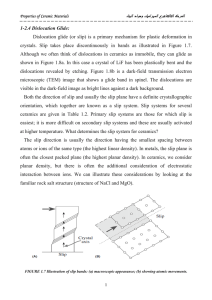
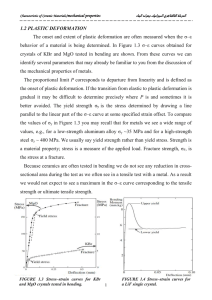
Materials Science
advertisement

Review: FE Exam
• Text: “Materials Science and Engineering:
An Introduction,” 6th ed., William D.
Callister, Jr., Wiley, 2003.
Review: FE Exam
– Part 1 – atomic structure & bonding
• What holds materials together?
– Part 2 – Imperfections in solids
• How are they packed?
– Part 3 – mechanical properties
• How do they deform?
Review: Chapter 1 – Introduction
• Types of Materials
– Metals
– Polymers
– Ceramics
Review: Chapt 2-Atomic Structure
• Atomic Number, Atomic Weight, etc.
• Periodic table
– Electron Structure - valence electrons –
unfilled shells
• Bonding
– ionic
– covalent
– metallic
– van der Waals
Review: Chapt 3 – Crystal
Structures
• Unit Cell
– Metals
• BCC
• FCC
• HCP
• Atomic packing factor
• Coordination number
• Crystallographic directions [uvw]
families of directions <uvw>
• Linear density of atoms (ld) = atoms/unit
length
Review: Chapt 3 – Crystal
Structures (cont.)
• Miller indices of planes (hkl)
families of planes {hkl}
• Planar density (pd) = # of atoms/ unit area
(pd) = S.A. atoms/S.A. unit cell
• X-Ray Diffraction
– Bragg’s law
dhk
n
2 sin
Review: Chapter 4
• Imperfections
– Point defects
•
•
•
•
Interstitial
Vacancy
Substitution
Solid solutions
– Line defects
• Edge dislocation - Burgers vector perpendicular to
dislocation line
• Screw dislocation - Burgers vector parallel to
dislocation line
– Planar defects
• Twin
• Stacking fault
• Grain Boundary
Review: Chapter 4 (cont.)
• Microscopy
– Optical
– Electron Microscopy
– Sample Prep – polishing & etching
Review: Chapter 5
• Diffusion
– Vacancy diffusion
– Interstitial diffusion
– Fick’s First Law
Second Law
– Temp effect
– Slab- non-steady state
dC
J D
dx
C
2C
D 2
t
x
Q
D D0 exp d
RT
C x C0
x
1 erf
C s C0
2 Dt
Review: Chapter 19
• Thermal Properties
– Heat Capacity
• C = dQ/dT Cp > Cv
– phonons
– thermal expansion coefficient
• l/l = l T
– thermal conduction of heat
• q = -k (dT/dx)
– k = heat transfer coefficient
Review: Chapter 6
Mechanical Properties
• Stress vs. strain
• Hooke’s law
s
F
A0
0
e
0
sEe
TS
sy
sF
E
Review: Chapter 6
• Poisson’s Ratio
• Toughness
• Resilience
• Hardness
ey
ex
ez
ez
Review – Chapter 7
Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms
• Deformation by motion of dislocations
– Slip plane – plane of easiest deformation
– Slip direction – direction of easiest slippage
– Slip system – direction and plane
• Applied stress must be resolved along slip direction
– = s cos cos
• Twinning
• Mechanism of strengthening
– Grain size reduction
– Solid-solution hardening
• impurities reduce mobility of dislocations
– Strain hardening %CW = 100 x (A0-Af)/A0
• Recovery, recrystallization, & grain growth
Review – Chapter 8
Fracture – failure
– Ductile fracture
• Large deformations
– cone & cup
– small necked regions
– Brittle fracture
• Almost no deformation other than failure
– transgranular – within grain
– intergranular- between grains
Review, Chapter 8 (cont.)
• Griffith Crack - Stress concentration
sm K t s0
– Critical stress
2E s
sc
a
1
2
• Fatigue – cyclic stress
• Creep
Review- Chapter 9
Phase Diagrams
• Isomorphous system
– 1. How many &
which phases
– 2. Use tie line to
read compositions
– 3. Use lever rule
to get weight
fractions
Review- Chapter 9
• binary eutectic system
– 1. How many & which phases
– 2. Use tie line to read compositions
– 3. Use lever rule to get weight fractions
Review- Chapter 9 (cont.)
• Eutectic
• Eutectoid
• Peritectic
L
S1
cool
heat
cool
heat
S1+L
• Hypoeutectoid
• Hypereutectoid
S1+S2
S2+S3
cool
heat
S2
Review - Chapter 10
Rate of Phase Transformation
• Nucleation process
Review - Chapter 10 (cont)
• Phase transformations vs. temperature
and time
– Pearlite
– Martensite
– Bainite
– Spheroidite
Chapter 11
• Heat Treatments
Review – Chapter 11
Fabrication of Metals
• Forming
– Forging
– Rolling
– Extrusion
– Drawing
• Casting
• Powder metallurgy
• Welding
• Machining
• Alloy Nomenclature
• Cast Irons – addition of Si catalyzes graphite
formation
• Refractories
Review – Chapter 12
Ceramics
• Crystal structures
– oxygen larger – generally in FCC lattice
– cations go in lattice sites based on
•
•
•
•
size
stoichiometry
charge balance
bond hybridization
– no good slip planes – brittle failure
• Silicates
– built up of SiO44– layered
– countercations to neutralize charge
Chapter 12 – Ceramics
• Carbon forms
– diamond
– graphite
– fullerenes
– amorphous
• Lattice imperfections
– Frenkel defect – cation displaced into
interstitial site
– Schottky defect – missing cation/anion pair
• Phase diagrams
• Mechanical properties
Chapter 13 – Ceramics (cont)
• Glasses
– amorphous sodium or borosilicates
– Forming
• pressing
• drawing
• blowing
• Clay products - forming
– Hydroplastic forming
– Slip casting
– Refractories
– Powder pressing
• Cements
• Advanced ceramics
Chapter 14 – Polymers
• Types of polymers
– Commodity plastics
•
•
•
•
•
PE = Polyethylene
PS = Polystyrene
PP = Polypropylene
PVC = Poly(vinyl chloride)
PET = Poly(ethylene terephthalate)
– Specialty or Engineering Plastics
•
•
•
•
Teflon (PTFE) = Poly(tetrafluoroethylene)
PC = Polycarbonate (Lexan)
Polysulfones
Polyesters and Polyamides (Nylon)
Chapter 14 – Polymers
• Molecular Weight
– Actually a molecular weight distribution
– Mn = Number-averaged molecular weight
– Mw = Weight-averaged molecular weight
– Polydispersity = Mw/Mn
• A measure of the width of the distribution
• Chain Shapes
– linear
– branched
– crosslinked
– network
Chapter 14 & 15 – Polymers
• Isomerism
– Isotactic
– Syndiotactic
– Atactic
– Cis vs. Trans
– Copolymers
• Random
• Alternating
• Block
• Crystallinity
– Spherulites
Chapter 16 – Composites
• Combine materials with objective of getting a
more desirable combination of properties
• Dispersed phase
• Matrix
• Particle reinforced
– large particle
– dispersion strengthened
• Rule of mixtures
– Upper limit
Ec(u) = EmVm + EpVp
EmEp
E c
– Lower limit
VmEp VpEm
Chapter 16 – Composites
• Reinforced concrete
• Prestressed concrete
• Fiber reinforced
– Short vs. long fibers
– Critical length
sfd
c
– allignment
2c
Chapter 18 – Electrical Properties
Definitions
• R = resistance = Ohms
• = RA/l = resistivity = ohm meter
• s = 1/ = conductivity
• C = Q/V = capacitance
• er = e/eo = dielectric constant
Chapter 18 – Electrical Properties
• Energy Bands – valance vs. conduction
– Conductor – no band gap
– Insulator – wide gap
– Semiconductor – narrow gap
• Intrinsic – pure or compound
– Electron vs. hole (which carries charge)
• Extrinsic (doped)
– n-type – donor levels – extra electrons
– p-type – acceptor levels – extra holes
• Microelectronics
– pn junction – rectifier diode
– npn transistor
Chapter 20 – Superconductivity
• Tc = temperature below which
superconducting
= critical temperature
Jc = critical current density if J > Jc not
superconducting
Hc = critical magnetic field if H > Hc not
superconducting
• Meissner Effect - Superconductors expel
magnetic fields
Chapter 21 – Optical Properties
• Electromagnetic radiation
hc
E h
c (velocity of light in vacuum)
n refractive index
v (velocity of light in medium)
• Angle of refraction at interface
n sin
n sin
Chapter 21 – Optical Properties
• Light interaction with solids
2
n
1
– Reflection
R
reflectivi ty
n 2
– Absorption
I
– Scattering
ln t
– Transmission
I0
• Semiconductors – absorb light with energy
greater than band gap
• Luminescence – emission of light by a material
– phosphorescence = If very stable (long-lived = >10-8 s)
– fluorescence = If less stable (<10-8 s)
• LASERS – coherent light
• Fiber optics
Questions???
• Contact Prof. David Rethwisch to discuss
questions.
– office 4139 SC
– Phone 335-1413
– email david-rethwisch@uiowa.edu