Unit 9: Boom to Bust 1920 - 1939 Study Guide Key Name
advertisement
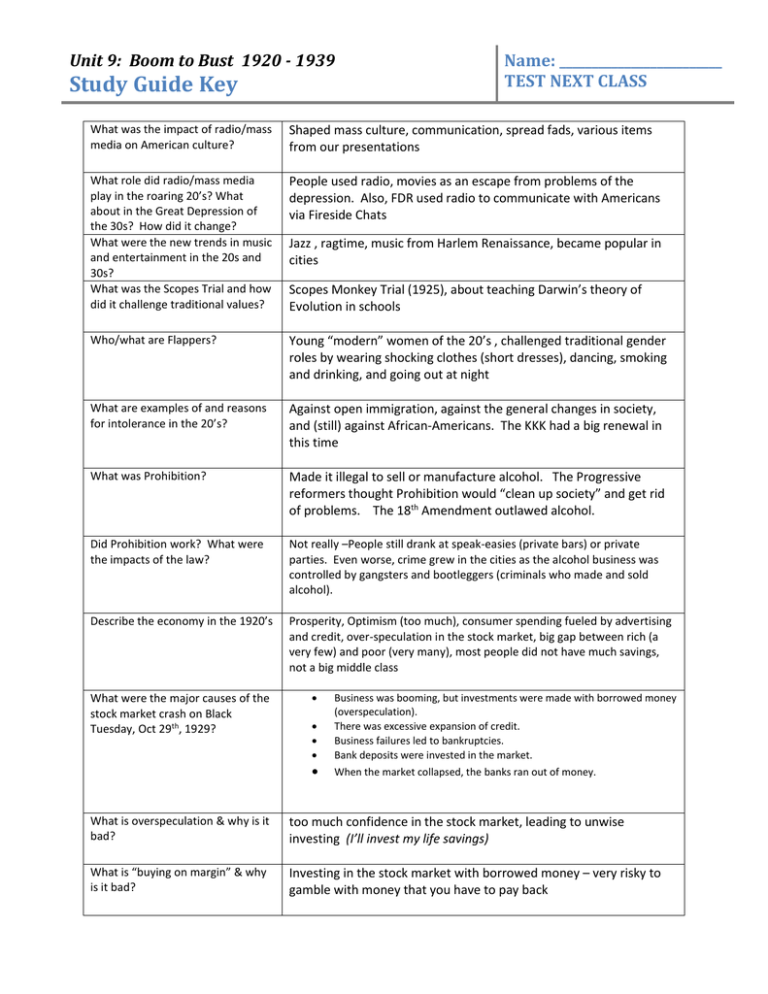
Unit 9: Boom to Bust 1920 - 1939 Study Guide Key Name: _________________________ TEST NEXT CLASS What was the impact of radio/mass media on American culture? Shaped mass culture, communication, spread fads, various items from our presentations What role did radio/mass media play in the roaring 20’s? What about in the Great Depression of the 30s? How did it change? What were the new trends in music and entertainment in the 20s and 30s? What was the Scopes Trial and how did it challenge traditional values? People used radio, movies as an escape from problems of the depression. Also, FDR used radio to communicate with Americans via Fireside Chats Who/what are Flappers? Young “modern” women of the 20’s , challenged traditional gender roles by wearing shocking clothes (short dresses), dancing, smoking and drinking, and going out at night What are examples of and reasons for intolerance in the 20’s? Against open immigration, against the general changes in society, and (still) against African-Americans. The KKK had a big renewal in this time What was Prohibition? Made it illegal to sell or manufacture alcohol. The Progressive reformers thought Prohibition would “clean up society” and get rid of problems. The 18th Amendment outlawed alcohol. Did Prohibition work? What were the impacts of the law? Not really –People still drank at speak-easies (private bars) or private parties. Even worse, crime grew in the cities as the alcohol business was controlled by gangsters and bootleggers (criminals who made and sold alcohol). Describe the economy in the 1920’s Prosperity, Optimism (too much), consumer spending fueled by advertising and credit, over-speculation in the stock market, big gap between rich (a very few) and poor (very many), most people did not have much savings, not a big middle class What were the major causes of the stock market crash on Black Tuesday, Oct 29th, 1929? Jazz , ragtime, music from Harlem Renaissance, became popular in cities Scopes Monkey Trial (1925), about teaching Darwin’s theory of Evolution in schools Business was booming, but investments were made with borrowed money (overspeculation). There was excessive expansion of credit. Business failures led to bankruptcies. Bank deposits were invested in the market. When the market collapsed, the banks ran out of money. What is overspeculation & why is it bad? too much confidence in the stock market, leading to unwise investing (I’ll invest my life savings) What is “buying on margin” & why is it bad? Investing in the stock market with borrowed money – very risky to gamble with money that you have to pay back What were the effects of the stock market crash? Clients panicked, attempting to withdraw their money from the banks, but there was nothing to give them. (Because all the bank’s customers had panicked and come to get their money, and/or the bank had invested some of their money in the stock market.) Banks failed, and closed, and businesses failed, because there were no new investments. What were the major causes of the Great Depression? 1. The stock market crash of 1929 and collapse of stock prices (obvious) 2. Federal Reserve’s failure to prevent widespread collapse of the nation’s banking system in the late 1920s and early 1930s, leading to severe contraction in the nation’s supply of money in circulation (the “heart” did not pump more $$ into the economy) 3. High protective tariffs that produced retaliatory tariffs in other countries, strangling world trade (Tariff Act of 1930, popularly called the Hawley-Smoot Act – dumb) What were the major impacts of the Great Depression? Why didn’t Hoover do more to fix the Depression when it started? What was FDR’s philosophy about the role of government? How did FDR communicate with the American people? What was FDR’s plan for fixing the Depression? What were the three R’s? SSA: Social Security Act of 1935 – What did it do? What was the goal of Relief programs of the New Deal? Give two examples and what they did. What was the goal of Recovery programs of the New Deal? Give two examples and what they did. What was the goal of Reform programs of the New Deal? Give two examples and what they did. What was the legacy of New Deal? Unemployment and homelessness Collapse of the financial system (bank closings) Decline in demand for goods Farm foreclosures and migration West Political unrest (growing militancy of labor unions) Didn’t think it was an appropriate role for the Fed gov’t. Thought it was business’s job to take care of boom/bust cycles in the economy (which were pretty common). He was a laissez-faire kind of Republican, pretty standard for his day.. He thought the government should have a more active role in solving problems. Fireside Chats. Radio addresses. Roosevelt rallied a frightened nation in which one in four workers 25% was unemployed. (“We have nothing to fear, but fear itself.”) New Deal: Relief, Recovery, Reform Social Security Act offered safeguards for workers. Safety Net social insurance, workers and empoyers pay into it, then when you’re too old or sick to work, you can get payments. direct payment to people for immediate help (Works Progress Administration) WPA provided all kinds of jobs, construction,arts, teaching, etc. Also, CCC – Civilian Conservation Corps – for young men , jobs outdoors. Recovery: bring the nation out of the depression over time – restart the economy’s major sectors (industry, farming, banking) Agricultural Adjustment Administration—AAA) and TVA. AAA – tried to regulate the farming industry Reform : corrected unsound banking and investment practices (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation—FDIC) and SEC Federal Deposit Insurance Corp – insures deposits, so if your bank goes out of business (or burns down, or the owner runs off with all the money), you won’t lose all your money. The gov’t insures it. The legacy of the New Deal influenced the public’s belief in the responsibility of government to deliver public services, to intervene in the economy, and to act in ways that promote the general welfare. Some programs are still around today.