Matter Study Guide - Effingham County Schools

(Henry)
Name:___________________________ Date: ______________________
Mass/Matter & Chemical/Physical Change Study Guide
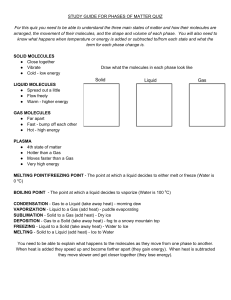
1. Solids, liquids, and gases are called the states of matter.
2. A single particle of matter made up of two or more atoms joined together are called
molecules.
3. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
4. The amount of matter in an object is called mass.
5. The smallest particle of matter is an atom.
6. A chemical change is a change in matter that produces new kinds of matter.
7. A physical change is a change in the size, shape, or state of matter that does not
change it into a new kind of matter.
8. The molecules in a gas do not stay close together
9. A scientist has a sheet of paper. After an experiment, the paper has turned to ash. The
scientist is investigating chemical changes.
10. Water changing from a liquid to a solid is an example of a physical change.
11. A bicycle left in the rain until it rusts is an example of a chemical change.
12. A puddle of water evaporating is an example of a physical change because no new
matter is being created. It is just changing from one state of matter to another state.
13. The mass of an object is equal to the sum of the mass of its parts - a whole banana will
have the same mass as a banana the same size that has been cut into pieces.
Physical Changes cutting paper a popsicle melting water evaporating breaking a window folding paper
State of Matter solid liquid
Chemical Changes rust on a baking pan wood burning in a campfire making blueberry muffins burning paper mixing vinegar and baking soda causing bubbles to form
Molecules molecules are packed close together in a regular pattern
Diagram
Molecules slide past each other but still stay close together. Molecules do not form a regular pattern gas Molecules move quickly and do not stay close together.
They do not form a regular pattern.