LWW PPT Slide Template Master
advertisement

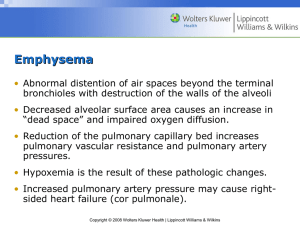
Chapter 5 Basic Human Needs Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs • Maslow defined the basic needs of all people as a progression from simple physical needs, or survival needs, to more complex ones, called aesthetic needs. • Progression from physical needs to aesthetic needs: – Physiological needs – Safety needs – Love needs – Esteem needs – Self-actualization needs Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Regression • Regression, is focusing on a lower-level need that has already been fulfilled. This is common in illness or injury. • For example, a client recovering from an illness will focus their physical and emotional energies on recovery (physical needs) before returning to employment (security). • Individuals in pain will revert to being concerned about personal appearance or relationships with others only after the pain has been relieved. Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Basic Physiologic Needs • *Physiologic needs – Primary or survival needs – Met to sustain life • *Secondary needs – Met to give quality to life Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Basic Physiologic Needs • Oxygen • Water and Fluids • Food and Nutrients • Elimination of Waste Products • Sleep and Rest • Activity and Exercise • Sexual Gratification • Temperature Regulation Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Nursing Considerations • Oxygen – Evaluate the oxygenation status of the client. – *Ex-emphysema, asthmatics, quadriplegics** • Water and Fluids – Measure intake and output, weigh the client daily, and observe intravenous infusion of fluids. – *Ex.- severe mental illness clients • Food and Nutrients – *Help feed the client, administer tube feedings, monitor calorie counts, or maintain alternative methods of nutrition. Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Nursing Considerations (cont’d) • Elimination of Waste Products – Give an enema, catheterize the person, or assist with dialysis. • Sleep and Rest – Provide safe, comfortable, and quiet surroundings. • Activity and Exercise – *Encourage client to walk after surgery or teach to walk with crutches. Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Nursing Considerations (cont’d) • Sexual Gratification – Be aware of sexuality issues when care is given. • *Temperature Regulation – Assist the client to meet the need for temperature regulation. Including excessive external heat or cold or high internal fever in response to an infection. – Body has mechanisms to temporarily regulate temperature including shivering, goose flesh, and perspiration Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Security and Safety • At this second level of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, there are both physical and psychological needs. • Freedom From Harm – *People must feel safe and secure, both physically and emotionally before being comfortable enough to move onto other needs – Remove threats to the client’s safety. – Take preventive measures. – Explain procedures, treatments, or medications. • Abuse – Report any suspected abuse in the clients. Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Security and Safety (cont’d) • Healthcare – Higher-level coping skills in relationship to planned versus unplanned healthcare • Shelter – Conduct comprehensive evaluation when interviewing clients to uncover the situation. – Homeless spend most of their energy trying to cope with daily life, have little energy to focus on meaningful relationships** • Arrange for regular monitoring and preventive healthcare in the above situations. Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Love, affection and belonging • Social needs – Assist long-term care client in their social needs by providing reading materials and/or videos* Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Nursing Activities That Help Individuals Obtain the Goal of Self-Esteem • The term self-esteem (self-image, self-respect) is related to the person’s perception of self. • Those who are ill or injured or who undergo surgery may have altered levels of self-esteem. The nurse will need to help such clients regain positive self-esteem by: – *Rewarding and encouraging an individual’s progress in rehabilitation – Allowing them to perform as much self-care as possible – *Observing these clients for symptoms of regression, depression, or chemical dependency Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Self-Actualization • *The self-actualized person has “reached his or her full potential.” • Psychologists believe that people reach this level many times throughout life, yet very few people believe they have reached the peak of self-actualization permanently* • The nurse can help clients obtain self-actualization by: – Assisting in achieving lower-level needs – Acknowledging accomplishments of the individual Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Basic and Aesthetic Needs of Individuals Who Are Homeless, Terminally Ill, or Have No Source of Income • People in this situation must find food and shelter not only for themselves, but for their children as well. These individuals are more concerned with meeting their primary rather than secondary needs. • They become ill first and then seek healthcare. Such behaviors are concrete methods of dealing with illness or emergency responses to the stimulus of illness (episodic healthcare). Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Community or Societal Needs • The community has basic needs concerning the welfare of all its residents. – Public healthcare measures (immunization programs) – Access to healthcare – Maintenance services (water and electricity) – Environmental concerns (pollution) – Safety (police and highways) – Emergency services (ambulances and paramedics) Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins