File - Environmental Habitat

*Hydrosphere Unit*
HYDROSPHERE CALENDAR
14
Monday
*Hydro Voc (Ch 7
&11)
*Finish up and turn in TDAT projects
21
*PROPERTIES
OF WATER POP
QUIZ
*Plankton, Nekton,
Benthos Game
*Chapter 7.1
Notes: Freshwater
Ecosystems
28
* From Flush to
Finish video with questions
* Chapter 11.2
Notes: Water Use and Management
*HYDROSPHERE
VOCABULARY
QUIZ
Tuesday
15
*TDAT Project
Presentations
*Water
Properties
Foldable
*Extraordinary
Properties of
Water SG Day
#1
22
*Chapter 7.2
Notes: Marine
Ecosystems
* Jeff Corwin
Wetlands video with questions
29
*Chapter 11.3
Notes: Water
Pollution
*Water
Pollution Case
Study (partner mini project)
16
Wednesday
*Extraordinary
Properties of
Water SG Day
#2
*Water
Properties Lab
Day #1
23
*Chapter 7.2
Notes: Marine
Ecosystems
*Socrative
Space Race with all
Hydrosphere
Vocabulary terms (bonus opportunity)
30
*Chapter 11.3
Notes: Water
Pollution
*Water
Pollution Case
Study (partner mini project)
*CHAPTER 11
POP QUIZ
17
#3
24
Thursday
*Extraordinary
Properties of
Water SG Day
*Water
Properties Lab
Day #2
*CHAPTER 7
POP QUIZ
* Chapter 11.1
Notes: Water
Resources
18
Friday
* Extraordinary
Properties of
Water SG Day #4
*Chapter 7.1
Notes: Freshwater
Ecosystems
25
* Chapter 11.1
Notes: Water
Resources
* Chapter 11.2
Notes: Water Use and Management
31
*Socrative
Space Race
Review Game for Hydrosphere
(bonus opportunity)
1
*HYDROSPHERE
TEST
1
*Hydrosphere Unit*
Extraordinary Properties of Water
1.
What is the formula for a molecule of water?
2.
Which atom in water attracts more negative electrons?
3.
Water is a ________________ molecule because it has an equal number of ________________ and
___________________.
4.
What is water’s net charge?
5.
Water is called a _______________ molecule because the oxygen end “acts” _____________ charged and the hydrogen end “acts” _______________ charged.
6.
One hydrogen bond is ____________, but many hydrogen bonds are ____________.
7.
How do hydrogen bonds form?
***PROPERTIES OF WATER
8.
At sea level, water boils at _______________ and freezes at ____________.
9.
What happens to the boiling point of water at higher elevations where the atmospheric pressure is less?
10.
Where will it take longer for an egg to boil ---- in Death Valley or Mt. Everest?
11.
Name 5 more properties of water that are important to life.
12.
What is cohesion?
13.
Cohesion produces _________________ _______________ when one water molecule attracts other
_________________ molecules.
14.
What is surface tension a measure of?
15.
How does the film produced by surface tension help organisms?
16.
What is adhesion?
17.
How does adhesion DIFFER from cohesion?
18.
Adhesion produces _______________________ _______________ as water is attracted to and pulled into a tube.
19.
What process in plants is due to capillary action (one word)?
20.
Plants absorb water through their ____________ and use _______________ action or _______________ to move water upward against gravity to the leaves.
21.
Name 2 other things observed in nature that are the result of adhesion.
22.
Define specific heat.
23.
Water _____________ a change in temperature and can absorb or release ______________ amounts of energy with very little temperature change.
24.
What is heat of vaporization?
25.
In order to evaporate, water must break its _______________ bonds.
26.
When water evaporates from a surface, it removes a lot of ___________________.
27.
What is water’s heat of vaporization?
28.
In order for a gram of water at 100 o C to change into steam at that same temperature, it must
______________ _______________ calories of energy. Therefore, which would contain more energy at
100 o C, steam or boiling water?
29.
How does water warm the Earth?
30.
Why does ice float in water?
31.
Frozen water forms _______________ holding the molecules at fixed distances from each other.
32.
Which is denser ---- ice or water?
33.
Define homeostasis.
34.
List 5 ways that water helps maintain homeostasis.
***SOLUTIONS & SUSPENSIONS
35.
Solutions and suspensions are two types of ________________ that both contain ______________.
36.
The _________________ is the substance being dissolved and the _______________ is what the substance is dissolved in.
37.
What acts as a “universal solvent” because it dissolves so many substances?
38.
How does a suspension form?
39.
What keeps particles suspended?
2
*Hydrosphere Unit*
***ACIDS, BASES, & pH
40.
Write the equation for the dissociation (separation) of water and label the hydrogen & hydroxide ions?
41.
What does the pH scale actually measure?
42.
The pH scale ranges from ________________ with a pH of ______ being neutral.
43.
Where are acids found on the pH scale?
44.
Where are the bases found on the pH scale?
45.
Each pH unit represents a factor of __________ change in concentration.
46.
How much stronger is a substance with a pH of 3 than a pH of 6. Show how you got your answer.
47.
Acids produce a lot of ____________ ions, while bases contain lots of __________ ions.
48.
What is a buffer?
49.
Buffers are produced by the body to _______________ acids and bases to maintain homeostasis.
50.
What pH do you think is best for most parts of the body --- cells, blood, etc?
Chapter 7 Study Guide
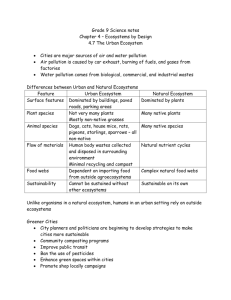
***Section 1: Freshwater Ecosystems
1.
Freshwater ecosystems include _________, lakes, streams, _______, and wetlands.
2.
What 4 factors determine where an organism can live in the water?
3.
Make a foldable with information on plankton, nekton, and benthos and add it to your notes.
4.
Describe the littoral zone of a lake.
5.
Describe the benthic zone of a lake.
6.
What is eutroiphication?
7.
What process accelerates eutrophication?
8.
List 4 environmental functions of wetlands.
9.
Make a chart comparing and contrasting marshes and swamps and add it to your notes.
10.
How have humans negatively impacted the wetlands?
11.
As a river flows down a mountain, it ______________________________.
12.
What are rhizoids?
13.
How do industries damage rivers?
***Section 2: Marine Ecosystems
1.
Marine ecosystems are located mainly in _______________ and ___________________.
2.
What is a coastal wetland?
3.
Why are estuaries such productive ecosystems?
4.
List 2 threats to estuaries.
5.
What is a salt marsh?
6.
What is a mangrove swamp?
7.
Compare and contrast the characteristics and organisms that can live in rocky and sandy shores.
8.
What is a barrier island?
9.
What are coral reefs made of?
10.
Are they plants or animals?
11.
Explain why coral reefs are so fragile.
12.
How far can light penetrate into the ocean?
13.
The sea’s smallest herbivore is _____________________.
14.
Name 3 threats to open oceans.
15.
In the Arctic and Antarctic, nearly all of the food comes from the ______________.
16.
The base of the food chain in the Arctic would be _________________.
3
*Hydrosphere Unit*
Chapter 11 Study Guide
***Section 1: Water Resources
1.
How long can humans live without water?
2.
Water is a _____________ resource. Why?
3.
Draw the 3 steps of the water cycle.
4.
_____% of Earth’s surface is covered by water.
5.
_____% of that is salt water.
6.
_____% of the fresh water on Earth is found in icecaps and glaciers.
7.
What is surface water?
8.
What is the largest river system in the world?
9.
The amount of water that enters a watershed ___________ throughout the year. Why?
10.
What is ground water?
11.
The water table has __________ and ___________ that match the shape of the land above.
12.
What is an aquifer?
13.
Compare porosity and permeability.
14.
Why are recharge zones environmentally sensitive areas?
15.
Structures such as ______________ and _____________ can act as impermeable layers that block water from entering the recharge zones.
16.
Why do some humans still rely on wells?
***Section 2: Water Use and Management
1.
Who is the W.H.O.?
2.
According to the WHO, ________ people lack access to clean water.
3.
Water is used for 3 main purposes. They are __________________________________.
4.
Most of the fresh water used worldwide is used to _____________________________.
5.
Industry accounts for about __________% of the water used in the world.
6.
Compare the amount of water used by the average American daily and the average Indian daily.
7.
According to the chart, what activity uses the most water?
8.
On average, brushing your teeth uses how much water?
9.
What does it mean that water is potable?
10.
What are pathogens? They can be removed by __________ or __________treatments.
11.
Make a foldable of the six steps of the water treatment process making sure to list the step #, name, and what happens.
12.
Most water used in industry is used for what purpose?
13.
What percentage of agricultural water evaporates before reaching the plants?
14.
In the US most irrigation is done by ____________________. Why are they considered to be inefficient?
15.
What can be done to supply dry areas with water?
16.
What is a reservoir?
17.
Name 2 negative consequences of building and maintaining a hydroelectric dam?
18.
How does a drip irrigation system conserve water?
19.
How can recycling wastewater conserve water?
20.
Where might xeriscaping be used to conserve water?
21.
Name 5 ways that you can conserve water in your home.
22.
Why doesn’t the United States use the process of desalination to cure the problem of not enough clean water?
4
*Hydrosphere Unit*
23.
How is water transported to the Greek Islands?
***Section 3: Water Pollution
1.
What are the 2 underlying causes of water pollution?
2.
Why is water pollution more of a problem in developing countries?
3.
Make a chart/foldable distinguishing 4 sources of point and nonpoint source pollution.
4.
Make a chart/foldable of all of the principal water pollutants and their sources.
5.
What is wastewater?
6.
Most wastewater is easy to clean. Why?
7.
What is sewage sludge?
8.
What are 2 ways that sewage sludge is being treated and reused?
9.
What is artificial eutrophication? It is mostly caused by __________________ and
____________________________.
10.
Why is thermal pollution such a danger?
11.
Why is cleaning up groundwater such a challenge?
12.
85% of all ocean pollution comes from what?
13.
Each year, about ___________ million gallons of oil from tanker accidents are spilled into the ocean.
14.
What is biomagnification?
15.
Make a chart/foldable of all of the 6 water laws making sure to include the name, years, and point of the law.
5