Chapter 3 Powerpoint
advertisement

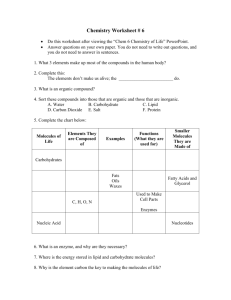
Table of Contents Chapter: Cell Processes Section 1: Chemistry of Life Section 2: Moving Cellular Materials Section 3: Energy for Life Chemistry of Life 1 The Nature of Matter • Matter - anything that has mass and takes up space. • Energy - anything that brings about change. Chemistry in Life 1 Atoms • Nucleus - center of atom • contains protons and neutrons (equal mass) • Proton (+) • Neutron ( ) • Electron (-) •orbits nucleus Click image to view movie. Chemistry in Life 1 Atoms • Electrons involved in chemical reactions. • Atom - mostly empty space Chemistry in Life 1 Elements • Element • made of one kind of atom • in most simple form • each has a 1 or 2 letter symbol Chemistry in Life 1 Elements • Periodic table • Mass • # of Protons • Symbol Chemistry in Life 1 Elements Chemistry in Life 1 Compounds and Molecules • Compounds - made of two or more elements • There are two types of compounds— molecular compounds and ionic compounds. Chemistry in Life 1 Molecular Compounds • Molecular compound • Made of molecules held together by chemical bonds • Share outermost electrons • Have different properties than atoms alone Chemistry in Life 1 Molecular Compounds • Chemical reactions • chemical bonds break • atoms rearranged • new molecules form Chemistry in Life 1 Ions • Ions • Electrically charged atoms • Formed when atoms combine after becoming (+) or (-) Chemistry in Life 1 Ionic Compounds • Ionic Compound – molecule held together because of opposite charges attracting one another • One atom loses electron(s) • Another atom gains electron(s) • Their charge holds them together Chemistry in Life 1 Mixtures • Mixture - combination of substances in which individual substances retain their own properties • Can be solids, liquids, gases, or any combination Chemistry in Life 1 Mixtures • Solution - 2 or more substances mixed evenly • Suspension • substance evenly spread throughout • Will sink to bottom after time Chemistry in Life 1 Organic Compounds • Organic Compounds • always contain carbon and hydrogen • usually are associated with living things. • Inorganic Compounds • make up nonliving things Chemistry in Life 1 Organic Compounds Chemistry in Life 1 Carbohydrates • Carbohydrates • organic molecules that supply energy for cell processes • Sugars and starches • Also part of cell structures Chemistry in Life 1 Lipids • Lipids • do not mix with water • Fats and oils • Large amounts of energy • Part of cell membrane Chemistry in Life 1 Proteins • Proteins • made of amino acids • building blocks of cellular structure • Enzymes • Proteins that regulate chemical reactions Chemistry in Life 1 Nucleic Acids • DNA • deoxyribonucleic acid • contains genetic material • RNA • ribonucleic acid • needed to make enzymes and proteins. Chemistry in Life 1 Inorganic Compounds • Can contain the elements nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. Chemistry in Life 1 Importance of Water • can live for weeks without food • only a few days without water. Chemistry in Life 1 Importance of Water • all the chemical reactions in living things take place in water solutions • most organisms use water to transport materials Chemistry in Life 1 Characteristics of Water • Negative part of a water molecule is attracted to the positive part of another water molecule Chemistry in Life 1 Characteristics of Water • temperature of water changes slowly • acts like insulation Chemistry in Life 1 Characteristics of Water • water freezes - ice crystals form • Ice floats – insulates water below Section Check 1 Question 1 _______ is anything that has mass and takes up space. Answer The answer is Matter. Everything in your environment is made of matter. Section Check 1 Question 2 A(n) _______ is made up of only one kind of atom. Answer The answer is element. An element can’t be broken down into a simpler form by chemical reactions. Section Check 1 Question 3 Which best describes the structure in this illustration? A. atom B. element C. molecular compound D. ionic compound Section Check 1 Answer The answer is C. Molecular compounds form when different atoms share their outermost electrons. Moving Cellular Materials 2 Passive Transport • Cell’s membrane selectively permeable • allows some things to enter or leave and keeps other things in or out Moving Cellular Materials 2 Passive Transport • Passive transport - movement of substances through the cell membrane without the use of energy • 3 Types • Diffusion • Osmosis • Facilitated diffusion Moving Cellular Materials 2 Diffusion • Diffusion - movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration • Equilibrium – when molecules become concentrated equally in all areas Moving Cellular Materials 2 Osmosis—The Diffusion of Water • Osmosis - the diffusion of water through a cell membrane is called. Moving Cellular Materials 2 Facilitated Diffusion • The movement of large molecules through a membrane with the help of transport proteins Moving Cellular Materials 2 Active Transport • Active transport - energy is needed to move materials through a cell membrane against the concentration gradient Moving Cellular Materials 2 Endocytosis and Exocytosis • Endocytosis process of taking substances into a cell by surrounding it with the cell membrane Moving Cellular Materials 2 Endocytosis and Exocytosis • Exocytosis - process of taking substances OUT of a cell by surrounding it with the cell membrane Section Check 2 Question 1 What is diffusion? Answer Diffusion is the type of passive transport in which molecules in a more dense area randomly move to an area that is less dense until equilibrium is reached. Section Check 2 Question 2 _______ is the diffusion of water through a cell membrane. Answer The answer is osmosis. Cells contain water and are surrounded by water. These water molecules move by diffusion into and out of cells. Section Check 2 Question 3 Which carries oxygen throughout your body? A. red blood cells B. white blood cells C. sex cells D. none of the above Section Check 2 Answer The answer is A. Oxygen molecules from the lungs diffuse into red blood cells which carry oxygen throughout your body. Energy for Life 3 Trapping and Using Energy • Metabolism - The total of all chemical reactions in an organism is called. Energy for Life 3 Trapping and Using Energy • Enzymes • Cause chemical reactions • Can be used over and over Click image to view movie. Energy for Life 3 Photosynthesis • Producers Organisms that make their own • Consumers - Organisms that cannot make their own food Energy for Life 3 Photosynthesis • Photosynthesis uses light energy to make sugars (chemical energy), which can be used as food. • Chlorophyll – green pigment found in chloroplasts that performs photosynthesis Energy for Life 3 Energy for Life 3 Storing Carbohydrates • Excess sugar made is stored as starches or other carbohydrates Energy for Life 3 Respiration • Cellular respiration – changes chemical energy into useable energy • Movement, heat, etc. • Requires oxygen Energy for Life 3 Breaking Down Carbohydrates • Carbohydrates Glucose Useable energy Cellular Respiration: Energy for Life 3 Energy for Life 3 Fermentation • Fermentation – releases smaller amount of energy when oxygen is not present • Occurs only in cytoplasm (not mitochondria) Section Check 3 Question 1 _______ is the total of all chemical reactions in an organism. Answer The answer is metabolism. All of the activities of an organism involve chemical reactions in some way. Section Check 3 Question 2 Which does this equation represent? A. respiration B. fermentation C. photosynthesis D. chemosynthesis Section Check 3 Answer The answer is C. During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide and water and combine it with light energy to make sugars, which they use for food. Section Check 3 Question 3 _______ is the type of food molecules most easily broken down by cells. Answer The answer is carbohydrates. As carbohydrates are broken down, energy is released. Help To advance to the next item or next page click on any of the following keys: mouse, space bar, enter, down or forward arrow. Click on this icon to return to the table of contents Click on this icon to return to the previous slide Click on this icon to move to the next slide Click on this icon to open the resources file. Click on this icon to go to the end of the presentation. End of Chapter Summary File