Acids Bases
advertisement

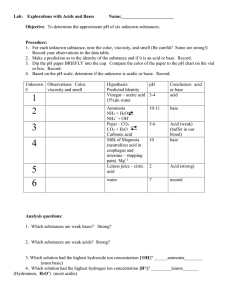
LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? Acids Bases Produce H+ ions in water Produce OH(hydroxide) ions in Form hydronium ions (H30+) water Feel slippery Taste bitter, chalky Change litmus paper blue Taste sour Produce hydrogen gas when react with metals Change litmus paper red LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? How are they alike? Corrosive React with indicators and change color Conduct electricity (electrolytes) React with each other to form salt and water LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? Common Acids Soda Coffee Wine Grapefruit (citric acid) Yogurt (lactic acid) Pickled foods in vinegar (acetic acid or CH₃COOH) Fertilizers (sulfuric, nitric, phosphoric, HCL) Car batteries (sulfuric acid or H₂SO₄) LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? Common bases Egg whites Baking powder Milk of magnesia Mg(OH)2 Antacids – Al(OH)3 Soap - NaOH Shampoo Ammonia - NH3 Oven cleaner - NaOH Drain cleaner - NaOH Fertilizers – NH3 LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? What does it mean to dissociate? To break apart Process in which an ionic compound separates into its positive and negative ions LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? How do acids dissociate in water and what products are formed? The negative areas of nearby6 water molecules attract the positive hydrogen in the acid. Produces a hydronium ion and an anion LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? How do bases dissociate in water and what products are formed? The negative areas of nearby water molecule attract the positive ion in the base. The positive area of the water molecule attract the hydroxide ion. Water molecules do not combine with the ions formed from the base. Produces a positive ion, a hydroxide ion, and water LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? Explain how ammonia (NH3) is considered a base when it does not contain OH-. The ammonia attracts a hydrogen from the water forming ammonium ion and a hydroxide ion. LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? Identify each as characteristic of an A) acid or B) base ____ 1. Sour taste ____ 2. Produces OH- in aqueous solutions ____ 3. Chalky taste ____ 4. Is an electrolyte ____ 5. Produces H+ in aqueous solutions LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? Describe the solution in each of the following as: 1) acid 2) base or 3)neutral. A. ___soda B. ___soap C. ___coffee D. ___ wine E. ___ water F. ___ grapefruit LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? Identify each as a characteristic of an A) acid or B) base _A_ 1. Sour taste _B_ 2. Produces OH- in aqueous solutions _B_ 3. Chalky taste A, B 4. Is an electrolyte _A_ 5. Produces H+ in aqueous solutions LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? Describe each solution as: 1) acid 2) base or 3) neutral. A. _1_ soda B. _2_ soap C. _1_ coffee D. _1_ wine E. _3_ water F. _1_ grapefruit LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? Strong acids Nearly all acids molecules dissociate into ions Strong electric current Single arrow in chemical equation HCl + H2O H3O+ + ClExample: HCl, HNO3, H2SO4 Weak acids Partially dissociate into ions in water Weak electric current Double arrow in chemical equation CH3COOH + H2O H3O+ + CH3COO Examples: acetic acid, carbonic acid LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? Differentiate between strong and weak bases. Strong completely dissociates and weak partially dissociates. NaOH Na + + OH NH3 + H2O NH4+ + OH- LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? Differentiate between strength and concentration. Strength Strong or weak How easily acids and bases dissociate in water Concentration Concentrated – a large amount of acid or base in a given amount of water Diluted – a little acid or base in a large amount of water Amount of acid or base dissolve LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? pH scale - measures how acidic or basic a solution is based on concentration of H+ions Ways to test pH pH paper pH meter ****litmus paper just tells if it is an acid or base**** Buffers – used to minimize the effects of acids or bases on pH pH lower than 7: acidic (high H+ concentration) pH higher than 7: basic (low H+ concentration) pH at 7: neutral LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? Neutralization A chemical reaction between an acid and a base that takes place in a water solution H+ + OH- H2O Cl- + Na+ NaCl Therefore, acid + base salt + water HCl + NaOH H2O + NaCl LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? What is titration? When a solution of known concentration and volume is used to determine the concentration of another solution LEQ: What techniques in the lab setting will be used to identify acids and bases? What are the steps of titration? Place a known volume of acid that has an unknown concentration in a beaker Add a few drops of phenolphthalein (indicator) to beaker (colorless in acid but turns bright pink in base) Slowly add base solution of known concentration (standard solution) to acid and indicator solution using the burette system Continue to add base drop by drop until solution turns pink and the color persist (end solution/neutralization) LEQ: What are some causes and effects of acid rain? Causes: Burning of fossil fuels Effects: Corrode or eat away at substances Destroy plant and animal life Solutions: Reduce pollution Add lime to acidic water Differentiate between acids and bases Acids produce hydrogen ions which attach to the water molecule forming a hydronium ion. They turn litmus paper red, are low on the pH scale and taste sour. Bases produce hydroxide ions in solution. They turn litmus paper blue, have a high pH, and taste bitter or chalky. How are acids and bases alike? Both acids and bases are corrosive to metals and can burn tissue. They change colors in the presence of indicators. They both produce electrolytes meaning that they have the ability to conduct electricity. When they react with each other to form salt and water. What is an example of an indicator? Litmus paper phenolphthalein Explain the process of dissociation of bases and be specific on what products are produced. When a base is added to water, the water molecule dissociates the base forming a cation and a hydroxide ion. The water molecule remains as a water molecule. Explain the process of dissociation of acids and be specific on what products are produced. When an acid is added to water, the negative side of the water molecule removes the hydrogen from the acid forming a hydronium ion and leaving an anion. Explain in detail how ammonia dissociates in water. Explain how this proves that ammonia is a base. Ammonia does not have a hydroxide ion as part of its formula. When ammonia is added to water, it removes a hydrogen ion from the water molecule leaving behind a hydroxide ion. The removed hydrogen attaches to the ammonia creating the ammonium ion. Due to the hydroxide ion being produced, this proves that ammonia is a base. Differentiate between strong acids/bases and weak acids/bases. Strong acids and bases dissociate completely in water. Strong acids have low pH numbers and strong bases have high pH numbers. Both of their equations contain a single arrow pointing toward the product side. Strong acids and bases both have the ability to produce a strong electric current. Weak acids and bases partially dissociate in water. Their pH numbers are closer toward the middle of the pH scale with the exception to 7 (seven) which is neutral. Their equations contain a double arrow. Weak acids and bases only produce a small electric current. Differentiate between strength and concentration. Strength refers to the ease at which acids and bases dissociate in water. If they dissociate completely; then, they are strong. If they only partially dissociate; then, they are weak. Concentration refers to the amount of acid or base present in a solution. The solution is considered concentrated if there is large amount of acid or base and little water. The solution is considered diluted if there is minimal amounts of acid or base in a large amount of water. What is the purpose of buffers? Buffers are used to minimize the effects of acids or bases on pH within the body so that the pH level of the body stays close to neutral.