H20 Lab
advertisement

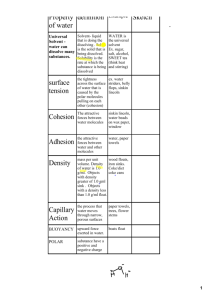
Name:____________ H2O FO SHO! Introduction to the Properties of Water All living things are dependent on water. Inside your body, cells are surrounded by a fluid that is mostly water, and your cells themselves are 70 to 95 percent water! The abundance of water is a major reason Earth can support life. Water is so common that it is easy to overlook its extraordinary properties, which are related to its structure and interactions of its molecules. Station 1: The Polarity of Water http://www.biology.arizona.edu/biochemistry/tutorials/chemistry/page3.html 1. Water molecules are polar, meaning they have a positively charged end and a negatively charged end as seen on the screen above. 2. Below, draw a picture of how water molecules arrange themselves. Include positive and negative charges in your drawing. 3. How does the above property explain why water molecules stick to each other (cohesion) so well? Station 2: The Surface Tension of Water 4. Using a steady hand, see if you can get the paper clip to rest on the surface of the water in such a way that it will not sink. Record your observations in the chart below. 5. Once you get the paper clip to “float” on the pure water, repeat the process with the salt water. Record your observations below. Tap Water Salt Water Observations a. The property of water that is being demonstrated is surface tension. Surface tension is the measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid. Water molecules are bound together by hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds are actually forces that result in a weak attraction between molecules. Using this information, explain how it is possible that the paper clip is able to float on the water. b. Using this information, what could be the cause of the differences you observed from the pure water and the salt water? c. From your knowledge of surface tension, attempt to explain the properties of water in the parentheses as compared to the object. i. Water Strider (surface tension): Station 3: Water as a Solvent A solvent is a substance that dissolves other substances known as a solute. Maybe you have experienced water as a solvent when you added hot chocolate mix (solute) to water and stirred it, or you added salt (solute) to water (solvent) before you cooked pasta. Water is a great solvent because of its polarity, and is often referred to as the “universal solvent.” Station 1 describes water’s polarity, or the fact that it has an end with a slightly positive charge and an end with a slightly negative charge. Do you think water dissolves ALL substances with ease? LET’S SEE! d. At your table you will find 3 beakers e. Fill the large one with water, then fill the other two smaller beakers with water from the large one. f. Acquire one full pipette full of vegetable oil and put it into beaker 1 g. Stir this mixture and observe the ease at which it dissolves. Record it in the table. h. Measure out half a spoonful of salt and add it to beaker 2. Stir this mixture and observe the ease at which it dissolves. Record in the table KEY +++ dissolves ~ 100% ++ or + partial dissolve 0 did not dissolve Substance Vegetable Oil Salt How well does water dissolve it? Water is polar. A general rule that determines whether a substance will dissolve in a solvent depends upon its polarity. Polar solvents dissolve polar solutes and non-polar solvents dissolve non-polar solutes. From your observations, how would you classify the above solutes (polar or non-polar?) Vegetable oil- Salt- 6. Predict what would happen if you added heat. Station 4: Adhesion Observe the chromatography paper. What does it look like (draw a picture) and how far has the ink climb up the paper? Record this in the table below. Qualitative Data Quantitative Data 7. Why was the water able to climb up the chromatography paper? 8. The property being demonstrated is adhesion. In your own words, write a definition for adhesion. 9. Where in nature do you see adhesion occurring? Station 5: Cohesion On one penny you will test tap water; on the other penny you will be testing salt water. Estimate how many drops each penny will hold. Then, perform the lab and record your results in the table below. Tap Water Estimate Observed Salt Water 10. The property of water that is being demonstrated is cohesion. Explain what cohesion is. 11. Explain why there was a difference in the # of drops using pure water compared with using salt water. Station 6: Density You have been given three different solutions and a test tube. The red solution, the yellow solution, and the green solution. Stir the red solution with the pipette and draw some of the solution up. Add about 25 drops of this solution to the test tube. Repeat this process for both the yellow and green solutions adding them all to the same test tube. 12. Draw and color what you see in the test tube in the box below. 13. Which solution was the least dense? How do you know? 14. Which solution was the most dense? How do you know? 15. Design an experiment that tests the density of different temperature of water. Explain how you would perform that experiment below.