Chapter 2 notes Objectives: Express numbers in scientific notation
advertisement

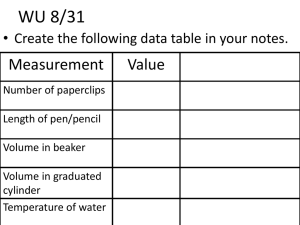
Chapter 2 notes Objectives: Express numbers in scientific notation Convert numbers written in scientific notation to decimal notation Determine the number of significant figures in a given number or measurement Difference between an exact number and measured number Report measured quantities to correct number of significant figures in calculation Learn about seven basic units and use of dimensional analysis to convert one unit to another unit Scientific Notation: Measurements are associated with very large numbers ( 14,000,000,000,000 meters) or very small numbers( 0.000000000001 seconds) Scientific notation can be used to write these numbers more compactly A number written in scientific notation consists of a decimal par and an exponential part The decimal part is a number between 1 and 10 The exponential part is 10 raised to an exponent 1.2 x 105 Expressing the numbers in scientific notation 36,458,000 0.000987 1,286,000 44.550000 19,307,000 0.0000015 514,000 0.00786 Expressing the numbers in decimal notation 3.89 x 109 1.2 x 10-2 8.76 x 1011 6.6 x 10-1 9.95 x 10-5 2.99 x 102 Uncertainty in measurement Uncertainty always exist in measures quantities because of a) Limitation in measuring device b) Visual estimation by an individual Measuring devices commonly used in chemistry lab Balance to find mass of a substance ( kg, g ,cg, mg, µg, ng, pg) 200.0g 200.08g 200.086g 200.0864g Meter stick and a ruler to find length( km, m, cm, mm, µm, nm, pm) 12.25 cm 12.25 m Graduated cylinder to find volume( kL, L, cL, mL, µL, nL, pL) 12.5 mL 20.0 mL Thermometer to find temperature ( ℃ , ℉ , K) 25.0 ℃ 23.3 ℃ All certain digits and the last digit ( estimated) are called significant figures. Uncertainty in the last digit is reported as ± 1 Uncertainty in the measurements 1.20 g ± 121g ± 15. 593 g ± 11.2 g ± Rules for counting significant figures: Nonzero digits are always significant 186 2365 56897 1234567 There are three types of zeros a) Leading zeros to the right of the decimal point that precede ( come before) all the nonzero digits 0.0087 0.0125 0.000023 0.000001 Captive zeros are always significant and they fall between nonzero digits. 4.0008 2.908038 32.0081 Trailing zeros are at the right end of a number. They are significant only if number is written with a decimal point 100 100. 100.0 100.00 1200 1200. 12.20 Exact numbers have unlimited number of significant figures. Exact numbers originate from three sources: Accurate counting of discrete objects, defined quantities, integral numbers that are part of an equation. 8 apples 1 in. = 2.54 cm radius = diameter/2 Rounding of numbers To show your answer to correct number of sig.figs you need to round off your answer 13.35 → 3 sig. figs 13. 34 → 3 sig.figs Round off these numbers to three sig.figs 251.904 0.00985643 3. 9999 5.535691 x 10-7