PPP – COPDstudent view

Nursing 110
Beverlyn M. Jackson RN MSN CCRN
COPD
Asthma
A chronic hyperactive disorder of the airways.
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic productive cough for 3 months during each of 2 consecutive years.
Emphysema
Abnormal permanent enlargement of the air spaces distal to the terminal bronchioles, accompanied by destruction of their walls.
Asthma
Chronic Airflow Limitation Disease
Asthma Types
Intrinsic
Non-allergic or atopic
Cause non-specific; seen in adults; worsens over life.
Extrinsic
Allergic or atopic
Increase bronchoconstriction and
Bronchospasms
Pathophysiology of Chronic Bronchitis
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF EMPHYSEMA
Pathophysiology of Emphysema
Pathophysiology of Emphysema
STRESSORS FOR COPD
CIGARETTE SMOKING IS
THE MOST IMPORTANT
STRESSOR FOR COPD
SECONDHAND SMOKE
CAN ALSO LEAD TO
RESPIRATORY
PROBLEMS
ALPHA
1
-ANTITRYPSIN
DEFICIENCY (AAT)
AIR POLLUTION
ASSESSMENT
Intake Summary/Patient History
Chief Complaint
SHORTNESS OF BREATH
Activities that cause SOB
Cough
Sputum
•INTAKE
SUMMARY/DEMOGRAPHIC
DATA
AGE, SEX & ETHNIC
ORIGIN
•PERSONAL AND FAMILY
HISTORY
MAJOR ILLNESSES
SMOKING
DIET
•SOCIOECONOMIC STATUS
MARITAL STATUS
OCCUPATION
ASSESSMENT
ASSESSMENT
Demographic
Data
Age
Race
Gender
ASSESSMENT
PERSONAL AND
FAMILY HISTORY
History of Major Illness
Medication History
Nutritional Status
SMOKING HISTORY
Family history
ASSESSMENT
Socioeconomic
History
Occupation
PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT
Appearance
Forward bending posture
Barrel chest
Use of accessory muscles
Color
Bronchitis (cyanosis –
Blue Bloater)
Emphysema) Pink Puffer
PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT
Respiratory Rate
Dyspnea
Use of accessory muscles
Abnormal breath sounds
Wheezing
No Breath Sounds
Pneumothorax
PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT
Cardiac Assessment
Rate and Rhythm
Cor Pulmonale
Edema
PSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT
Isolation
Change in economic status
Anxiety
LABORATORY ASSESSMENT
Arterial Blood Gas (ABG)
Hypoxemia -decreased PaO
2
< 80mmHG
Hypercarbia -increased Pa CO
2
> 45mmHG
Respiratory acidosis, with metabolic alkalosis compensation
Pulse Oximetry
Less than the normal range of 95% -100%
AAT
LABORATORY ASSESSMENT
H&H
Polycythemia
Sputum
C&S
WBC
IMAGING ASSESSMENT
Chest xray
Hyperinflation
Blebs
Bullae
PFT ASSESSMENT
Diagnosis of COPD
Obstructive versus
Restrictive lung disease
FEV1/FVC used primarily to diagnose COPD.
Forced Expiratory
Volume (FEV) compared to Forced Vital Capacity
(FVC) expressed as ratio used to determine severity
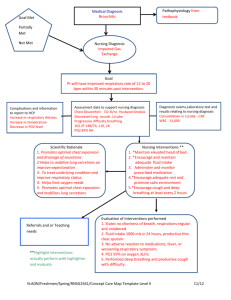
Analysis/Nursing Diagnosis
Impaired Gas Exchange R/T altered oxygen supply caused by obstruction of airways by secretions, bronchospasm/reduced airway size, alveoli destruction;
AEB- dyspnea, weak cough, changes in VS, cyanosis, altered ABG, anxiety.
Expected Outcome: Respiratory rate of 20-26, able to cough up secretions without difficulty, VS within patient’s normal range, no cyanosis, baseline ABG, normal mental status.
Nursing Diagnosis
Ineffective Breathing Pattern R/T Airway obstruction, diaphragm flattening, fatigue, and decreased energy.
AEB: Increased respiratory rate, limited diaphragmatic movement, excessive use of accessory muscles
Expected outcomes: Normal respiratory rate, synchronous thoracoabdominal movement, normal use of accessory muscles
Nursing Diagnosis
Ineffective Airway Clearance R/T Bronchospasm, thick retained secretions, fatigue
AEB: dyspnea, use of accessory muscle, wheezing, persistent cough
Expected Outcomes: Maintain patent airway with clear breath sounds, effective cough and expectoration of secretions
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
Primary Interventions
Assess VS and respiratory rate q2 hours
Elevated HOB and position patient to ease the work of breathing
Assess color
Assess level of anxiety
Assess for confusion
Monitor pulse ox and ABG’s
NO SMOKING
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
Primary Interventions
Assess the breathing pattern
Secondary
Interventions
Breathing Techniques
Diaphragmatic breathing or belly breathing
Pursed lip Breathing
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
Secondary Interventions
Encourage patient to cough
Suction as needed
Administer O 2 therapy
USE CAUTION
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
Secondary Interventions
AM Coughing
Chest physiotherapy
Suction as needed
Hydration
Tertiary Interventions
Teach and review coughing techniques and hydration
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
Secondary Interventions
Drug Therapy
Bronchodilators
Cholinergic Antagonist
Atrovent
Short and Long Acting Beta
2
Agonist
Albuterol
Serevent
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
Secondary Interventions
Drug Therapy
NSAIDS
Tilade
Mucolytic Agents
Mucomyst
Guaifenisin
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
Secondary Interventions
Drug Therapy
Methylxanthines
Theophylline
Anti-inflammatories
Corticosteroids
Flovent
Prednisone
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
Secondary Interventions
Positioning
Energy Conservation
Tertiary Interventions
Teach and review the breathing techniques, positioning and energy conservation
Complications of COPD
Infection
Pulmonary HTN
Secondary
Polycythemia
Hypoxemia and
Acidosis
Other
Chronic Airflow Limitation diseases
Bronchiectasis
Cystic Fibrosis
THE END!!!
Reference:
Iggy pg. 548-566 (8 th ed.)