ORGANIZATIONAL SET UP OF Financial Institutions
advertisement

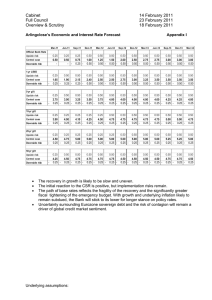
ORGANIZATIONAL SET UP OF FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS Functions of Financial Institutions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Aids the flow of capital Credit allocation Provides economies of scale and scope Satisfies the needs of general public Provides specialization and expertise Assists asset transformation Offers INTERMEDIATION Intermediation The process of transforming a secondary security into a primary security by a financial institution. It relates to financial investments by savors cash Savors cash Financial Borrowers Institutions secondary securities primary securities Dis-intermediation The process of reversing or rejecting the transfer of funds into the financial institutions. This refers to the low deposit interest rates or high operating costs charge to customers. Illustration of Disintermediation The removing of Middlemen The dis- or re-channeling funds flow from the FI Changing Role to the Servicing of Markets Security Investments Mutual Funds Insurance Types of Intermediation 1. 2. 3. 4. Liquidity Maturity Denomination Risk Types of Financial Institutions By Banking Business Nature: Banks Non-Banks Non-Finance By Business Operations: Thrift type Contractual type Investment type Other type Thrift-type Financial Institutions Banks: Commercial Banks Savings Banks Investment Banks (Merchant Banks) etc Non-Banks: Deposit-taking Company, Savings and Loan, Home Loans, Building Society, Credit Unions Contract-type Financial Institutions Insurance Companies: Life Insurance Accident and Healthy Insurance Pension Funds: Mandatory Providence Funds Retirement Funds/Pension Funds Investment-type Financial Institutions Investment Companies: Closed-end Investment Companies - Investment Brokers Open-end Investment Companies - Mutual Funds/Unit Trust Real Estate Trust Investment Companies Other Financial Institutions Finance Companies Factors Companies Lease Companies Mortgage Companies Credit Card Companies Non-finance Financial Institutions: General Electric, Ford Motors, Toyota Motors wholesalers, Manufactures, Department Stores Why Financial Institutions? Fulfill economic goals Reduce transaction and information costs Provide liquidity Prevent risks As transmission of monetary policy Provide payment mechanism Supply credit allocation Analysis of Financial Institutions 1. 2. 3. 4. Transaction Costs Information Asymmetry -- Moral Hazard Financial Risks Financial Innovation Solution Information Asymmetry--Moral Hazard: Information Symmetry and Full Disclosure Regulation Reform Financial Intermediation Financial Risks: Risk Management and Control Burden Administration Solutions Financial Innovations: Enhance Internal Control-Planning, Control, and Administration Tighten Asset Management and Quality Modernized Operation System Strengthen Regulation and Monitoring Duties of the Management of Financial Institutions 1. Determining the optimal capital structure Assets, Liabilities, and Capital 2. Managing interest rate/currency/credit risks 3. electing/Pricing investments and liabilities Maturity Matching, Profit Making 4. Operating effectively Information Processing Communication Technology