to revisit the same aspects of grammar as a focus also for re-drafting (both as a modelled process and for the children’s own writing). It is very important that teachers use the correct terminology (listed at the top of each phase) when they talk about aspects of grammar. Grammar Teaching During Grammar Focus/Children’s Editing Teachers should use the time leading into children’s editing of their work to promote the mechanical skills of writing: spelling, punctuation and general syntactical checks such as subject/verb agreement and tense consistency. This can be modelled using either the appropriate lesson in the SFA Grammar for Editing manuals or as a group edit (enlarged version) of one child’s piece of writing. Again, it should be made clear that the purpose of this is to allow the meaning of what the children have written previously to shine through for their readers. SPaG Test The above is not a preparation for passing the KS2 SPaG test. Research has proven that the two skills of learning grammar for application to writing and learning grammar classification for the purpose of passing a test are not transferable. Formal classification of aspects of grammar should be taught as a class exercise in short but frequent slots. There are plenty of good interactive programmes and children’s workbooks available that present and give practice in these skills but as a general guide, children should be taught to identify one particular aspect of grammar (e.g. prepositions) – teachers should explain the function of the word class and give examples; then to classify (find other examples/pick other examples from a list of words); then to apply (synthesise) the aspect of grammar (e.g. by filling in blank spaces in a sentence). Spelling Teachers should use the SFA spelling programme as a guide to the methodology of teaching spelling, using the guidance given here as to which words/spelling patterns they should be covering. As above, once certain words/spelling patterns are mastered then either teach words from a higher age expectation or fill in identified gaps in the children’s spelling skills. In either case, children should be encouraged to look for general patterns and rules for spelling words in English. 5 Grammar and Spelling Teaching during Delivery of Year Six Revision Programme It is anticipated that during the second term of Year Six (from January), teachers will be teaching the Year Six children discretely in preparation for the SATs reading test and teacher-assessed writing. During the writing parts of the lessons, grammar and spelling foci should be modelled in exactly the same way (using years 5 and 6 descriptors of skills and, if necessary, filling in any gaps in knowledge relating to Years 3 and 4). Children Working Below Age-related Expectations Children who are assessed at needing tuition below the level that would normally be associated with their chronological age should still be placed in the appropriate Wings level for their needs (bearing in mind that placement should be at the challenge level for them – i.e. they are exposed to skills and concepts that they have not yet mastered rather than those with which they are already skillful) – as Success for All is an accelerated learning programme, the children should, by degrees, move at a pace that lessens the gap between them and their peers who are already working at age-expected levels. These children should be carefully monitored to ensure that their progress is as swift as possible and interventions put in place if this does not seem to be the case. Wings 5, Term 3/Children Working Towards Level 6 By Wings 5, term 3, all aspects of the required curriculum have been visited and revisited several times: for this reason, there is no direct guidance for spelling as to what aspects should be delivered to the children by this stage and the guidance for grammar is fluid; the teacher should focus on skills they have observed that the children need practice with. (In order to obtain Level 6 for Sentence Structure and Punctuation, children should be demonstrating that they can use a wide range of sentence structures and supporting punctuation as in Level 5, but the difference being that they should be completely fluent and accurate at this level.) 6 Wings 2.1 Treasure Hunts Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma Writing Goal: Rita the Rescuer The Little Polar Bear Newspaper report Letter to describe a place Mini Lesson: Time connectives Other uses of capitalisation Focus for Modelled/Guided Grammar/Editing Focus Writing Adverbs Full stops/capital letters Complex sentences linked with when/because Consistent past tense Use of exclamation marks China 1st person recount – a day in Writing in cohesive the life of a child in China sections Jim and the Beanstalk Can't You Sleep Little Bear? Write next part of story Recognising that reflecting the giant’s sentences must make thoughts and feelings about sense (verbs) what happens Write story opening Marking sentence boundaries Dumpling Write character profile Linking words Compound sentences linked with and/but Expanded noun phrases for description Continuous present tense Complex sentences linked with that/because Continuous past tense Creating adjectives to describe feelings using –ful Compound sentences linked with or/but Writing questions Complex sentences linked with if/because Creating nouns using –ness (e.g. darkness) Expanded noun phrases Compound sentences linked with and/but Comparative / superlative adjectives Full stops/capital letters Consistent present tense Commas in lists Full stops/capital letters Consistent past tense Apostrophes for possession Full stops/capital letters Consistent past tense Question marks Full stops/capital letters Consistent past tense Apostrophes for contraction Full stops/capital letters Consistent present tense Commas in lists Suggested Spelling focus Soft ‘g’ sound (age, badge, gem) Tricky words: they’re/there/their; here/hear; quite/quiet Suffixes – less Tricky words: kind, find, mind, behind, child/(children), wild, climb Soft ‘c’ sound (rice, cell, fancy) Tricky words: door, floor, poor, because Suffixes –ful Tricky words: most, only, both, old, cold, gold, hold, told Suffixes – ness Tricky words: see/sea; bare/bear; one/won Suffixes -er/-est/-ly added to a root word ending in –y with a consonant before it Tricky words: every, everybody, even, great, break, steak, pretty, beautiful 7 Floss Write story from Floss’ point Consistent use of verb of view tense Complex sentences linked with when/because Writing commands What I like Stars Twinkle Write nonsense poem Recount of moon landing Play with sounds of words (predict) Consistent use of past tense Stars Twinkle Non-chron report (zig-zag book) Secure use of sentences Effective vocabulary choices ‘Flow’ of poem when read aloud Complex sentences linked with when/that Expanded noun phrases Compound sentences linked with and/but Comparative / superlative adjectives Full stops/capital letters Consistent past tense Apostrophes for contraction inverted commas for speech Suffixes -ing/-ed added to a root word ending in ‘e’ with a consonant before it Tricky words: after, father, last, past, fast, class* Capital letters to begin The /n/ sound spelt ‘kn’ or ‘gn’ at the beginning of lines words Full stops/capital letters Consistent past tense Commas in lists Full stops/capital letters Consistent past tense Apostrophes for possession Tricky words: sun/son; to/too/two; be/bee The /r/ sound spelt ‘wr’ at the beginnings of words Tricky words: class, pass, grass, glass, plant, bath, path* Suffixes –er/-est/-y added to a word ending in ‘e’ with a consonant before it Tricky words: blue/blew; night/knight; they’re/there/their *These are only tricky words if your regional accent pronounces the ‘a’ as an /ar/ sound – if your regional accent pronounces these as a short /a/ sound, then select other words to present as ‘tricky’. 8 Wings 2.1 Writing Modules Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma Purpose To be used after Mini Lesson: Story-writing characterisation Story-writing - planning Jonah and the Whale/Dumpling Can’t you Sleep Little Bear? Characterisation Story-writing – sequencing events Rita The Rescuer Synonyms for ‘then’ Non-chronological reports China/I Wonder Why Stars Twinkle Layout of NF text Planning Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Compound sentences linked with and/but Continuous past tense Complex sentences linked with because Compound sentences linked with then/so 1st Person recount Floss/Little Polar Bear Creating vivid mind movies (of settings) Continuous present tense Compound sentences linked with and/but Details to show thoughts and feelings Adjectives for description Grammar/Editing Focus Consistent past tense Full stops/capital letters Full stops/capital letters Apostrophes for possession Consistent past tense Question marks/exclamation marks Consistent present tense Commas in a list Consistent past tense Apostrophes for possession 9 Wings 2.2 Treasure Hunts Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks) Writing Goal: Seaside Poems Mrs Vole the Vet Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing To write another poem on a To play with the sounds Adverbs seaside theme of words and phrases Expanded noun phrases Lonely Hearts ad Mini Lesson: Capital letters The Lonely Giraffe To write a story that teaches a lesson To add extra details to interest the reader Dr Xargle’s Earthlets To write a postcode from Earth Word choices that reflect viewpoint Danger, To write the next part of the Writing dialogue Monsters, Aliens! story Digitext Danger, Monsters To write a recount of the Adjectives and adverbs Aliens! story from the point of view of two of characters Compound sentences linked with and/but Expanded noun phrases for description Modal verbs must/will Grammar/Editing Focus* Complex sentences linked with when/after Paragraphs to organise ideas Creating adjectives to describe feelings using –ful Complex sentences linked with while/so Present perfect form of verbs (we have arrived..) Complex sentences linked with before/while/so Creating new words by joining words together (spacesuit) Paragraphs organised by time sequence Adverbs: then/next/soon Comparative / superlative adjectives Commas in lists Consistent present tense Commas in lists Consistent past tense Exclamation marks Consistent present tense Apostrophes for contraction Consistent past tense Inverted commas for speech punctuation Consistent past tense Apostrophes for possession Suggested Spelling focus Suffixes – ly Tricky words: hour, move, prove, improve, sure, sugar Prefixes superTricky words: accident(ally), actual(ly), address, answer, appear, arrive ‘-le’ at end of words Tricky words: eye, could, should, would, who, whole Suffixes –ful Tricky words: believe, bicycle, breath, breathe, build, busy/business Compound words (e.g. spacesuit/spacecraft) Tricky words: any, many, clothes, busy, people, water Prefixes antiTricky words: accept/except; affect/effect; ball/bawl 10 Fur and Feathers To write a well-known story Play script format in the form of a play The Selfish Giant To write a letter to persuade Subject/verb agreement I wonder Why Spiders Spin Webs I wonder Why Spiders Spin Webs Bog Baby To create an annotated life Consistent verb tense cycle of a butterfly To make a zig-zag book about bees To write the story of how something came about Writing in cohesive sections Consistent past tense Present perfect form of verbs Writing commands Consistent present tense Apostrophes for contraction Consistent present tense Use of a/an Tricky words: they’re/there/their; here/hear; quite/quiet Adding suffixes beginning with vowel letters to words of more than one syllable** Consistent present tense Commas in lists Tricky words: calendar, caught, centre, century, certain, circle ‘-el’ at the end of words (camel, towel, tinsel, tunnel, squirrel, travel) Prepositions of cause – because of Present continuous tense (I am writing…) Paragraphs to organise material by stage of process Expanded noun phrases Conjunctions when/after Heading and sub-headings to organise material Adverbs – then/next//therefore Complex sentences linked with when/because Continuous past tense (he was running) Consistent present tense Apostrophes for possession (plural) Consistent past tense Inverted commas for direct speech Word families Tricky words: all, ball, call, walk, talk, always Adding suffixes beginning with vowel letters to words of more than one syllable** Tricky words: complete, consider, continue, decide, describe, different ‘-al’ at the end of words Tricky words: other, mother, brother, nothing, Monday *If children remain insecure with use of full stops to structure sentences, then it is imperative to focus on this at every writing opportunity until this is embedded. **If the last syllable of word is stressed and ends with one consonant letter which has just one vowel letter before it, the final consonant letter is doubled before any ending beginning with a vowel letter is added (forgetting, preferred); the consonant letter is not doubled if the syllable is unstressed (gardening, limited). 11 Wings 2.2 Writing Modules Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks) Purpose Story-writing characters To be used after The Selfish Giant Mini Lesson: Characterisation Story-writing – setting Dr Xargle’s Earthlets Descriptive words and phrases Story-writing sequence The Honey Hunters Time connectives Non-chronological report I Wonder Why Spiders Spin Webs Supporting details for main ideas Personal recount Mrs Vole the Vet Viewpoint (thoughts and feelings) Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Conjunctions for time/place/cause (when, before, after, while, so, because) Continuous past tense Prepositions for time/place/cause (before, after, during, in) Present perfect tense (we have landed) Adverbs for time/place/cause (then, next, soon) Continuous past tense Conjunctions for cause (because) Headings and sub-headings Adverbs for time/place/cause (then, next, soon) Paragraphs to group events Grammar/Editing Focus Apostrophes for possession Inverted commas for direct speech Commas in lists Question marks/exclamation marks Apostrophes for contraction Inverted commas for direct speech Apostrophes for possession Commas in lists Commas in lists Question marks/exclamation marks 12 Wings 2.3 Treasure Hunts Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks) Writing Goal: The Paper Bag Princess Mini Lesson: To retell story ending from To extend sentences by Elizabeth’s point of view. adding extra detail. The Gruffalo To describe the Gruffalo’s Commas to separate cousin items in a list Burglar Bill To make a wanted poster Apt and adventurous vocab choices Burglar Bill To write another section of the story in the same style as the original Linking words and phrases Rapunzel To write the opening of a Fairy Tale Punctuation for dialogue The Tiger Child To write a letter to the author Capitalisation Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Adverbs to express time – then/next/later Complex sentences linked with when/because Paragraphs organised in time sequence Compound sentences linked with and/but Expanded noun phrases for description Paragraphs to organise material Complex sentences linked with that/which Pronouns he/his Expanded noun phrases Grammar/Editing Focus* Consistent past tense Words ending in ‘-il’ Use of exclamation/question Tricky words: again, half, money, Mr, Mrs, parents, Christmas marks Consistent present tense Commas in lists Adding suffixes beginning with vowel letters to words of more than one syllable** Consistent present tense Commas in lists Exclamation marks -y (cry, fly, fry, dry etc.) at the end of words Conjunctions – before/after/so Compound sentences linked with or/but/and Writing direct speech Conjunctions – because/so Prepositions for time – during/before/after Writing direct speech Suggested Spelling focus Compound sentences linked with and/but Comparative / superlative adjectives (good, better, best) Tricky words: want, wander, quantity, squash Consistent past tense The /i/ sound spelt ‘y’ (e.g. Inverted commas for mystery, gym) direct speech Tricky words: young, touch, double, trouble, country Consistent past tense Adding the endings –ed/-ing to Inverted commas for words ending in ‘e’ with a consonant before it direct speech Consistent present tense Commas in lists Tricky words: word, work, worm, world, worth Suffixes -er/-est Tricky words: berry/bury; brake/break; fair/fare 13 Amazing Grace Poems to be Read Aloud The Lighthouse Keeper’s Catastrophe Exteme Weather Digitext To write a new story about Powerful verbs Grace To write another poem to Word choices in poems be read aloud Newspaper report Linking words and phrases To write a speech against Apt and adventurous climate change vocab choices. Oceans and Seas To write a poem about life Adjectives underwater Presentation Skills- Media To use PowerPoint to deliver a presentation Features of PowerPoint Prepositions for time – before/after/during Pronouns – she/her Writing direct speech Adjective choices Expanded noun phrases Complex sentences linked with when/that Prepositions for place/direction – over/under/along/towards Prepositions of cause (because of) Language of rhetoric (e.g. rhetorical questions, addressing audience directly) Expanded noun phrases Headings and bullet points to organise material (Speaking in extended sentences) (Speaking in standard English) Consistent past tense Suffixes – ful Inverted commas for Tricky words: can’t, didn’t, hasn’t, direct speech couldn’t, it’s, I’ll Prefixes super-,, auto -, antiCommas in lists Tricky words ; grate/great; groan/grown; its/it’s Consistent past tense Adding –es to verbs ending in ‘y’ Exclamation marks/question marks Tricky words: door, floor, poor, Inverted commas for because quotes Consistent present tense Apostrophes for possession Suffixes –er/-est Commas in lists Adding –ing, -ed, -er, -est and –y to words of one syllable ending in a single consonant letter after a single vowel letter (e.g. pat/patting; hum/hummed) Commas in lists Tricky words: difficult, disappear, early, earth, eight/eighth Tricky words: its/it’s; sea/see; bare/bear Negative prefixes un-, dis-, misTricky words: here/hear; heel/heal/he’ll *If children remain insecure with use of full stops to structure sentences, then it is imperative to focus on this at every writing opportunity until this is embedded. **If the last syllable of word is stressed and ends with one consonant letter which has just one vowel letter before it, the final consonant letter is doubled before any ending beginning with a vowel letter is added (forgetting, preferred); the consonant letter is not doubled if the syllable is unstressed (gardening, limited). 14 Wings 2.3 Writing Modules Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks) Purpose Narrative – fairy tales To be used after 12 Dancing Princesses/The Paperbag Princess/Rapunzel Mini Lesson: Writing a story ending Narrative - characterisation Amazing Grace Viewpoint (character’s thoughts and feelings) Narrative –characterisation/plot The Gruffalo Effect on plot of introducing fantasy character Non-chronological report – cause and effect Oceans and Seas Cause and effect conjunctions Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Conjunctions for time/place/cause (when, before, after, while, so, because) Continuous past tense Prepositions for time/place/cause (before, after, during, in) Present perfect tense (She has gone out) Adverbs for time/place/cause (then, next, soon) Continuous past tense Conjunctions for cause (because) Headings and subheadings Grammar/Editing Focus Apostrophes for possession Inverted commas for direct speech Inverted commas for direct speech Apostrophes for contraction Inverted commas for direct speech Question marks/exclamation marks Apostrophes for possession Commas in lists Also in Phase 3 Consolidation Units (to be used as stand-alones towards end of Wings 2 year: personal recounts and letters (focus on any grammar features from 2.3 the children are still weak on). 15 Wings 3.1 Treasure Hunts Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks) The Hodgeheg Writing Goal: Mini Lesson: Write a Conventions of speech conversation punctuation between Max and his Pa The Hodgeheg Write a radio advert for a road safety campaign Sentence type and style in adverts The Owl Who Was Afraid of the Dark The Owl Who Was Afraid of the Dark To write a story opening To vary sentence openers To write the ending to a given story To use a variety of sentence structures Incredible Insects To write a booklet about insects To identify and use features of NF text Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Prepositions of time (before/after/during) Adverbs of place (here/there/everywhere/nowhere) Present perfect tense (I have given it to him.) Prepositions of place (across/under/over) Adverbs of time (often/always/usually/never) Rhetorical questions Grammar/Editing Focus Suggested Spelling focus Words ending in –ey Inverted commas for direct speech Capitalisation of proper Tricky words: find, kind, mind, behind, child/children; wild/climb nouns Adverbial phrases to open sentences (place or time) Pronouns – he/his; they/their Paragraphs organised by time sequence/ place of action Using variety of sentence structures (e.g. simple, complex, fronted adverbial) Pronouns – he/his; they/their Paragraphs organised by time sequence/ place of action Headings and sub-headings to organise ideas and material Conjunctions of cause (because of/so) Expanded noun phrases (introduction to commas Adding suffixes beginning with vowel letters to words of more to mark clauses) than one syllable** Exclamation marks/question marks Tricky words: knot/not; mail/male; main/mane Inverted commas for direct speech Consistent past tense Subject/ verb agreement Inverted commas for direct speech Consistent past tense Subject/ verb agreement Exclamation marks Commas in lists (commas to mark clauses) The /zh/ sound spelt ‘s’ (television, treasure, usual) Tricky words: every, everybody, even, great, break, steak, pretty, beautiful Prefix in(be sure to point out both meanings: ‘not’ (inedible) or ‘in’/’into’ (‘inhale’) Adding –es/-ed to nouns and verbs ending in ‘y’ Tricky words: after, fast, last, past, father, class, grass, glass, pass, plant, path, bath* 16 Shape Poems Grace and Family To write a shape poem with a watery theme To describe setting To classify words types and judge which are essential/non-essential to understanding text Words to suggest viewpoint Natural Record To write Breakers holiday brochure Making Past in to Presents Continuous present tense (it is raining/the sun is shining) Intensifying adverbs (really/very/quite) Pronouns To write Imperative verbs instructions for board game Adverbs -ly Continuous present tense Headings and sub-headings to organise material Adverbs of place (nearby/outside) Prepositions of place (near/across/over) Superlative adjectives (the hottest/the best) Format of instructions Imperative commands A/an Consistent present tense Question marks/exclamation marks (commas to mark clauses) Suffix –ly Tricky words: half, money, parents, Mr, Mrs, Christmas Adding –ing/-ed/-er/-est/-y to words of one syllable ending in a single consonant letter after a single vowel letter Tricky words: hour, move, prove, improve, sure, sugar Consistent present Prefixes de-, distense Tricky words: any, many, clothes, Subject/verb busy, people, water, again agreement Commas in lists (of adjectives) Adding –ed/-ing/-er and –est to a Commas in lists root word ending in –y with a Imperative verbs Subject/verb agreement consonant before it Tricky words: eye, could, should, would, who, whole *These are only tricky words if your regional accent pronounces the ‘a’ as an /ar/ sound – if your regional accent pronounces these as a short /a/ sound, then select other words to present as ‘tricky’. **If the last syllable of word is stressed and ends with one consonant letter which has just one vowel letter before it, the final consonant letter is doubled before any ending beginning with a vowel letter is added (forgetting, preferred); the consonant letter is not doubled if the syllable is unstressed (gardening, limited). 17 Wings 3.1 Writing Modules Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks) Purpose Instructions Story-writing - dialogue Story-writing - settings Non-chronological reports To be used after Making the Past into Presents The Hodgeheg Mini Lesson: Clarity and accuracy Synonyms for ‘said’ The Willow Pattern Story/Grace and Family Adjectives to enhance description Natural Record Breakers Sub-headings to organise ideas Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Writing for clarity Imperative verbs Present perfect tense (She has gone out) Standard/non-standard English Adverbs for time/place/cause (then, next, soon) Continuous past tense Conjunctions for cause (because) Headings and subheadings Grammar/Editing Focus Commas in lists Inverted commas for direct speech Apostrophes for contraction Inverted commas for direct speech Question marks/exclamation marks Question marks/exclamation marks Commas in lists 18 Wings 3.2 Treasure Hunts Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks), determiner, pronoun, possessive pronoun, adverbial Writing Goal: Robin Hood Robin Hood Mini Lesson: Write another adventure for RH Conventions of dialogue Write a magazine-style profile of RH Adjectives Fairy Tales Rewrite story from POV of queen First and third person Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Adverbial phrases to open sentences Continuous past tense/simple past tense/ past perfect (the men were sleeping/the men slept/the men had slept) Expanded noun phrases with modifying adjectives and prepositional phrases (the famous outlaw with the big heart) Paragraphs to organise material around by theme Adverbial phrases to open sentences (place or time) Pronouns – he/his, she/her, they/their Paragraphs organised by change of mood in story Grammar/Editing Focus Suggested Spelling focus Inverted commas and end punctuation for direct speech Commas after fronted adverbials Adding suffixes beginning with vowel letters to words of more than one syllable* (introduction to commas to mark clauses) Exclamation marks/question marks Prefixes en-, em- Inverted commas and end punctuation for direct speech Consistent past tense Subject/ verb agreement (we were, I did) Suffix –ation Tricky words: enough, exercise, experience, experiment, extreme, famous Tricky words: meet/meat; medal/ meddle; missed/mist 19 Fairy Tales Feargal Fly Digitext Redraft FT to include more features of genre Varying sentence types To continue one Commas of the newspaper reports in the Digitext 101 Ways to Save Write a report on Conventions of the Earth/Save an ideal ‘green’ punctuation the Planet before environment Bedtime 101 Ways to Save Write the Earth/Save instructions for the Planet before an experiment Bedtime Play scripts Imperative To rewrite a Conventions of play story in the form scripts of a play Using variety of sentence structures (e.g. simple, complex, fronted adverbial) Pronouns – he/his, she/her, they/their Paragraphs to organise material by theme Conjunctions of cause (because /so) Expanded noun phrases with modifying adjectives and preposition phrases (the valuable gem with the checkered history) Sensational language choices Expanded noun phrases with modifying adjectives and preposition phrases (the natural grass roof over the main hall) Intensifying adverbs (really/very/quite/extremely/ha rdly) (Introduction to passive voice) Conventions of instructional writing Imperative commands Adverbs –ly Prepositions of place (near/across/over) Non-standard English for dialogue (characters’ voices) Inverted commas and end punctuation for direct speech Consistent past tense Subject/ verb agreement (we were/she did) Apostrophes for possession (including plural nouns) Apostrophes for contraction Commas to (begin to) mark clauses Words ending –ture General punctuation Subject/verb agreement Prefixes il-, im-, ir- Tricky words: favourite, February, forward(s), fruit, grammar, group Words ending –sion Tricky words: peace/piece; plain/plane; rain/rein/reign Tricky words: guard, guide, heard, heart, height, history Commas in lists and to (begin to) mark clauses Prefixes reTricky words: imagine, increase, important, interest, island, knowledge Subject/verb agreement Question marks and exclamation marks Prefixes sub-, inter-, superTricky words: seen/scene; weather/whether; who’s/whose 20 Amazing Creatures To produce a Cohesive paragraphing persuasive flyer Amazing Creatures Noisy Poems The Willow Pattern Story To produce an information leaflet Varying sentence types To write a noisy Identify word types poem To write a description of a setting Adjectives Paragraphs to organise material around a theme Modal verbs (should, must, could, would) Rhetorical questions Adverbial phrases to open sentences Extended sentences with a variety of co-ordinating and subordinating conjunctions Appropriate word choices ‘Flow’ of poem when read out loud Prepositions of place (near/across/over/behind) Adverbs of place (nearby/everywhere) Subject/verb agreement Question marks and exclamation marks Commas after fronted adverbials Apostrophes for possession (including plural nouns) Exclamation marks Commas to guide reader Commas in lists and to (begin to) mark clauses Subject/verb agreement Suffix –ous Tricky words: learn, length, library, material, medicine, mention Words which sound like /shoon/ spelt -tion, -sion, ssion Tricky words: minute, natural, naughty, notice, occasion(ally), often Words which sound like /shoon/ spelt --cian Tricky words: opposite, ordinary, particular, peculiar, perhaps, popular Words with the /k/ sound spelt ‘ch’ (e.g. school) Tricky words: position, possess(ion), possible, potatoes, pressure, probably *If the last syllable of word is stressed and ends with one consonant letter which has just one vowel letter before it, the final consonant letter is doubled before any ending beginning with a vowel letter is added (forgetting, preferred); the consonant letter is not doubled if the syllable is unstressed (gardening, limited). 21 Wings 3.2 Writing Modules Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks), determiner, pronoun, possessive pronoun, adverbial Purpose Story-writing - legends To be used after Robin Hood Mini Lesson: Characterisation Story-writing – traditional tales Fairy Tales Cohesion Story-writing – traditional tales Fairy Tales Descriptive words and phrases Play-script Play-scripts 1. Dialogue to move action forward 2. Stage directions Structure of recount Personal recount (Any) Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Preposition phrases (the lovable rogue with the green suit) Nouns/pronouns (Robin/he) Fronted adverbials (later that day, the next afternoon) Complex sentences linked with when/because Grammar/Editing Focus Paragraphs organised by theme Prepositions of time/ place/cause (while/during/after/past/over/bec ause of) Adverbs (-ly) Modal verbs (could, might) Expanded noun phrases to enhance viewpoint Non-chronological report 101 Ways to Save the Earth (No mini lesson but in-depth planning focus) Complex sentences linked with a variety of conjunctions Inverted commas for direct speech (and end punctuation) Subject/verb agreement Apostrophes for possession (including plural nouns) Commas after fronted adverbials Commas in a list Consistent past tense Apostrophes for contraction Question marks/exclamation marks Apostrophes for possession (including plural nouns) Question marks/exclamation marks Commas in lists Subject/verb agreement 22 Wings 3.3 Treasure Hunts Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks), determiner, pronoun, possessive pronoun, adverbial Writing Goal: Flat Stanley Mini Lesson: Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing To rewrite part Conventions of speech of the story from punctuation Arthur’s point of view Adverbial phrases to open sentences Continuous past tense/simple past tense/ past perfect (we were walking/we walked/we had walked) Grammar/Editing Focus Flat Stanley To write another Adverbs adventure for Stanley George’s Marvellous Medicine To write the To use adverbs to next part of the change the mood of a Magic Finger piece of writing. George’s Marvellous Medicine To review the work of Roald Dahl. To replace ‘weak’ verbs with more powerful ones. George’s Marvellous Medicine To write a new ending for the story. Powerful verbs. Adverbs to convey point of view (-ly) Adverbs of intensity (very/quite/hardly/almost) Paragraphs to organise material around by theme Adverbial phrases to open sentences (place, time or mood) Adverbs of intensity (very/quite/hardly/almost) Paragraphs organised by change of mood in story Using variety of sentence structures (e.g. simple, complex, fronted adverbial) Pronouns to avoid repetition – he/his, she/her, they/their Authoritative voice Paragraphs to organise material by mood of story Expanded noun phrases with modifying adjectives and preposition phrases (the brave little hero full of pluck) Suggested Spelling focus Adding suffixes beginning Inverted commas and end punctuation for direct speech with vowel letters to words of more than one Commas after fronted syllable* adverbials Subject/verb agreement Tricky words: accept/except; affect/effect; ball/bawl Prefixes anti-, auto-, interInverted commas and end punctuation for direct speech Tricky words: promise, Commas after fronted purpose, quarter, adverbials question, recent, regular Subject/verb agreement Prefixes trans-, under-, Inverted commas and end punctuation for direct speech semiCommas after fronted Tricky words: reign, adverbials remember, sentence, Subject/ verb agreement separate, special, straight Words with /sh/ sound Consistent present tense spelt ‘ch’ Subject/ verb agreement Apostrophes for possession Tricky words: strange, (including plurals) strength, suppose, surprise, therefore, though/although Apostrophes for possession Words with the /s/ sound spelt ‘sc’ (including plural nouns) Apostrophes for contraction Tricky words: berry/bury; Commas to (begin to) mark brake/break; fair/fare clauses 23 Cliffhanger To write a new Powerful adjectives story about the characters Cliffhanger Understanding TV Understanding TV To continue last Commas to structure week’s story sentences concentrating on building tension To write Future tense autocue script for breakfast show To write Superlatives presenter’s script for game show Expanded noun phrases with modifying adjectives and preposition phrases (the friendly dog with the waggy tail) Intensifying adverbs (really/very/quite/extremely/hardly) Adverbial phrases to open sentences Short, simple sentences to increase pace/longer extended sentences to decrease pace Paragraphs to organise material by change of mood Prepositions of time (before/after/during) Non-standard English for chatty and informal tone Intensifying adverbs (really/very/quite/extremely/nearly) Non-standard English for chatty and informal tone Inverted commas and end punctuation for direct speech Subject/verb agreement Commas after fronted adverbials Words with the /g/ sound spelt ‘-gue’ and the /k/ sound spelt ‘– que’ Tricky words: thought, through, various, weight, woman, women Words ending –tion, -sion, Inverted commas and end punctuation for direct speech -ssion Subject/verb agreement Tricky words: grate/great; Commas to (begin to) mark groan/grown; here/hear clauses Subject/verb agreement Words ending –tion, -sion, -ssion Apostrophes for contraction Tricky words: accident(ally), actual(ly), address, answer, appear , arrive Words with the /i/ sound Apostrophes for contraction spelt ‘y’ Question marks and exclamation marks Tricky words: here/hear; heel/heal/he’ll; knot/not; male/mail 24 How a Book is Made The Search for Tutankhamen To write a letter To vary sentences for to an author clarity, purpose and effect To write a newspaper report. Sentence structure and punctuation Extreme Habitats To write a Language of Digitext magazine comparison feature comparing and contrasting two habitats Paragraphs to organise material around a theme Extended sentences with a variety of co-ordinating and subordinating conjunctions Pronouns to avoid repetition Adverbial phrases to open sentences Sensational language Extended noun phrases (including prepositional phrases) Adverbs of comparison (Similarly/however/on the other hand) Commas after fronted adverbials Apostrophes for possession (including plural nouns) Commas to (begin to) mark clauses Apostrophes for possession (including plural nouns) Prefixes in-, im-, ilTricky words: believe, bicycle, breath, breathe, build, busy/business Prefix un- Tricky words: calendar, caught, centre, century, certain, circle Commas in lists and to (begin Suffix –ly to) mark clauses Tricky words: complete, Commas in lists (e.g. of adjectives) and after fronted consider, continue, decide, describe, different adverbials *If the last syllable of word is stressed and ends with one consonant letter which has just one vowel letter before it, the final consonant letter is doubled before any ending beginning with a vowel letter is added (forgetting, preferred); the consonant letter is not doubled if the syllable is unstressed (gardening, limited). 25 Wings 3.3 Writing Modules Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks), determiner, pronoun, possessive pronoun, adverbial Purpose Narrative – extra chapter for known book Short story in style of known author Narrative - mystery To be used after Flat Stanley George’s Marvellous Medicine Julian Secret Agent/Cliffhanger Mini Lesson: Analysing various drafts of same chapter Roald Dahl’s style Managing mood Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Preposition phrases (the silly boy in the green hat) Nouns/pronouns (Stanley/he) Fronted adverbials (later that day, the next afternoon) Complex sentences linked with when/because Paragraphs organised by theme Prepositions of time/ place/cause (while/during/after/past/over/bec ause of) Grammar/Editing Focus Inverted commas for direct speech (and end punctuation) Subject/verb agreement Apostrophes for possession (including plural nouns) Commas after fronted adverbials Commas in a list Consistent past tense Also in Phase 3 Consolidation Units (to be used as stand-alones towards end of Wings 3 year: letters, description, persuasion (focus on any grammar features from 3.3 the children are still weak on). 26 Wings 4.1 Treasure Hunts Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks), determiner, pronoun, possessive pronoun, adverbial Writing Goal: Mini Lesson: Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Grammar/Editing Focus The Wreck of the Zanzibar Write Description of Storm Synonyms Adverbial phrases to open sentences Use of pronouns to avoid repetition Continuous past tense/simple past tense/ past perfect (we were walking/we walked/we had walked) The Wreck of the Zanzibar Write a Newspaper Report To use a range of connectives in sentences Use of pronouns to avoid repetition Range of sentence types using variety of co-ordinating and subordinating conjunctions Paragraphs to organise material around by theme Paragraphs organised by theme Linking words and phrases within and between paragraphs Expanded noun phrases (including prepositional phrases – the sunny meadow across the stream) The Silver Swan Describe place Cohesiveness within that children and between know well paragraphs Suggested Spelling focus Adding suffixes Inverted commas and end punctuation for direct speech beginning with vowel letters to words of more Commas after fronted than one syllable* adverbials Subject/verb agreement Tricky words: difficult, disappear, early, earth, eight, eighth Commas after fronted adverbials Subject/verb agreement Suffix –ation Subject/ verb agreement Commas in lists (of adjectives) and to (begin to) mark clauses Prefixes ir-, il- Tricky words: meet/meat; medal/meddle; missed/mist Tricky words: enough, exercise, experience, experiment, extreme, famous 27 The Good Time Character Boys Sketch Language of comparison and contrast The Good Time Instructions for Imperative verbs Boys scenery and costumes Extended sentences with a variety of coordinating and subordinating conjunctions Use of pronouns to avoid repetition Adverbs (and adverbial phrases) of comparison (Similarly/on the other hand/unlike his brother) Adverbs –ly Adverbs of place and time (nowhere/everywhere; sometimes/never/usually) Prepositions of place and time (near/across/over; before/after during) Non-standard English for dialogue (characters’ voices) Language and format of instructions Use of pronouns to avoid repetition Poems about Write poem in Adjectives the Sea ( Under style of another the Moon Over the Sea) Vocabulary choices for effect ‘Flow’ of poem when read out loud The Good Time Write a Play Boys script Drag ‘n’ Drop Digitext Life in Space recounts and video diary to relate events from perspective of more than one character Write an imaginary diary entry Function of adverbs Commas to separate clauses Writing to show thoughts and feelings Adverbs of time (including adverbial phrases) Non-standard English for chatty and informal tone Intensifying adverbs (really/very/quite/extremely/nearly) Paragraphs to organise material around a theme Non-standard English for chatty and informal tone Consistent present tense Subject/ verb agreement Apostrophes for possession (including plural nouns) Prefix re- Words ending –ture Subject/verb agreement Apostrophes for contraction and possession (including plural nouns) Tricky words: young, touch, double, trouble, country Tricky words: favourite, February, forward(s), fruit, grammar, group Words ending –sure Subject/verb agreement Commas in lists and to (begin Tricky words: to) mark clauses piece/peace; plain/plane; rain/rein/reign Prefixes sub-, inter-, Exclamation marks superUse of commas to guide reader Tricky words: guard, guide, heard, heart, height, history Words ending –sion Apostrophes for contraction and Tricky words: possession (including scene/seen; plural nouns) weather/whether; Commas to (begin to) whose/who’s mark clauses and after fronted adverbials Suffix –ous Apostrophes for contraction and possession (including Tricky words: imagine, plural nouns) increase, important, Commas to (begin to) mark interest, island, clauses and after fronted knowledge adverbials 28 *If the last syllable of word is stressed and ends with one consonant letter which has just one vowel letter before it, the final consonant letter is doubled before any ending beginning with a vowel letter is added (forgetting, preferred); the consonant letter is not doubled if the syllable is unstressed (gardening, limited). 29 Wings 4.1 Writing Modules Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks), determiner, pronoun, possessive pronoun, adverbial Purpose Story-writing To be used after The Wreck of the Zanzibar Mini Lesson: Characterisation Non-Chronological report (information leaflet) Life in Space Planning (main ideas) Play-script – developing a problem and solution Instructions The Good Time Boys No book – use as a standalone (deconstruct e.g. cookbooks to introduce) Developing problem and solution Writing for clarity and precision Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Fronted adverbials (later that day, the next afternoon) Nouns/pronouns/varied references to same thing Paragraphs to organise ideas by theme Prepositions of time/ place/cause (while/during/after/past/over/bec ause of) Complex sentences linked with various conjunctions Adverbs (-ly) Preposition phrases (you over there with the funny face) Imperative verbs Writing for clarity and precision Layout of instructions Grammar/Editing Focus Inverted commas for direct speech (and end punctuation) Commas after fronted adverbials Apostrophes for possession (including plural nouns) Subject/verb agreement Apostrophes for contraction Consistent present tense Commas in lists 30 Wings 4.2 Treasure Hunts Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks), determiner, pronoun, possessive pronoun, adverbial, modal verb, relative pronoun, relative clause, parenthesis, bracket, dash, cohesion, ambiguity Writing Goal: Room 13 Room 13 To write the beginning of a horror story To write an extract from a sci-fi story Mini Lesson: Speech Punctuation Precise noun choices Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Room 13 To write the continuation of an adventure story Creating tension and suspense Adverbial phrases to open sentences Use of pronouns to avoid repetition Use of tense choice to sequence events and reference backwards and forwards (he had a horrible feeling something had happened to Ellie while he had been asleep/she hoped Dad wouldn’t be late home tonight) Variety of references to the same thing to avoid repetition (Alfred/the boy/he/the youngster) Range of sentence types using variety of co-ordinating and subordinating conjunctions Paragraphs to organise material around by theme Paragraphs organised by theme Linking words and phrases within and between paragraphs (then/after that/later that evening) Expanded noun phrases (including prepositional phrases – the red planet covered in a swirling yellow dust cloud) Grammar/Editing Focus Suggested Spelling focus Words with /k/ sound Inverted commas and end punctuation for direct speech spelt ‘ch’ Commas after fronted Tricky words: learn, adverbials length, library, material, Subject/verb agreement medicine, mention Commas to mark clauses and Words ending –cious to avoid ambiguity/clarify Tricky words: meaning descent/dissent; Subject/verb agreement desert/dessert; draft/draught Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Speech punctuation Adding suffixes beginning with vowel letters to words of more than one syllable* Tricky words: accept/except; affect/effect; ball/bawl 31 Room 13 To set the scene for a fantasy story Adjectives The Amazing Story of Adolphus Tips The Amazing Story of Adolphus Tips The Amazing Story of Adolphus Tips Recount of imaginary evacuation Adventurous and precise vocabulary Series of diary Adverbs and impact on entries from the mood of writing point of view of another character Write a letter from Ivy to Barry Vary Sentence Structures Medieval Knight Letter Plurals requesting help Extended sentences with a variety of coordinating and subordinating conjunctions Variety of references to the same thing to avoid repetition (Grampy/the old man/he/the old-timer) Adverbials of place to link ideas across paragraphs (nearby/further away) Adverbials of time to link ideas across paragraphs (later/earlier that day) Prepositions of place, time and cause (near/across/over; before/after during; because of) Non-standard English for dialogue (characters’ voices) Show point of view using powerful verbs Variety of references to the same thing to avoid repetition (Alfred/the boy/he/the youngster) Relative clauses (with or without relative pronouns) Vocabulary choices for effect Variety of references to the same thing to avoid repetition Relative clauses (with or without relative pronouns) Relative clauses (with or without relative pronouns) Cohesive devices within and between paragraphs Modal verbs Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Apostrophes for contraction and possession (including plural nouns) Words ending –tious Speech punctuation Apostrophes for contraction and possession (including plural nouns) Words with the /sh/ sound spelt ‘ch’ Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Parenthesis (brackets/dashes) to indicate extra information Words ending –cial Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Parenthesis (brackets/dashes) to indicate extra information Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Parenthesis (brackets/dashes) to indicate extra information Prefixes inter-, super-, under- Tricky words: accommodate, accompany, according, achieve, aggressive, amateur Tricky words: minute, natural, naughty, notice, occasion(ally), often Tricky words: ancient, apparent, appreciate, attached, available, average Tricky words: berry/bury; brake/break; fair/fare Words ending –tial Tricky words: advice/advise; device/devise; practice/practise 32 Have your Say 1 Letter to persuade Have your Say 2 Discursive report Connecting words and phrases Have your Say 2 Caribbean Poetry (Uses Under the Moon and Over the Sea and The Works) Spooky Poems (Uses Under the Moon and Over the Sea and the Works) To write a poem in the style of one of those read Caribbean Poetry (Uses Under the Moon and Over the Sea and The Works) To write a spooky poem Spooky Poems (Uses Under the Moon and Over the Sea and the Works) Intensifying adverbs (really/very/quite/extremely/nearly) Cohesive devices within and between paragraphs Modal verbs (should/would/must) Standard English for formal tone Modal verbs (should/would/must) Relative clauses (with or without relative pronouns) Standard English for formal tone Use of commas to guide reader/avoid ambiguity Invented words to convey a mood or idea Use of commas to guide reader/avoid ambiguity Invented words to convey a mood or idea Apostrophes for contraction and possession (including plural nouns) Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Parenthesis (brackets/dashes) to indicate extra information Prefixes anti-, autoTricky words: opposite, ordinary, particular, peculiar, perhaps, popular Words ending –ant, ance, -ancy Tricky words: principal/principle; profit/prophet; stationary/stationery Commas to guide the reader Words with the /g/ and to avoid ambiguity/clarify ending spelt ‘-que’ meaning Tricky words: vein, weigh, eight, eighth, neighbour, they, obey Commas to guide the reader Words ending –ent, and to avoid ambiguity/clarify ence, -ency meaning Tricky words: awkward, bargain, bruise, category, cemetery, committee *If the last syllable of word is stressed and ends with one consonant letter which has just one vowel letter before it, the final consonant letter is doubled before any ending beginning with a vowel letter is added (forgetting, preferred); the consonant letter is not doubled if the syllable is unstressed (gardening, limited). 33 Wings 4.2 Writing Modules Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks), determiner, pronoun, possessive pronoun, adverbial, modal verb, relative pronoun, relative clause, parenthesis, bracket, dash, cohesion, ambiguity Purpose To be used after Non-chronological report Any NF book (adjust prompt to fit topic) Collaborative writing Room 13 Story structure Story-writing Mini Lesson: Collaborative storywriting Room 13 1. Collaborative writing 2. Managing suspense Personal recount Stand-alone Powerful verbs and adverbs (viewpoint) Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Devices to build cohesion within paragraph Nouns/pronouns/varied references to same thing Paragraphs to organise ideas by theme Relative clauses Complex sentences linked with various conjunctions Linking ideas across and within paragraphs using tense choices Fronted adverbials (later that day, the next afternoon Adverbs to indicate degrees of possibility (perhaps, maybe, certainly) Paragraphs to organise ideas by theme Paragraphs to organise ideas by theme Linking ideas across paragraphs (adverbials of time) Modal verbs to indicate degree of possibility Grammar/Editing Focus Commas to clarify meaning (mark clauses) Brackets/dashes/commas for parentheses Inverted commas for direct speech (including end punctuation) Commas to clarify meaning (mark clauses) Subject/verb agreement Inverted commas for direct speech (including end punctuation) Commas to clarify meaning (mark clauses) Brackets/dashes/commas for parentheses 34 Wings 4.3 Treasure Hunts Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks), determiner, pronoun, possessive pronoun, adverbial, modal verb, relative pronoun, relative clause, parenthesis, bracket, dash, cohesion, ambiguity Writing Goal: Secret Friends Secret Friends Mini Lesson: To write a letter Vary sentences for to persuade clarity, purpose and effect To write an alternative ending to the story Commas to separate clauses Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing The Suitcase Kid To write the opening of a story about an issue Showing and telling sentences Adverbs of possibility (perhaps/maybe/surely) Use a range of sentence types: simple and complex using a range of conjunctions Modal verbs (should/would/must) Standard English for formal tone Variety of references to the same thing to avoid repetition Range of sentence types using variety of co-ordinating and subordinating conjunctions Paragraphs to organise material by change of mood Grammar/Editing Focus Cohesive devices within and between paragraphs (including tense choices) Relative clauses (with or without relative pronouns) Suggested Spelling focus Commas to mark clauses and Suffix –ous to avoid ambiguity/clarify Tricky words: meaning Parenthesis to indicate extra grate/great; groan/grown; here/hear information Commas to mark clauses and Words ending –able, ably to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Tricky words: Speech punctuation communicate, community, competition, conscience, conscious, controversy Commas to mark clauses and Suffix –ation to avoid ambiguity/clarify Tricky words: position, meaning possess(ion), possible, Speech punctuation potatoes, pressure, probably 35 The Suitcase Kid To resolve the Powerful paragraphs story begun last week The Suitcase Kid Poems to Perform (uses the Works) To write critically about an issue Powerful paragraphs To write a poem Punctuation and line based on one of breaks the poems read Range of sentence types using variety of co-ordinating and subordinating conjunctions Variety of references to the same thing to avoid repetition Adverbials of time to link ideas across paragraphs Devices to build cohesion within a paragraph Prepositions of cause (because of) Relative clauses (with or without relative pronouns) Standard English for authoritative voice Vocabulary choices for effect ‘Flow’ of poem when read aloud Please Mrs Butler To write a poem To recognize which based on one of words are essential to the poems read the poem Vocabulary choices for effect ‘Flow’ of poem when read aloud When Jessie Came Across the Sea Diary entries Adverbs Use a range of sentence types: simple and complex, using a range of conjunctions Adverbs of possibility (perhaps/maybe/surely) Cohesive devices within and between paragraphs Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Apostrophes for contraction and possession (including plural nouns) Words ending –ible, -ibly Tricky words: steal/ steel; wary/weary; who’s/whose; its/it’s Commas to mark clauses Words ending –sion and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Tricky words: knot/not; mail/male; main/mane Parenthesis to indicate extra information Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Parenthesis to indicate extra information Adding suffixes beginning with vowel letters to words ending – fer** Tricky words: father/farther/further; guessed/guest; heard/herd Commas to mark clauses and Words ending –sure to avoid ambiguity/clarify Tricky words: promise, meaning Parenthesis to indicate extra purpose, quarter, question, recent, regular information Commas to mark clauses Use of hyphen (e.g. cooperate) and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Tricky words: Parenthesis to indicate convenience, extra information correspond, criticise, curiosity, definite, desperate 36 Film Narrative Media Film synopsis Present tense Roman Chronicles To write a letter Comparatives and to persuade superlatives Roman Chronicles Ice Brick and Straw Digitext To complete a story To create an informative poster about a new building material To use commas to create complex sentences Language of instruction Cohesive devices within and between paragraphs Précising information Tense choices (present continuous/present perfect/future) to refer backwards and forwards Adverbs of possibility (perhaps/maybe/surely) Use a range of sentence types: simple and complex, using a range of conjunctions Modal verbs Standard English for formal tone Relative clauses (with or without relative pronouns) Use a range of sentence types: simple and complex using a range of conjunctions Fragmented sentences for speech Relative clauses (with or without relative pronouns) Précising information Apostrophes for contraction and possession (including plural nouns) Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Parenthesis to indicate extra information Words ending –ssion, tian, -cian Tricky words: meet/meat; medal/meddle; missed/mist Words with the /ee/ sound spelt ‘ei’ after ‘c’ Tricky words: determined, develop, dictionary, disastrous, embarrass, environment Prefixes un-, dis-, mis- Speech punctuation Commas to mark clauses and Tricky words: reign, to avoid ambiguity/clarify remember, sentence, meaning separate, special, straight Commas to mark clauses and Prefixes (general) to avoid ambiguity/clarify Tricky words: doubt, meaning Parenthesis to indicate extra island, lamb, solemn, thistle, knight information *If the last syllable of word is stressed and ends with one consonant letter which has just one vowel letter before it, the final consonant letter is doubled before any ending beginning with a vowel letter is added (forgetting, preferred); the consonant letter is not doubled if the syllable is unstressed (gardening, limited). **The ‘r’ is doubled if the –fer is still stressed when the ending is added; the ‘r’ is not doubled if the –fer is no longer stressed. 37 Wings 4.3 Writing Modules Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks), determiner, pronoun, possessive pronoun, adverbial, modal verb, relative pronoun, relative clause, parenthesis, bracket, dash, cohesion, ambiguity Purpose Newspaper report To be used after The Roman Chroncicles Mini Lesson: Opening paragraph Narrative - plot Secret Friends Plot development Personal Recount The Suitcase Kid Cohesive devices Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Devices to build cohesion within and between paragraphs Nouns/pronouns/varied references to same thing Relative clauses Complex sentences linked with various conjunctions Linking ideas across and within paragraphs using tense choices Modal verbs (could, should, might) Adverbs to indicate degrees of possibility (perhaps, maybe, certainly) Paragraphs to organise ideas by theme Grammar/Editing Focus Commas to clarify meaning (mark clauses) Brackets/dashes/commas for parentheses Inverted commas for direct speech (including end punctuation) Commas to clarify meaning (mark clauses) Subject/verb agreement Commas to clarify meaning (mark clauses) Brackets/dashes/commas for parentheses Also in Phase 3 Consolidation Units (to be used as stand-alones towards end of Wings 4 year: Planning, powerful paragraphs, prompt interpretation (focus on any grammar features from 4.3 the children are still weak on). 38 Wings 5.1 Treasure Hunts Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks), determiner, pronoun, possessive pronoun, adverbial, modal verb, relative pronoun, relative clause, parenthesis, bracket, dash, cohesion, ambiguity, (colon, semi-colon) Writing Goal: Kensuke’s Kingdom Mini Lesson: To write a Complex sentences character profile Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Kensuke’s Kingdom To write another Varying sentence character into lengths for accuracy, the story clarity and interest Kensuke’s Kingdom Book review More complex sentences Johnny and the To write an Standard and nonDead additional scene standard English for the play Grammar/Editing Focus Range of sentence types using variety of co-ordinating and subordinating conjunctions Variety of references to the same thing to avoid repetition Paragraphs to organise material by change of mood Cohesive devices within a paragraph (referring forwards and backwards) Use a range of sentence types: simple and complex, using a range of conjunctions Cohesive devices within and between paragraphs (including adverbs of number) Relative clauses (with or without relative pronouns) Characterisation in dialogue – non standard English, fragmented sentences etc. Use of adverbs and prepositions to guide stage directions Suggested Spelling focus Commas to mark clauses and Adding suffixes beginning with vowel to avoid ambiguity/clarify letters to words of more meaning Parenthesis to indicate extra than one syllable* information Tricky words: strange, strength, suppose, surprise, therefore, though, although Commas to mark clauses and Words ending –cious to avoid ambiguity/clarify Tricky words: ought, meaning bought, thought, nought, Speech punctuation brought, fought Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Apostrophes for possession (including plural nouns) Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Apostrophes for contraction and possession (including plural nouns) Suffix –ous Tricky words: peace/piece; plain/plane; rain/rein/reign Words ending –tious Tricky words: practice/practise; prophecy/prophesy; licence/license 39 Johnny and the To write advice Modal verbs Dead to the actor Johnny and the To write a Dead review of the play Film Stars Subordinate clauses Write a letter to Complex punctuation a celebrity I Like this Poem Write poem Adjectives based on structure of ‘The Sound Collector’ Anne Frank Write journal Punctuation entry for memorable day The Daily Life of Leaflet to a WW2 Evacuee persuade Modal verbs Devices to build cohesion within and between paragraphs (e.g. adverbs of number) Adverbs of possibility (perhaps/maybe/surely) Modal verbs Adverbs of intensity (very/quite/fairly) Relative clauses (with or without relative pronouns) ‘ Range of sentence types using variety of co-ordinating and subordinating conjunctions Variety of references to the same thing to avoid repetition Adverbials of time to link ideas across paragraphs Effective vocabulary choices ‘Flow’ of poem when read aloud Commas to mark clauses and Prefixes il-, irto avoid ambiguity/clarify Tricky words: meaning scene/seen; Semi-colons weather/whether; whose/who’s Cohesive devices within and between paragraphs (including adverbs of time/prepositions of time) Tense choices (past continuous/past perfect/present) to refer backwards and forwards Use a range of sentence types: simple and complex using a range of conjunctions Adverbs of possibility (maybe/certainly/perhaps) Modal verbs Standard English for formal tone Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Parenthesis to indicate extra information Prefixes in-, imTricky words: thought, through, various, weight, woman, women Commas to mark clauses and Words ending –cial to avoid ambiguity/clarify Tricky words: rough, meaning Parenthesis to indicate extra tough, enough, cough information Commas to mark clauses Words ending –tial and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Tricky words: equip(ped, -ment), especially, exaggerate, excellent, existence, explanation Commas to mark clauses and Words with /k/ sound spelt ‘ch’ to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Tricky words: vein, Apostrophes for contraction weight, eight, neighbor, and possession (including they, obey plural nouns) Commas to mark clauses and Words ending –ant, ance, -ancy to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Tricky words: though, Colons/semi-colons although, dough, through *If the last syllable of word is stressed and ends with one consonant letter which has just one vowel letter before it, the final consonant letter is doubled before any ending beginning with a vowel letter is added (forgetting, preferred); the consonant letter is not doubled if the syllable is unstressed (gardening, limited). 40 Wings 5.1 Writing Modules Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks), determiner, pronoun, possessive pronoun, adverbial, modal verb, relative pronoun, relative clause, parenthesis, bracket, dash, cohesion, ambiguity, (colon, semi-colon) Purpose Story-writing To be used after Journey to Jo’Burg Mini Lesson: Developing problem and solution Story-writing Kensuke’s Kingdom Descriptive language to enhance characterisation Personal recount Zlata’s Diary/Anne Frank Structure and language of personal recount Play-script Johnny and the Dead Characterisation Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Devices to build cohesion within and between paragraphs Nouns/pronouns/varied references to same thing Relative clauses Complex sentences linked with various conjunctions Linking ideas across and within paragraphs using tense choices Modal verbs (could, should, might) Adverbs to indicate degrees of possibility (perhaps, maybe, certainly) Paragraphs to organise ideas by theme Devices to build cohesion within and between paragraphs Nouns/pronouns/varied references to same thing Grammar/Editing Focus Inverted commas for direct speech (including end punctuation) Commas to clarify meaning (mark clauses) Inverted commas for direct speech (including end punctuation) Commas to clarify meaning (mark clauses) Subject/verb agreement Commas to clarify meaning (mark clauses) Brackets/dashes/commas for parentheses Commas to clarify meaning (mark clauses) Brackets/dashes/commas for parentheses 41 Wings 5.2 Treasure Hunts Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks), determiner, pronoun, possessive pronoun, adverbial, modal verb, relative pronoun, relative clause, parenthesis, bracket, dash, cohesion, ambiguity, colon, semi-colon, ellipsis, hyphen, bullet points, subject, object, active, passive, synonym, antonym Greek Myths Writing Goal: Mini Lesson: To plan a new myth and write part of it Sentence openers Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Space Probe Digitext To write sci-fi story Cohesion (sentence openers and pronouns) The Mousehole To write the Cat opening passage to a story including figurative language Figurative language Range of sentence types using variety of co-ordinating and subordinating conjunctions and fronted adverbials Variety of references to the same thing to avoid repetition Linking ideas across paragraphs using, e.g. repetition Paragraphs to organise material by change of mood Cohesive devices between paragraphs (e.g. referring forwards and backwards, grammatical connections, ellipses) Range of sentence types: simple and complex, using a range of conjunctions Grammar/Editing Focus Relative clauses (with or without relative pronouns) Range of sentence types: simple and complex, using a range of conjunctions Synonyms Suggested Spelling focus Commas to mark clauses and Words ending –ent, ence, -ency to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Parenthesis to indicate extra Tricky Words: thorough, borough, plough, bough information Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Speech punctuation Ellipses Adding suffixes beginning with vowel letters to words ending – fer** Tricky words: familiar, foreign, four/forty, frequently, government, guarantee Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Use of colon and semi-colon to indicate relationship between independent clauses Words with the /ee/ sound spelt ‘ei’ after ‘c’ Tricky words: led/lead; morning/mourning; passed/past; precede, proceed 42 The Highwayman The Lady of Shalott To write Conventions (incl. narrative poem punctuation) to guide reader Refine (last Vocabulary choices week’s) poem with addition of poetic devices Quakes, Floods To write a and Other newspaper Disasters report Pronouns Journey to Jo’burg To write a new scene for the book Synonyms Vocabulary associated with a period in history/to give a sense of occasion Synonyms Linking ideas across stanzas using, e.g. repetition Vocabulary associated with a period in history/to give a sense of occasion Synonyms Linking ideas across stanzas using, e.g. repetition Adverbs of intensity (very/quite/fairly) Relative clauses (with or without relative pronouns) Vocabulary associated with formal/informal speech and writing Passive voice Range of sentence types using variety of co-ordinating and subordinating conjunctions Variety of references to the same thing to avoid repetition Adverbials of time and place to link ideas across paragraphs Synonyms Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Use of colon and semi-colon to indicate relationship between independent clauses Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Use of dash to mark relationship between independent clauses Words ending -ible, -ibly Tricky words: harass, hindrance, identify, immediately, individual, interfere Words ending –able, ably Tricky words: interrupt, language, leisure, lightning, marvellous, mischievous Use of hyphen (e.g. reenter) Use of colon and semi-colon to indicate relationship between independent clauses Parenthesis to indicate extra Tricky words: muscle, necessary, neighbour, information nuisance, occupy, occur Commas to mark clauses and Words ending –cious, tious to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Tricky words: Speech punctuation opportunity, parliament, persuade, physical, prejudice, privilege 43 Journey to Jo’burg Becoming Media Savvy To write an alternative ending for the book Viewpoint Write script for Tone established chat show in style of another Becoming Media Savvy Spy School Create cinema Persuasive words and ad for new soft phrases drink Create a spy Punctuation training manual St George and the Dragon Writing legend in the style of original Plural nouns/verbs Cohesive devices between paragraphs (including repetition, grammatical connections and ellipses) Structures of formal/informal speech (characterisation through dialogue) Vocabulary associated with formal/informal speech and writing Structures of formal/informal speech (characterisation through dialogue) Vocabulary associated with formal/informal speech and writing Synonyms Use a range of sentence types: simple and complex, using a range of conjunctions Adverbs of possibility Vocabulary associated with formal/informal speech and writing Structures and vocabulary associated with formal speech and writing Passive voice Subjunctive tense (if you were to find yourself in a tight situation..) Use a range of sentence types: simple and complex using a range of conjunctions Cohesive devices between paragraphs (including repetition, grammatical connections and ellipses) Tense choices (past continuous/past perfect/present) to refer backwards and forwards Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Use of dash to mark relationship between independent clauses Ellipses Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Apostrophes for contraction and possession Words ending –tial, -cial Tricky words: profession, programme, pronunciation, queue, recognise, recommend Words ending –ant, ance, -ancy Tricky words: relevant, restaurant, rhyme, rhythm, sacrifice, secretary Commas to mark clauses and Words ending –ent, ence, -ency to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Use of colon and semi-colons Tricky words: shoulder, signature, sincere(ly), to introduce items in a list soldier, stomach, sufficient Commas to mark clauses and Words ending –ent, ence, -ency to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Use of colon and semi-colons Tricky words: suggest, symbol, system, to introduce items in a list temperature, thorough, twelfth Use of colon and semi-colon Adding suffixes beginning with vowel to indicate relationship between independent clauses letters to words ending – Parenthesis to indicate extra fer** information Tricky words: variety, Speech punctuation vegetable, vehicle, yacht, although, though 44 *The ‘r’ is doubled if the –fer is still stressed when the ending is added; the ‘r’ is not doubled if the –fer is no longer stressed. 45 Wings 5.2 Writing Modules Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks), determiner, pronoun, possessive pronoun, adverbial, modal verb, relative pronoun, relative clause, parenthesis, bracket, dash, cohesion, ambiguity, colon, semi-colon, ellipsis, hyphen, bullet points, subject, object, active, passive, synonym, antonym Purpose Story-writing - legends Story-writing - myths Non-chronological report Discursive report To be used after St George and the Dragon/The Mousehole Cat Greek Myths Quakes, Floods and other Disasters Stand-alone (no book) Mini Lesson: Characterisation Building suspense Formal and impersonal style Discursive language Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Language structures of informal speech (e.g. fragmented sentences/question tags)/narration Varied references to same thing to avoid repetition Language structures of informal speech (e.g. fragmented sentences/question tags)/narration Linking ideas across and within paragraphs using tense choices Formal language choices Passive voice Devices to build cohesion within and between paragraphs Varied references to same thing to avoid repetition Subjunctive tense Grammar/Editing Focus Inverted commas for direct speech (including end punctuation) Commas to clarify meaning (mark clauses) Inverted commas for direct speech (including end punctuation) Commas to clarify meaning (mark clauses) Commas to clarify meaning (mark clauses) Colon/semi-colon to mark independent clauses Commas to clarify meaning (mark clauses) Colon to introduce list and semi-colon to separate items in list 46 Wings 5.3 Treasure Hunts Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks), determiner, pronoun, possessive pronoun, adverbial, modal verb, relative pronoun, relative clause, parenthesis, bracket, dash, cohesion, ambiguity, colon, semi-colon, ellipsis, hyphen, bullet points, subject, object, active, passive, synonym, antonym Writing Goal: Mini Lesson: The Firework Maker’s Daughter To rewrite part of Powerful verbs the story from another POV The Firework Maker’s Daughter To write a book review The Firework Maker’s Daughter To rewrite ending Powerful paragraphs Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Meaningful sentences Paragraphs to organise material by change of mood Cohesive devices between paragraphs (e.g. referring forwards and backwards, grammatical connections, ellipses) Synonyms Structures and vocabulary associated with formal speech and writing Passive voice Subjunctive tense Grammar/Editing Focus Paragraphs to organise material by change of mood Cohesive devices between paragraphs (e.g. referring forwards and backwards, grammatical connections, ellipses) Synonyms Suggested Spelling focus (Respond to gaps in Ellipses Use of colon and semi-colon children’s knowledge) to indicate relationship Tricky words: take from between independent common mistakes in clauses children’s writing (Respond to gaps in Commas to indicate children’s knowledge) parentheses Use of dash to indicate Tricky words: take from relationship between common mistakes in independent clauses children’s writing (Respond to gaps in Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify children’s knowledge) meaning Attention to end punctuation Tricky words: take from common mistakes in in speech children’s writing 47 Classic Extracts To add details Speech punctuation (including dialogue) to a scene from ‘Little Women’ Range of sentence types using variety of co-ordinating and subordinating conjunctions Vocabulary associated with a period in history Synonyms Classic Extracts To write an Prepositions additional scene for ‘Black Beauty’ Poems from To write an oldDifferent Times fashioned sounding poem Archaic Language/language devices Poems to be Performed Conventions of poetry writing To write a monologue Vocabulary associated with a period in history Range of sentence types using variety of co-ordinating and subordinating conjunctions Cohesive devices between paragraphs (e.g. referring forwards and backwards, grammatical connections, ellipses) Vocabulary associated with a period in history Synonyms Cohesive devices between stanzas, e.g. repetition Synonyms ‘Flow’ of poem when read aloud Poems to be Performed To write a collaborative poem to be performed Word order Synonyms ‘Flow’ of poem when read aloud Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Use of colon and semi-colon to indicate relationship between independent clauses Commas to indicate parentheses Use of dash to mark relationship between independent clauses (Respond to gaps in children’s knowledge) Tricky words: take from common mistakes in children’s writing (Respond to gaps in children’s knowledge) Tricky words: take from common mistakes in children’s writing Use of semi-colon to indicate (Respond to gaps in children’s knowledge) relationship between independent clauses Tricky words: take from common mistakes in children’s writing (Respond to gaps in Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify children’s knowledge) meaning Use of colon, semi-colon and Tricky words: take from dash to indicate relationship common mistakes in children’s writing) between independent clauses Commas to mark clauses (Respond to gaps in children’s knowledge) and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Tricky words: take from Use of dash to mark common mistakes in relationship between children’s writing independent clauses Ellipses 48 How to Persuade People To write a Building complex persuasive letter sentences How to Persuade People To write the Commas to separate script for a radio clauses advert Lost Boy Digitext To rewrite part of Punctuation skills the story in conventional form Vocabulary and sentence structures associated with formal/informal speech and writing Range of sentence types using variety of co-ordinating and subordinating Subjunctive tense Modal verbs Commas to indicate parentheses Use of colon, semi-colon and dash to indicate relationship between independent clauses (Respond to gaps in children’s knowledge) Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Use of colon and semi-colons to introduce items in a list (Respond to gaps in children’s knowledge) Commas to mark clauses and to avoid ambiguity/clarify meaning Commas to indicate parentheses (Respond to gaps in children’s knowledge) Use a range of sentence types: simple and complex using a range of conjunctions Adverbs of possibility Vocabulary and sentence structures associated with formal/informal speech and writing Cohesive devices between paragraphs (e.g. referring forwards and backwards, grammatical connections, ellipses) Use a range of sentence types: simple and complex using a range of conjunctions Structures and vocabulary of informal speech (characterisation through dialogue) Tricky words: take from common mistakes in children’s writing) Tricky words: take from common mistakes in children’s writing Tricky words: take from common mistakes in children’s writing 49 Fields of Glory Digitext To write autobiography Cohesion within and between paragraphs Use a range of sentence types: simple and complex using a range of conjunctions and relative clauses Cohesive devices between paragraphs (including repetition, grammatical connections and ellipses) Tense choices (past continuous/past perfect/present) to refer backwards and forwards Use of colon and semi-colon to indicate relationship between independent clauses Parenthesis to indicate extra information (Respond to gaps in children’s knowledge) Tricky words: take from common mistakes in children’s writing *The ‘r’ is doubled if the –fer is still stressed when the ending is added; the ‘r’ is not doubled if the –fer is no longer stressed. N.b. Instruction on layout devices (e.g. headings, sub-headings, columns, bullets and tables) to structure text is not provided for in the above scheme (as it is does not feed directly into improving writing skills) – this will need to be covered in other curriculum areas (e.g. science). 50 Wings 5.3 Writing Modules Noun, noun phrase, statement, question, exclamation, command, compound, suffix, adjective, adverb, verb, tense (past, present), apostrophe, comma, preposition, conjunction, word family, prefix, clause, subordinate clause, direct speech, consonant, consonant letter, vowel, vowel letter, inverted commas (or speech marks), determiner, pronoun, possessive pronoun, adverbial, modal verb, relative pronoun, relative clause, parenthesis, bracket, dash, cohesion, ambiguity, colon, semi-colon, ellipsis, hyphen, bullet points, subject, object, active, passive, synonym, antonym Purpose Narrative To be used after Classic Extracts Mini Lesson: Context (setting) Narative - plot The Firework Maker’s Daughter Plot development Focus for Modelled/Guided Writing Language structures of informal speech (e.g. fragmented sentences/question tags)/narration Varied references to same thing to avoid repetition Language structures of informal speech (e.g. fragmented sentences/question tags)/narration Linking ideas across and within paragraphs using tense choices Grammar/Editing Focus Inverted commas for direct speech (including end punctuation) Commas to clarify meaning (mark clauses) Inverted commas for direct speech (including end punctuation) Colons and semi-colons to mark independent clauses Also in Phase 3 Consolidation Units (to be used as stand-alones towards end of Wings 5 year: planning, powerful paragraphs, prompt interpretation (focus on any grammar features the children are still weak on). 51