CHAPTER 16 Bailments

CHAPTER
16
Bailments
16-1 Bailments
16-2 Bailor and Bailee Duties
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
16-1 Bailments
GOALS
Discuss the ways in which bailments are created and ended
Identify common real-life bailments
Chapter 16
Slide 2
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
FOCUS
What is a bailment and have you been involved in one?
Chapter 16
Slide 3
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
HOW ARE BAILMENTS
CREATED AND ENDED?
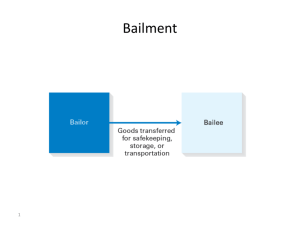
Bailment
Transfer of possession and control of personal property subject to an agreement to return the property or deliver it to a 3 rd party
Delivery
Acceptance
Consideration
Bailor
Chapter 16
Bailee
Slide 4
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
Examples
Business
Hold something as security
You give someone something of yours to sell
Dispose of as you direct
Personal
Have someone look after for safekeeping
Lending something to someone to keep
Chapter 16
Slide 5
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
HOW ARE BAILMENTS
CREATED AND ENDED?
Possession
1.
Actual bailments
Actual or constructive delivery
2.
Constructive bailments
Person in possession of property holds it while law decides who to deliver it to
Control
Custody
Chapter 16
Slide 6
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
Disposition of Goods
Typically agreed that goods get returned to bailor
Sometimes goes to another party
Goods must be returned identical to previous state
Wear and tear
Modifications
Fungible
No difference
Chapter 16
Slide 7
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
Termination of the Bailment
Previously agreed upon time, purpose, or mutual decision to end bailment
Death, insanity, or bankruptcy
Rights can be transferred to deceased’s estate
Chapter 16
Slide 8
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
What are the three ways in which bailments are ended?
Chapter 16
Slide 9
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
COMMON EXAMPLES OF
BAILMENTS
Bailments for transport
Common carrier
Bailments for hire
Rental of property
Bailments for services
Repairs
Bailments for sale
Consignment
Chapter 16
Slide 10
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
Name four common examples of bailments.
Chapter 16
Slide 11
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
16-2 Bailor and Bailee Duties
GOALS
Describe the duties owed by the bailee in a bailment
State the bailor’s duties in a bailment
Chapter 16
Slide 12
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
FOCUS
Characteristics of bailment
The subject is tangible personal property
The bailor transfers temporary possession to the bailee
The bailor transfers temporary control to the bailee
The goods must be returned to the bailor or to someone the bailor specifies
Chapter 16
Slide 13
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
Levels of Care
Extraordinary bailment
Goods are bailed with common carriers and hotels
Extraordinary care
Generally means the bailee will be strictly liable for any damage, loss, or injury to the goods
Chapter 16
Slide 14
Only exception is act of war, unforeseeable acts of nature, or acts of police
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
Levels of Care
When only one party benefits from the bailment
Gratuitous bailment
Ordinary care
The bailee will be liable only if negligence occurs
Mutual benefit bailment
Chapter 16
Slide 15
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
Levels of Care
Involuntary bailments
Typically arise accidentally and without consent of the bailee
Minimal care
Only liable for harm to the bailed property if they ignore, waste, or destroy it
Chapter 16
Slide 16
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
DUTIES OWED BY THE BAILEE
IN A BAILMENT
Duty to care for the property (previously mentioned)
Modification of the level of care
Modification by legislation
Modification by contract
Modification by disclaimer
Duty to return the goods
Chapter 16
Slide 17
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
Modification of the Level of Care
By legislation
Airline industry limiting liability for luggage
By contract
By disclaimer
A sign, label, or warning reducing the bailee’s duty of care
Chapter 16
Slide 18
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
Duty to Return the Goods
According to terms
Bailee’s lien
Right of a bailee to retain possession of the bailed property until payment is made
Bailee gives property back to bailor without payment, the bailor loses the right to force the sale of the bailed property to pay the amount due
Chapter 16
Slide 19
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
Name the three levels of care owed bailed goods.
Chapter 16
Slide 20
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
WHAT DUTIES ARE OWED BY
THE BAILOR IN A BAILMENT?
Mutual-benefit bailments
Bailments for the sole benefit of bailor
Bailments for the sole benefit of bailee
Chapter 16
Slide 21
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western
Name the types of bailments in which a bailor has duties.
Chapter 16
Slide 22
Law for Business and Personal Use
© Thomson South-Western