D.1.2 Outline the experiments of Miller and Urey into
advertisement

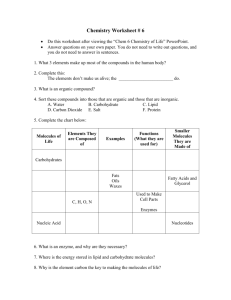
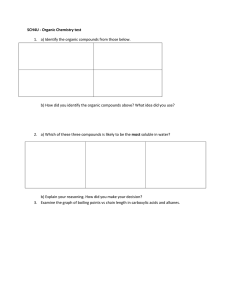
IB Biology Option D D1 Origin of Life on Earth D.1.1 Describe four processes needed for the spontaneous origin of life on Earth 1) The non-living synthesis of simple ______________________: • Obviously if nothing was alive yet, then the source of these molecules had to be _______________ • We can presume that the early Earth had all of the base elements and compounds required • They were somehow combined to make _______________ _____________________ • Maybe the organic compounds were generated here, maybe they were _______________________! D.1.1 Describe four processes needed for the spontaneous origin of life on Earth 2) The assembly of these molecules into _______________: • In order to make the larger molecules necessary for life, the simple organic compounds would have to _________ 3) The origin of _____________________ molecules made inheritance possible: • DNA can’t self replicate, it needs protein enzymes • However some ______ can self-replicate - it can catalyze the formation of copies of itself. • They are called ______________ and are the basis of the RNA World Hypothesis D.1.1 Describe four processes needed for the spontaneous origin of life on Earth 4) The packaging of these molecules into _______________ with internal chemistry different from their surroundings: • The formation of _________________an important step • Closed membrane vesicles can form spontaneously from ____________ • This allowed ________________ between the internal and external environments D.1.2 Outline the experiments of Miller and Urey into the origin of organic compounds Earth’s atmosphere was _____________ in the early days. It did not contain __________ gas until after plants started photosynthesizing Can you identify these molecules? D.1.2 Outline the experiments of Miller and Urey into the origin of organic compounds Earth’s atmosphere was ‘reducing’ in the early days. It did not contain oxygen gas until after plants started photosynthesizing The atmosphere contained: The gases came from abundant volcanic activity D.1.2 Outline the experiments of Miller and Urey into the origin of organic compounds These monomers mixed in the ________________, shallow oceans with chemicals, where it is thought that they reacted to form biological molecules Miller and Urey tried to recreate these conditions in the lab in 1953 They were trying to demonstrate ___________________, the formation of more complex molecules from simpler stock in the primordial soup They combined the molecules from the previous page in a closed glass vessel (simulated ___________), they heated the water (simulated __________________) and sparked electricity through the gases (simulated ____________) D.1.2 Outline the experiments of Miller and Urey into the origin of organic compounds D.1.2 Outline the experiments of Miller and Urey into the origin of organic compounds D.1.2 Outline the experiments of Miller and Urey into the origin of organic compounds After a week they found: Thirteen of the twenty naturally occurring ___________________ Around 15% of the carbon was now in organic compounds D.1.3 State that comets may have delivered organic compounds to Earth ______________ is the hypothesis that life on Earth originated from material delivered by a _________, either in the form of amino acids or as hardy bacteria Space is so empty, yet full of the potential for life Existing bacteria and archaebacteria have been found in odd and extreme environments on Earth: In hot springs, kilometres deep in the crust and even embedded in ice cores from deep inside Antarctica It is feasible that they could survive on or in a comet D.1.3 State that comets may have delivered organic compounds to Earth __________________ could provide the energy for reactions that lead to the formation of complex organic molecules Analysis of the spectra of light coming from the comets reveals the presence of hydrocarbons, _______________ and peptides The bombardment of Earth by comets ___ ________ years ago could have ‘kick started’ chemical evolution D.1.3 State that comets may have delivered organic compounds to Earth The hypothesis that life came an extraterrestrial source: As previously mentioned, ___________________ are out there Mars is smaller than Earth and therefore ______ ______ more quickly, life could have begun there while Earth was still scorching Meteorites and comets impacting on mars could have thrown up debris with early life attached, this could then have crashed on Earth. Meteorites of Mars origin have been found in Antarctica D.1.3 State that comets may have delivered organic compounds to Earth The hypothesis that life came an extraterrestrial source: There is no evidence that life has been transferred in this way. Every now and then there is a news story about “Fossils found in Mars meteorite” but so far this has not been confirmed The extraterrestrial hypothesis still doesn’t address how life formed, just how it could _____________________________ D. 1.4 Discuss possible locations where conditions would have allowed the synthesis of organic compounds • Locations needed to be a ____________ (electron adding) environment to encourage compound formation • communities around – deep-sea _________________ – ______________ – ________________ locations (carried to earth on a comet). D.1.5 Outline Two properties of RNA that would have allowed it to play a role in the origin of life RNAs can store, transmit and replicate genetic Information • RNA is composed of a ________________. The bases are exposed and ready to combine with a complement, making replication simpler • RNA was probably the first hereditary molecule having the ability to __________________ • RNA shows enzymatic (__________) properties – called _______________ – Ribozyme: an RNA molecule that catalyzes a chemical reaction D.1.5 Outline Two properties of RNA that would have allowed it to play a role in the origin of life • Once RNA became enclosed in __________, these protobionts would have a form of ________. • These protobionts may be selected for ___________. • RNA may have directed the sequencing of ______________to form primitive enzymes. D.1.6 State that living cells may have been preceded by protobionts, with an internal chemical environment different from their surroundings • Origin of cell formation Began as _________________ Separate inside from outside Divide often (______________) Grow larger in size Bubbles… Maintain a level of ______________ internally Tiny bubbles… Produce __________________across surfaces Absorbs materials from the surface (________ ______________) ___________ actvity D.1.6 State that living cells may have been preceded by protobionts, with an internal chemical environment different from their surroundings Protobionts = Aggregation of abiotically produced molecules in ___________ - Maintain an _____________________ different from their surroundings. - Exhibit some properties associated with life: ___________ and ____________ - May have arisen from ____________, ___________, or _____________ D.1.6 State that living cells may have been preceded by protobionts, with an internal chemical environment different from their surroundings • Coacervate = droplets 1. Colloidal suspension of _______________ of _________________ 2. A water film acts as a barrier like a __________________ 3. _________ in size 4. When large enough, it _______________ into small globules with the same traits as that of the “parent” D.1.6 State that living cells may have been preceded by protobionts, with an internal chemical environment different from their surroundings • Microsphere = polypeptides with a semipermeable ____________________ formed by adding _________ to polypeptides show an ________________________ - may absorb materials from the surrounding environment membranes are made of phospholipid bilayers with __________ may give clues to the evolution of the cell membrane undergo shrinking and swelling due to _____________ D.1.6 State that living cells may have been preceded by protobionts, with an internal chemical environment different from their surroundings • Liposome = form spontaneously when the organic molecules includes ___________ Form ________________membrane Grow by __________ other liposomes and may split to form two D.1.6 State that living cells may have been preceded by protobionts, with an internal chemical environment different from their surroundings How Polymerization could Occur? • _____ was thought to be a possible site for polymerization (rather than primordial soup in the sea) • ________ well to organic molecules • Contains Zinc, iron, nickel, etc serving as a __________ • Has been shown to occur experimentally: dry clay...heat it...200 amino acids can spontaneously join & form polypeptides!! ...can possibly form ______________ D.1.7 Outline the contribution of prokaryotes to the creation of an oxygen-rich atmosphere • Prokaryotes dominated life on Earth from ________________ 3.5 billion year old fossil of bacteria modern bacteria chains of one-celled cyanobacteria D.1.7 Outline the contribution of prokaryotes to the Lynn Margulis creation of an oxygen-rich atmosphere The first cells were ___________ __________________ offer more fossil evidence – rocklike columns composed of many minute layers of prokaryotic cells (usually ________________) Living stromatolite reefs are still found in ___________ and in warm, shallow pools of fresh and salt water D.1.7 Outline the contribution of prokaryotes to the creation of an oxygen-rich atmosphere Fossilized Stromatolites – 3.5 billion years old Modern day stromatolites D.1.7 Outline the contribution of prokaryotes to the creation of an oxygen-rich atmosphere • Oxygen begins to accumulate ________ – reducing ___________ atmosphere • evidence in banded iron in rocks = _______ • makes ____________________ possible – photosynthetic bacteria (______________) D.1.7 Outline the contribution of prokaryotes to the creation of an oxygen-rich atmosphere • • • first photosynthetic organism were autotrophs which split _____ as a hydrogen donor (purple and green sulfur bacteria) the first photosynthetic organisms to use _____ as a hydrogen donor were the cyanobacteria (released _____ as by-product) source of the first free oxygen in aquatic environment and atmosphere – O2 existed in significant quantities by _________ ________ D.1.7 Outline the contribution of prokaryotes to the creation of an oxygen-rich atmosphere The increase in Oxygen led to: • The breakdown of the chemicals in the ‘chemical soup’ to ______________and oxidized sediments • The formation of the ______________, which blocked out UV and stopped the production of more of the ‘soupy’ molecules • The oxygen concentration rose to 0.45% of the atmosphere - not much compared to today’s 21%, but it led to the rise of the _____________ D.1.8 Discuss the endosymbiotic theory for the origin of eukaryotes Endosymbiosis is the theory that ____________ and _____________ were once free-living prokaryotes that were engulfed by larger prokaryotes and survived to evolve into the modern organelles D.1.8 Discuss the endosymbiotic theory for the origin of eukaryotes First Eukaryotes ~_______ • Development of ________________ – create internal micro-environments – advantage: ______________ = increase efficiency infolding of the plasma membrane plasma membrane endoplasmic reticulum (ER) nuclear envelope nucleus DNA cell wall Prokaryotic cell Prokaryotic ancestor of eukaryotic cells plasma membrane Eukaryotic cell D.1.8 Discuss the endosymbiotic theory for the origin of eukaryotes Endosymbiosis • Evolution of eukaryotes – origin of mitochondria – engulfed _________________, but did not digest them – ___________________ relationship internal membrane system aerobic bacterium mitochondrion Endosymbiosis Ancestral eukaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell with mitochondrion D.1.8 Discuss the endosymbiotic theory for the origin of eukaryotes Eukaryotic cell with mitochondrion Endosymbiosis • Evolution of eukaryotes – origin of chloroplasts – engulfed _____________________, but did not digest them – ____________________ relationship photosynthetic bacterium chloroplast Endosymbiosis Eukaryotic cell with chloroplast & mitochondrion mitochondrion D.1.8 Discuss the endosymbiotic theory for the origin of eukaryotes • Evidence Theory of Endosymbiosis – structural • mitochondria & chloroplasts resemble _____________________ – genetic • mitochondria & chloroplasts have their own _______________, like bacteria – functional • mitochondria & chloroplasts move _________ within the cell • mitochondria & chloroplasts reproduce ________________ from the cell