Osmosis lab 2009
advertisement

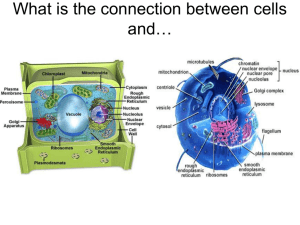
What is the connection between cells and… Desalination plant –Middle East Converts salt water into fresh water Snowboarding parka shell and snow pants Dialysis machine Draw a cross section of a “typical” cell membrane. What variables affect the passage of molecules through cell membranes? • Investigation introduction Objectives 1. To observe the effects of distilled water and salt solution on living plant and animal cells. 2. To investigate the influence of molecular size and concentration on the passage of molecules in and out of model cells. 3. To create a hypothesis to explain what you observed. Elodea and red blood cell observation • Key question to consider: • What happens to individual Elodea and red blood cells when bathed in a salt solution and in pure (distilled) water? • Make good observations • Generate at least two alternative hypotheses to explain your observations for procedures 3 and 5:) • Post the alternative hypothesis using the Active Expressions (1 hypothesis per responder) Some chemistry terms used • Solutions can be solids dissolved in liquids. They could also be gases dissolved in liquids (such as carbonated water). • There can also be gases in other gases and liquids in liquids. If you mix things up and they stay at an even distribution, it is a solution. • A simple solution is basically two substances that are going to be combined. One of them is called the solute. A solute is the substance to be dissolved (sugar). The other is a solvent. The solvent is the one doing the dissolving (water). As a rule of thumb, there is usually more solvent than solute. Homework • Speculate on the possible effects of molecular size and concentration on movement through cell membranes. Using a model cell- design an experiment or experiments to test your ideas. Construct a pre-lab flowchart for your experimental design. Materials available for investigation (found in lab packet) • • • • Dialysis tubingRubber bands to tie off the ends of the dialysis tubing Beakers IKI solution (Lugol’s solution) to detect starch molecules. (demo +/- test results) • Glucose test strips- used to detect glucose molecules. (demo +/test results) • Dropper bottles containing the following concentrations of solutions: – Distilled water (100% H20) – 1% starch solution – 5% starch solution – 1.5% glucose solution – 3% glucose solution – Quadruple beam balances Day 2• After your pre-lab flowchart has been stamped off for completion, decide as a group the different experiments that you will run to test your hypotheses. • Professional points will be lost for groups who do not clean up their stations • Record all of your results. Graph your quantitative data and be ready to present your findings to the class in 30 minutes. • Did the class results reveal a consistent pattern? If so, what was it? • Which of the proposed hypotheses were supported by the experimental findings? Explain • Homework complete question 11 Day 3 • Draw a cross section of your model cell membrane. Label your diagram. What effect does molecular size and concentration have on movement through cell membranes? solution, hypertonic, n a mixture containing a concentration of solute in excess of the concentration of the same solute in another mixture to which it is compared. When the two solutions are placed on opposite sides of a permeable membrane (either artificial or natural, as with cell membranes), the hypertonic solution attracts the solvent from the hypotonic solution, equalizing the concentration of the solute in both. See also solution, hypotonic; solution, isotonic; and osmosis. solution, hypotonic, n a mixture containing a concentration of solute that is lower than the concentration of the same solute in another mixture to which it is compared. When two such solutions are separated by a permeable membrane, the solvent of the hypotonic solution flows through the membrane to the hypertonic solution, equalizing the concentration of the solute in both. See also solution, hypertonic; solution, isotonic; and osmosis. solution, isotonic, n a mixture containing the same concentration of solute as another mixture to which it is compared. When separated by a permeable membrane, osmosis does not occur. See also solution, hypertonic; solution, hypotonic; and osmosis. What causes molecules to pass in and out of cells? How would you now explain what happened to the plant and animal cells when placed in salt water and distilled water? Application: what are some practical applications of semi permeable membranes?- Write a one page synopsis of how these technologies work. Or write a one page summary of what the process of salinization is, how it is caused by humans and how this process can impact living organisms. http://science.howstuffworks.com/reverse-osmosis.htm