The Humanist Approach
advertisement

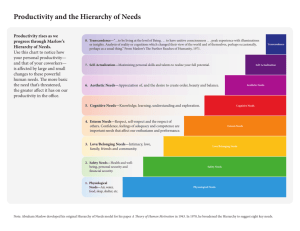
The Humanist Approach Overview of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EH04OsNuvcw Humanists Psychologists who believe people work hard to become the best they could possibly become School of thought is neither biology nor empirical behaviour Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers – believed they were into a new frontier of understanding, founded the Humanist School of Thought Rogers and Maslow’s views were different Rogers believed that every living creature has actualizing tendency Maslow believed only 2% of the human population are self-actualizing Both believed that neither psychoanalysts nor the behaviourists acknowledged the role of values, intentions, and meaning in understanding human behaviour Abraham Maslow (1908-1970) Hierarchy of Needs (1943) – used to explain and understand human motivation Believed that human nature was either neutral or inherently good Maslow is credited with being founder of the Humanist approach to psychology His argument: some needs take precedence over others For example: when we are critically ill, our need for sleep overtakes our need for self-esteem. Once rested and healthy, we can resume fulfilling our esteem needs and return to work. In Canada, Hierarchy of Needs is in accordance with Canadian norms and standards of living Maslow applied the principle of homeostasis – the body’s desire to maintain balance (internal monitor that alerts us when we need something) First 4 needs (Physiological, safety and security, love and belonging, esteem needs) are primarily physical in nature and go unnoticed unless they are not met. These are the D-needs or deficit needs When not met, an individual experiences anxiety and its needs have to be fulfilled Physiological needs Oxygen, water, minerals, food, sleep (what our bodies need) Basic needs Obtaining water and food is not a problem in Canada – in other parts of the world it is the primary motivational force Safety and Security Needs Once our physiological needs are met, we need to obtain safety and security Job security, benefits, union protection, economic stability, universal health coverage The need to feel safe overrides the need for love and belonging Still seen as a basic need Love and Belonging Needs Once we feel safe and secure, we want to “fit in” with our families and friends We want to be accepted and we conform to the implicit or explicit behavioural codes of the social, community, and work groups we join Failure to reach belonging needs results in alienation, isolation and loneliness Esteem Needs Then we strive for recognition Maslow said that esteem needs have a “lower” and “higher” order “Lower-order” esteem needs are satisfied when we experience respect and recognition from others (often temporary, it can be lost just as easily as it was gained) “Higher-order” self-esteem are based on the respect we have for ourselves (not as easily lost) From Deficit to Being Once these primary physical needs were met, we are free to pursue needs which are more psychological We strive to use our capacities and develop to our fullest Maslow expanded theory to include cognitive and aesthetic needs and selfactualizing needs He called this Being or B-needs Cognitive needs “A desire to understand, to systematize, to organize, to analyze, to look for relations and meanings” Aesthetic Needs Believing that we turn from ugliness and that we feel calmer and healthier in beautiful surroundings Self-actualization Individualized expression of self in terms of doing what we believe we are best suited for Mother Theresa is an example Peak moments – we are able to transcend physical and social conventions Only 2% of the population and few, if any, young people could attain selfactualization because of social and economic pressures keep our internal monitors directed at filling deficits A fun way to look at the Hierarchy of needs Through “Up” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Iucf76E-R2s Test yourself https://www.wisc-online.com/learn/socialscience/psychology/i2p401/maslows-hierarchy-of-needs-exercise