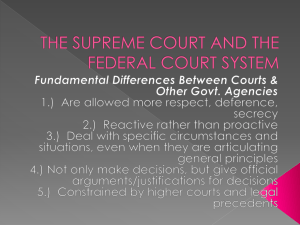
The Judiciary
advertisement
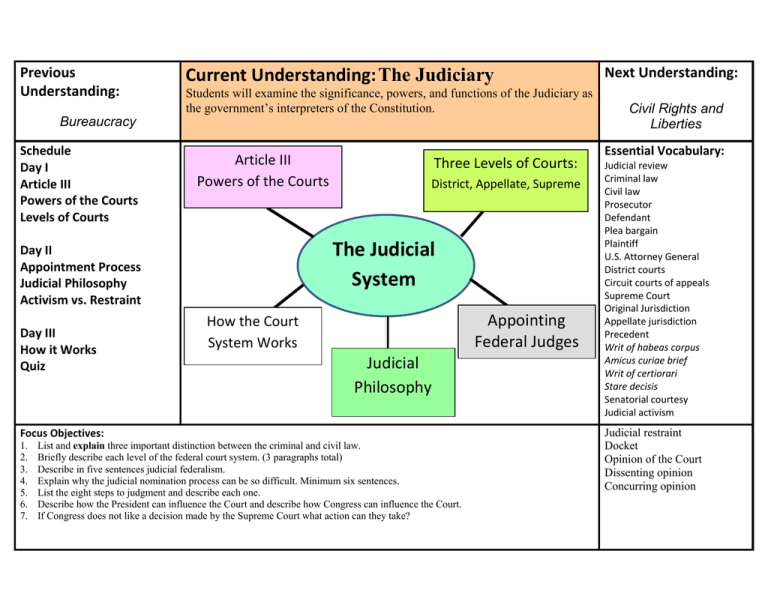
Previous Understanding: Current Understanding: The Judiciary Students will examine the significance, powers, and functions of the Judiciary as the government’s interpreters of the Constitution. Bureaucracy Schedule Day I Article III Powers of the Courts Levels of Courts Article III Powers of the Courts District, Appellate, Supreme The Judicial System Day II Appointment Process Judicial Philosophy Activism vs. Restraint Day III How it Works Quiz Three Levels of Courts: Appointing Federal Judges How the Court System Works Judicial Philosophy Focus Objectives: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. List and explain three important distinction between the criminal and civil law. Briefly describe each level of the federal court system. (3 paragraphs total) Describe in five sentences judicial federalism. Explain why the judicial nomination process can be so difficult. Minimum six sentences. List the eight steps to judgment and describe each one. Describe how the President can influence the Court and describe how Congress can influence the Court. If Congress does not like a decision made by the Supreme Court what action can they take? Next Understanding: Civil Rights and Liberties Essential Vocabulary: Judicial review Criminal law Civil law Prosecutor Defendant Plea bargain Plaintiff U.S. Attorney General District courts Circuit courts of appeals Supreme Court Original Jurisdiction Appellate jurisdiction Precedent Writ of habeas corpus Amicus curiae brief Writ of certiorari Stare decisis Senatorial courtesy Judicial activism Judicial restraint Docket Opinion of the Court Dissenting opinion Concurring opinion